Difference Between Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Nervous System: The sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems are like a dynamic duo, constantly playing tug-of-war within you. The sympathetic system, your "fight or flight" hero, revs you up in stressful situations – speeding your heart, dilating pupils, and pumping energy to your muscles. Think facing a lion! Then, the parasympathetic system, your calming sage, takes over – slowing your heart, easing digestion, and promoting relaxation. It's like hitting the brakes after the danger passes. These two systems work together, constantly adjusting your internal state to keep you safe and thriving.
Difference Between sympathetic and Parasympathetic Nervous Systems
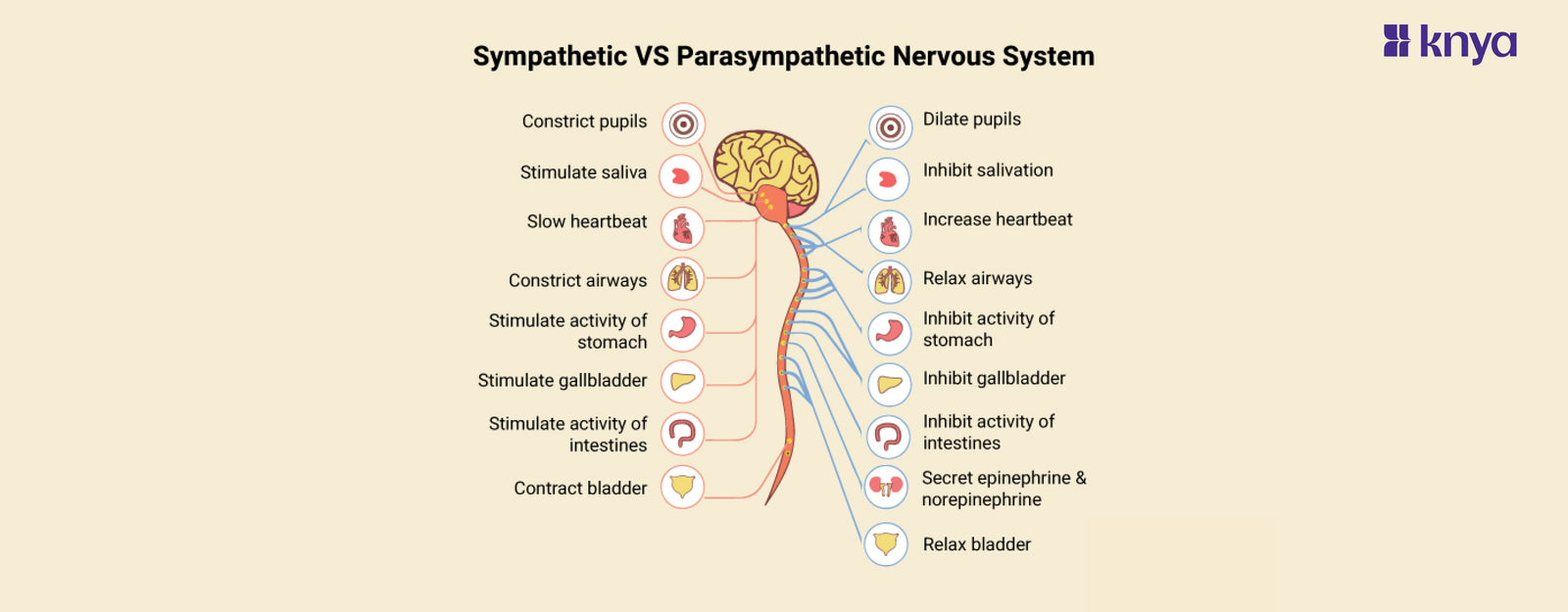
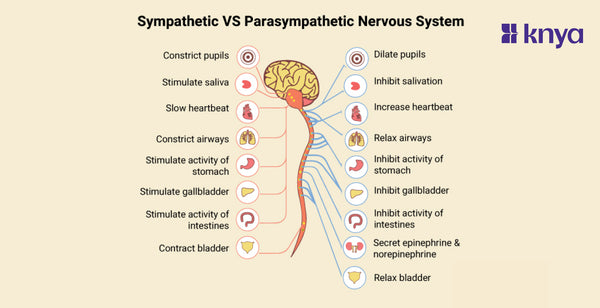
The sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems are the two main branches of the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary functions like your heart rate, digestion, and breathing. Let’s untangle the differences between sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
|
Feature |
Sympathetic Nervous System |
Parasympathetic Nervous System |
|
Origins of Nerves |
Thoracic and lumbar spinal regions |
Cranial and sacral spinal regions |
|
Neurotransmitter Release |
Norepinephrine at postganglionic synapses |
Acetylcholine at postganglionic synapses |
|
Ganglia Location |
Close to the spinal cord |
Near or within target organs |
|
Preganglionic Fiber Length |
Short |
Long |
|
Adrenal Medulla Influence |
Innervates adrenal medulla |
Does not directly innervate adrenal medulla |
|
Effect on Heart Rate |
Increases heart rate |
Decreases heart rate |
|
Effects on Digestive System |
Inhibits digestive processes |
Stimulates digestive processes |
|
Pupil Dilation |
Dilates pupils (mydriasis) |
Constricts pupils (miosis) |
|
Response to Stress |
"Fight or flight" response activation |
Dominant during rest and relaxation |
|
Location of Ganglia |
Near spinal cord in chain formation |
Near or within target organs |
What is a Sympathetic Nervous System?
This is the "fight-or-flight" system. When you're stressed or in danger, it releases adrenaline and other hormones that prepare your body for action. Your heart rate and blood pressure increase, your pupils dilate, and your breathing quickens.
Key Features of Sympathetic Nervous System:
- This system kicks in during stress or danger, preparing your body for immediate action. Imagine facing a lion!
- It uses adrenaline to trigger a cascade of effects: increased heart rate, dilated pupils, constricted blood vessels, and heightened alertness.
