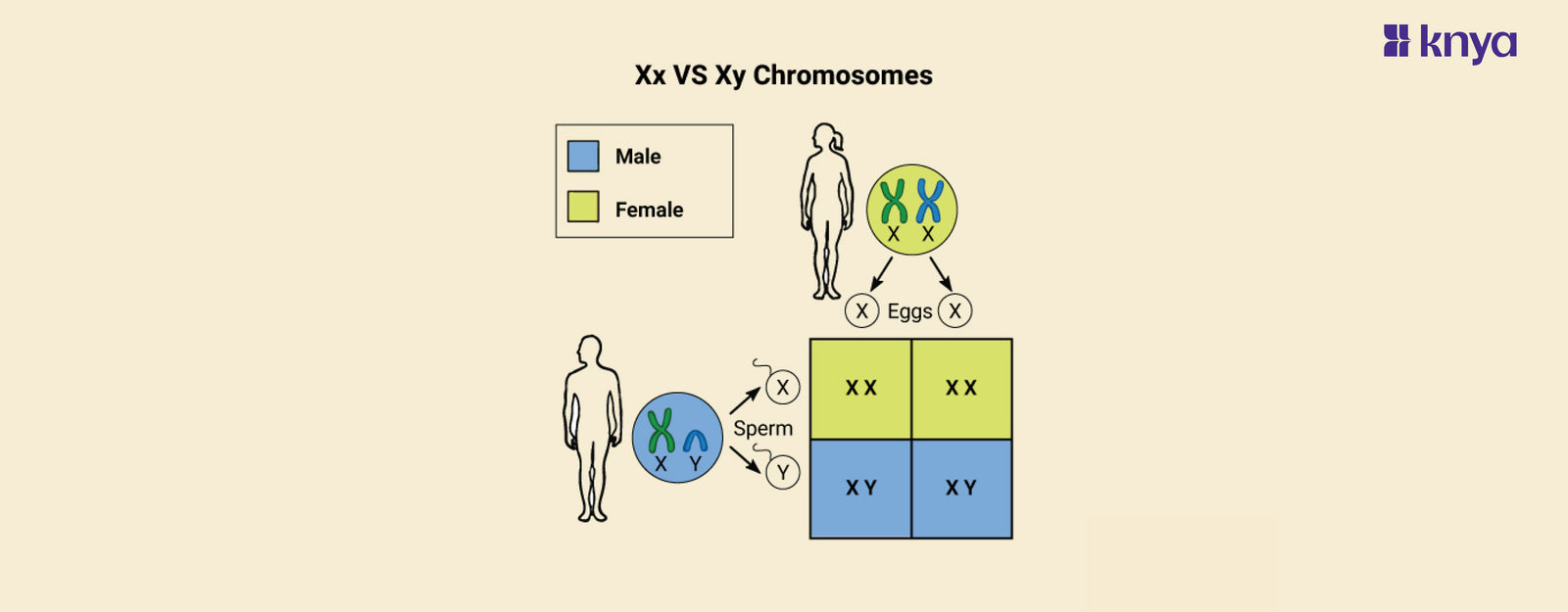
When it comes to genetics, one of the most common questions people ask is: “What is the difference between XX vs XY chromosomes?” While they may sound similar, their roles in the human body are very different. The XX chromosome is usually found in females, where two X chromosomes work together to balance gene expression. On the other hand, the XY chromosome is found in males, where the Y chromosome carries the SRY gene that triggers male development. That’s why people often say XX chromosome = female and XY chromosome = male.
Xx Vs Xy Chromosomes: The XX and XY chromosomes determine biological sex in humans and several other species. Females have two X chromosomes, which allow for complete expression of X-linked genes. Males have one X chromosome and one smaller Y chromosome, which mostly contains genes for male development. Interestingly, whereas females exclusively create X-carrying eggs, males generate sperm with either an X or a Y, which ultimately determines the offspring's gender: XX for females and XY for males. This method, known as XY sex determination, is why dads basically "choose" the sex of their offspring.
In this article, we’ll break down the differences and similarities between XX and XY chromosomes, explain how they shape human biology, and answer the most frequently asked questions to clear every doubt.
Xx Chromosomes
- Two X chromosomes, usually found in females
- Carries genes for various traits, including some unrelated to sex.
- Females inherit one X from each parent.
- Linked to conditions like colorblindness and Turner syndrome.
Xy Chromosomes
- One X chromosome and one Y chromosome, typically found in males.
- Smaller than X, primarily responsible for male sex development.
- Males inherit an X from their mother and a Y from their father.
- May influence height and risk of certain cancers.
