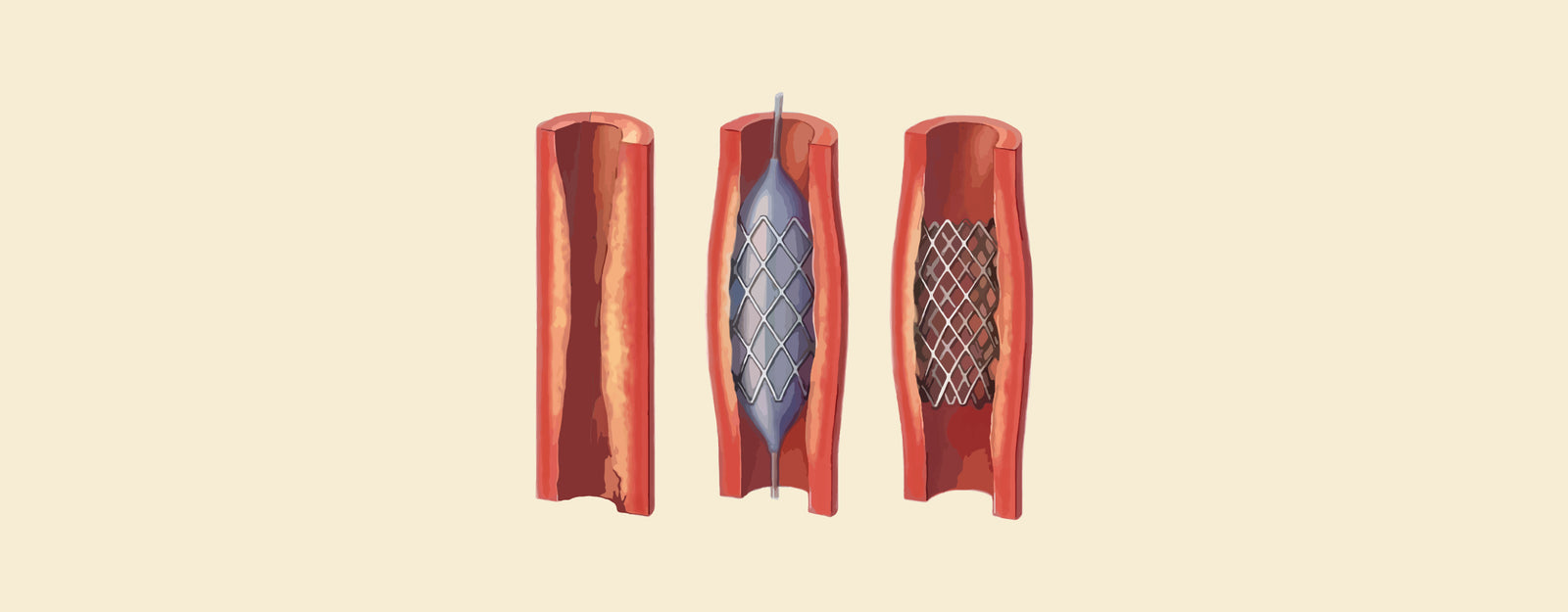
Difference between Balloon Angioplasty and Stent: Balloon angioplasty and stent insertion are two interventional procedures used to treat blocked or narrowed arteries, particularly the coronary arteries. While both are aimed at improving blood flow to the heart muscle, they differ in their approaches and outcomes. Understanding the differences between these procedures is essential for patients and healthcare professionals involved in heart disease treatment.