- It is designed for quick bursts of energy, not sustained activity. After the danger passes, it hands over control to the parasympathetic system.
- The Sympathetic Nervous System prioritizes blood flow to muscles and vital organs, temporarily reducing digestion and other non-essential functions.
What is a Parasympathetic Nervous System?
This is the "rest and digest" system. It counteracts the sympathetic system and helps your body calm down after a stressful event. It slows your heart rate and breathing, lowers your blood pressure, and promotes digestion.
Key Features of Parasympathetic Nervous System:
- This system takes over when you're calm and safe, promoting relaxation and recovery. Picture yourself enjoying a peaceful meal after escaping the lion!
- It slows down the heart rate, relaxes muscles, dilates blood vessels, and stimulates digestion and other bodily processes.
- It works continuously in the background, maintaining homeostasis (internal balance) and supporting essential bodily functions.
- The Parasympathetic Nervous System prioritizes digestion and nutrient absorption, diverting blood flow away from muscles and towards the gut.
Shop Best Lab Coats from Here!
Similarities Between Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Nervous System
- Involuntary Control: Both systems work involuntarily and are not conscious.
- Maintaining Homeostasis: Both systems collaborate to keep the body's homeostasis by regulating numerous physiological activities.
- Dual Innervation: Many organs have dual innervation, which means they are impacted by both the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, resulting in a balance of regulation.
- Acetylcholine as a neurotransmitter: Acetylcholine is used as a neurotransmitter at preganglionic synapses in both systems.
- Autonomic Ganglia: Both systems have autonomic ganglia, which contain connections between pre- and postganglionic neurons.
While the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems may appear to be foes, they really function in perfect harmony as the autonomic nervous system's yin and yang. Imagine a dramatic pursuit scene: the sympathetic nervous system cranks you up, increasing your heart rate, narrowing your blood vessels, and pumping adrenaline in preparation for the "fight-or-flight" reaction. However, after the threat has passed, the parasympathetic nervous system takes over, calming you down, slowing your heart rate, dilating blood vessels, and aiding digestion - the "rest and digest" phase. This delicate balance guarantees that your body can adapt flexibly to challenges while preserving critical internal processes, preparing you for life's adventures.