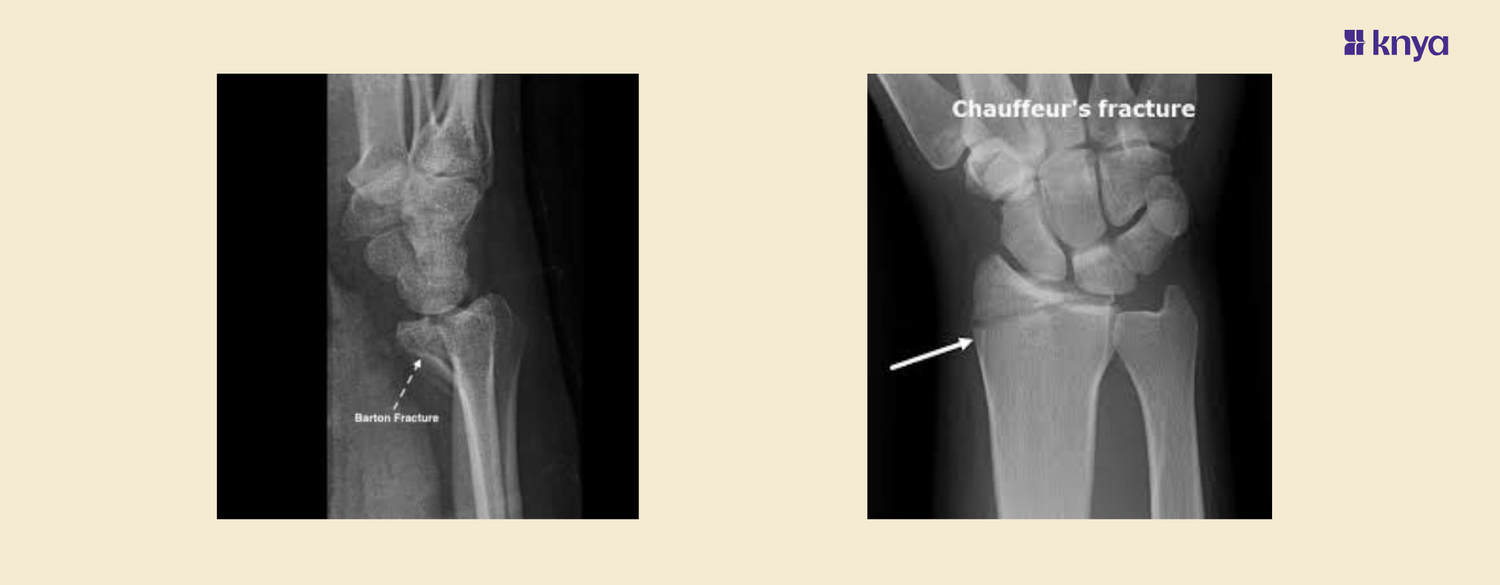
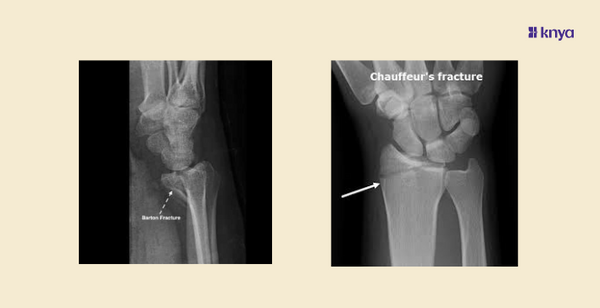
Fractures of the distal radius are common injuries often resulting from falls onto an outstretched hand. Among these, Barton fractures and Chauffeur’s fractures are two specific types .Barton fractures typically result from high-energy trauma, such as a fall from a height or a motor vehicle accident, causing the wrist to hyperextend whereas,Chauffeur's is commonly caused by a direct blow to the wrist or a fall onto an outstretched hand with the wrist in radial deviation
Comparative Analysis
Below is the difference between Barton Fracture and Chauffeus's Fracture in the tabular format:
| Feature | Barton Fracture | Chauffeur’s Fracture |
| Location | Distal radius (dorsal or volar rim) | Radial styloid process |
| Type | Intra-articular fracture-dislocation | Intra-articular fracture |
| Mechanism of Injury | High-energy trauma (fall, motor vehicle accident) | Direct blow, fall on outstretched hand, radial deviation |
| Clinical Presentation | Pain, swelling, wrist deformity | Pain, tenderness over radial styloid, swelling |
| Diagnosis | X-ray, CT scan | X-ray, MRI, CT scan |
| Treatment | Non-surgical (casting), Surgical (ORIF) | Non-surgical (immobilization), Surgical (ORIF) |
| Prognosis | Depends on severity and treatment | Generally good with appropriate treatment |
What is Barton Fracture?
A Barton fracture is an intra-articular fracture of the distal radius characterized by a fracture-dislocation of the radiocarpal joint. It was first described by John Rhea Barton in 1838. Barton fractures are classified into two types: dorsal and volar, depending on the direction of the displacement.
Dorsal Barton Fracture
Involves a dorsal displacement of the carpus along with a dorsal rim fracture of the distal radius.
Volar Barton Fracture
Involves a volar displacement of the carpus along with a volar rim fracture of the distal radius.
Symptoms
- Pain and swelling in the wrist
- Deformity of the wrist with displacement
- Limited range of motion
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made through clinical examination and imaging studies.
- X-rays are the primary imaging modality, revealing the fracture and the direction of displacement
- CT scans can provide additional detail in complex cases.
Treatment
Treatment involves realigning the fracture (reduction) and stabilizing it. Options include:
- Non-surgical: Closed reduction and casting, typically for non-displaced or minimally displaced fractures.
- Surgical: Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) using plates and screws for displaced fractures.
What is Chauffeur's Fracture?
A Chauffeur’s fracture, also known as a Hutchinson fracture, is an intra-articular fracture of the radial styloid process. It was originally termed "chauffeur’s fracture" because early 20th-century chauffeurs often sustained this injury when hand-cranking cars backfired.This type of fracture is commonly caused by a direct blow to the wrist or a fall onto an outstretched hand with the wrist in radial deviation. It can also result from high-energy trauma such as motor vehicle accidents.
Symptoms
- Localized pain and tenderness over the radial styloid
- Swelling and bruising
- Limited wrist motion, particularly in radial deviation
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is typically made through physical examination and confirmed with imaging studies.
- X-rays are essential to visualize the fracture.
- MRI or CT scans can be used to assess associated soft tissue injuries.
Treatment
Treatment strategies for a Chauffeur’s fracture depend on the displacement and stability of the fracture:
- Non-surgical: Immobilization with a cast or splint for nondisplaced fractures.
- Surgical: ORIF for displaced fractures or those with instability, involving fixation with screws or plates.
Prognosis and Outcomes
The prognosis for Barton fractures varies, Complications such as malunion, nonunion, and post-traumatic arthritis are concerns. Conversely, When compared with Bartons, Chauffeur’s fractures generally have a better prognosis, especially when appropriately managed, with fewer long-term complications expected.
| Check out More Articles | |
| Difference Between Cartilage And Bone | |
| Difference Between Endocrine And Exocrine Glands | |
| Difference Between Cell Wall And Cell Membrane | |