Difference Between Balloon Angioplasty and Stent
|
Feature |
Balloon Angioplasty |
Stent |
|
Procedure |
Involves inflating a balloon to widen the artery. |
Balloon angioplasty followed by insertion of a mesh tube (stent). |
|
Purpose |
Opens narrowed or blocked coronary arteries. |
Provides structural support to the artery and prevents re-narrowing |
|
Risks |
Re-narrowing of the artery, blood clots, infection or bleeding at the insertion site, heart attack, coronary artery damage, kidney injury, stroke, irregular heartbeats. |
Similar to balloon angioplasty, but may include additional risks related to stent insertion. |
|
Post-Procedure Care |
Patients are monitored for a few hours in the recovery room. Medications can prevent blood clots. Most patients can resume normal activities within a week. |
Similar to balloon angioplasty. Blood clots can be prevented with medications. |
|
Use of Stents |
Does not involve stent insertion. |
Involves the insertion of a mesh tube (stent) into the artery to keep it open. |
Browse best Scrubs Collection
What Is Balloon Angioplasty?
Balloon angioplasty, also known as percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA), is a minimally invasive procedure used to open narrowed or blocked coronary arteries. This procedure involves threading a deflated balloon through the artery to the site of the blockage. Once in place, the balloon is inflated, compressing the plaque and widening the artery to restore blood flow to the heart muscle. Balloon angioplasty is often the first-line treatment for patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) who have single or multiple blockages.
Key Features of Balloon Angioplasty
Procedure:
- A catheter with a deflated balloon is inserted into the blocked artery.
- The balloon is inflated, compressing the plaque and widening the artery.
Purpose:
- Opens narrowed or blocked coronary arteries to improve blood flow to the heart.
Risks:
- Re-narrowing of the artery
- Blood clots
- Infection or bleeding at the point of catheter insertion
- Heart attack
- Coronary artery damage
- Kidney injury
- Stroke
- Irregular heartbeats
Healing Capacity:
- Limited regenerative capacity
- Challenging due to the absence of its blood supply
- Slow and sometimes incomplete repair
Post-Procedure Care:
- Patients are monitored for a few hours in the recovery room.
- Medications can prevent the occurrence of blood clots.
- Most patients can resume normal activities within a week.
Use of Stents:
- Sometimes, a stent is placed during the angioplasty procedure to help keep the artery open.
What Is Stent ?
Stent insertion, often performed alongside balloon angioplasty, involves placing a small mesh tube, called a stent, into the newly widened artery to help keep it open. The stent acts as a scaffold, providing structural support and preventing the artery from re-narrowing. Stents are commonly made of metal or polymer materials and can be coated with medications to further reduce the risk of re-narrowing.
Key Features of Stent
Procedure:
- After balloon angioplasty, a stent is inserted into the widened artery to keep it open.
Purpose:
- Provides structural support to the artery and prevents re-narrowing.
Risks:
- Re-narrowing of the artery
- Blood clots
- Bleeding or infection at the stent insertion site
- Heart attack
- Coronary artery damage
- Kidney injury
- Stroke
- Irregular heartbeats
Healing Capacity:
- Involves callus formation and remodeling of the artery
- Relatively robust healing capacity with proper care
Post-Procedure Care:
- Similar to balloon angioplasty
- Medications may be given to prevent blood clots.
Types of Stents:
- Bare-metal stents (BMS)
- Drug-eluting stents (DES)
Shop the Best Lab Coats from Here!
Similarities Between Balloon Angioplasty and Stent:
Both balloon angioplasty and stent insertion are minimally invasive procedures performed in a hospital's cath lab. They both aim to improve blood flow to the heart muscle by opening narrowed or blocked arteries. Additionally, both procedures carry similar risks, including re-narrowing of the artery, blood clots, bleeding or infection at the insertion site, heart attack, coronary artery damage, kidney injury, stroke, and irregular heartbeats. Although they have some differences in their healing capacity, both procedures involve some degree of healing and remodeling of the artery. Following the procedure, patients require similar post-procedure care, including monitoring and medication to prevent blood clots. Stent insertion can involve different types of stents, including bare-metal stents (BMS) and drug-eluting stents (DES).
| Check out More Articles | |
| Difference Between Cartilage And Bone | |
| Difference Between Endocrine And Exocrine Glands | |
| Difference Between Cell Wall And Cell Membrane | |