Difference between Xx and Xy Chromosomes
XX and XY chromosomes are two types of sex chromosomes that determine the biological sex of an individual in many species, including humans. Listed are the differences between XX and XY chromosomes.
|
Differences Between XX and XY Chromosomes |
XX Chromosomes |
XY Chromosomes |
|
Combination of Sex Chromosomes |
Found in females |
Found in males |
|
Inheritance from Parents |
Inherit X chromosome from both parents (XX) |
Inherit X from mother, Y from father (XY) |
|
Size of Chromosomes |
Generally larger |
Generally smaller |
|
Genes on Y Chromosome |
Lacks genes for male-specific traits |
Contains genes for male-specific characteristics |
|
Presence of Barr Bodies |
One X chromosome undergoes inactivation, forms Barr body |
Not applicable |
|
Hemizygosity in Males |
Not hemizygous |
Hemizygous for many X-linked genes |
|
Genetic Disorders |
Less prone to X-linked disorders |
More prone to X-linked disorders |
|
Gamete Formation |
Produce eggs with an X chromosome |
Produce sperm with either X or Y chromosome |
|
Role in Sexual Differentiation |
Leads to female primary sexual characteristics |
Leads to male primary sexual characteristics |
|
Determination of Primary Sexual Characteristics |
Develops female reproductive structures |
Develops male reproductive structures |
Browse Best Scrubs Collection
What are Xx Chromosomes?
XX people often develop feminine traits. They have two X chromosomes, which means they contain twice as many critical genes that influence sex determination and other activities. To avoid gene overexpression, cells inactivate one of their X chromosomes. XX people exclusively develop egg cells with an X chromosome.
Key Features of Xx Chromosomes:
- Females typically possess two X chromosomes, represented as Xx. These chromosomes carry genes essential for various functions, including cell growth, metabolism, and the development of female reproductive organs.
- Each X chromosome holds unique sets of genes, contributing to genetic diversity in females. This redundancy also provides a protective effect, as inactivating one X chromosome in each cell helps compensate for potential mutations on the other.
- Turner Syndrome: Anomalies involving the X chromosome, such as monosomy X (absence of one X chromosome), can lead to Turner syndrome. This condition presents with delayed growth, ovarian insufficiency, and skeletal abnormalities.
- X-linked Traits: Genes located on the X chromosome can give rise to X-linked traits, passed from mother to offspring. These traits, like color blindness, can be more prevalent in males with only one X chromosome to inherit the affected gene.
What are Xy Chromosomes?
XY people tend to develop masculine qualities. The Y chromosome is substantially smaller than the X chromosome and largely contains genes for male sex determination and sperm production. It lacks numerous genes found on the X chromosome, resulting in certain distinctive characteristics in males. XY people generate half X-bearing sperm and half Y-bearing sperm, resulting in the sex of the baby.
Key Features of Xy Chromosomes:
- Males normally have two sex chromosomes, one X and one Y (represented as Xy). The Y chromosome is substantially smaller than the X and contains genes involved in male sex determination and sperm production.
- The Sex-determining Region Y (Sry) gene, which is found on the Y chromosome, causes the formation of testes and masculinization throughout embryonic development. Individuals without this gene have feminine sexual traits while having an X and Y chromosome.
- Klinefelter syndrome is caused by an extra X chromosome in males (XXY). This disorder can have an impact on fertility, hormonal balance, and physical growth.
- Some characteristics, such as hairy ears and sensitivity to certain skin disorders, are Y-linked and only handed on from father to son. Females seldom display these features due to the lack of a second Y chromosome.
Explore All Women's Scrub
Similarities Between Xx and Xy Chromosomes
- An individual's biological sex is determined by both the XX and XY chromosomes.
- Humans and many other creatures include XX and XY chromosomes.
- Both XX and XY chromosomes have distinct inheritance patterns from parents to offspring.
- Both kinds of chromosomes participate in the reproduction process, adding to the genetic composition of kids.
- Both the XX and XY chromosomes include genetic material that codes for different features and characteristics in each individual.
Both Xx and Xy Chromosomes play a crucial role in human development, their differences are profound. The female XX chromosomes are homologous, or nearly identical pairs that carry genes for a variety of purposes other than determining sex. On the other hand, males have heterogamous XY chromosomes, with the Y chromosome being substantially smaller and carrying genes mostly relevant to the development of male sex. An individual's biological sex is determined by the difference in chromosomal composition; normally, XX results in feminine features and XY in male qualities. In addition, a remarkable mechanism known as X inactivation occurs on the single X chromosome in men, guaranteeing that the dosage of X-linked genes is the same in both sexes.
| Check out More Articles | |
| Difference Between Psychosis and Neurosis | |
| Dorsal Vs Ventral | |
| Difference Between Striated and Unstriated Muscles | |