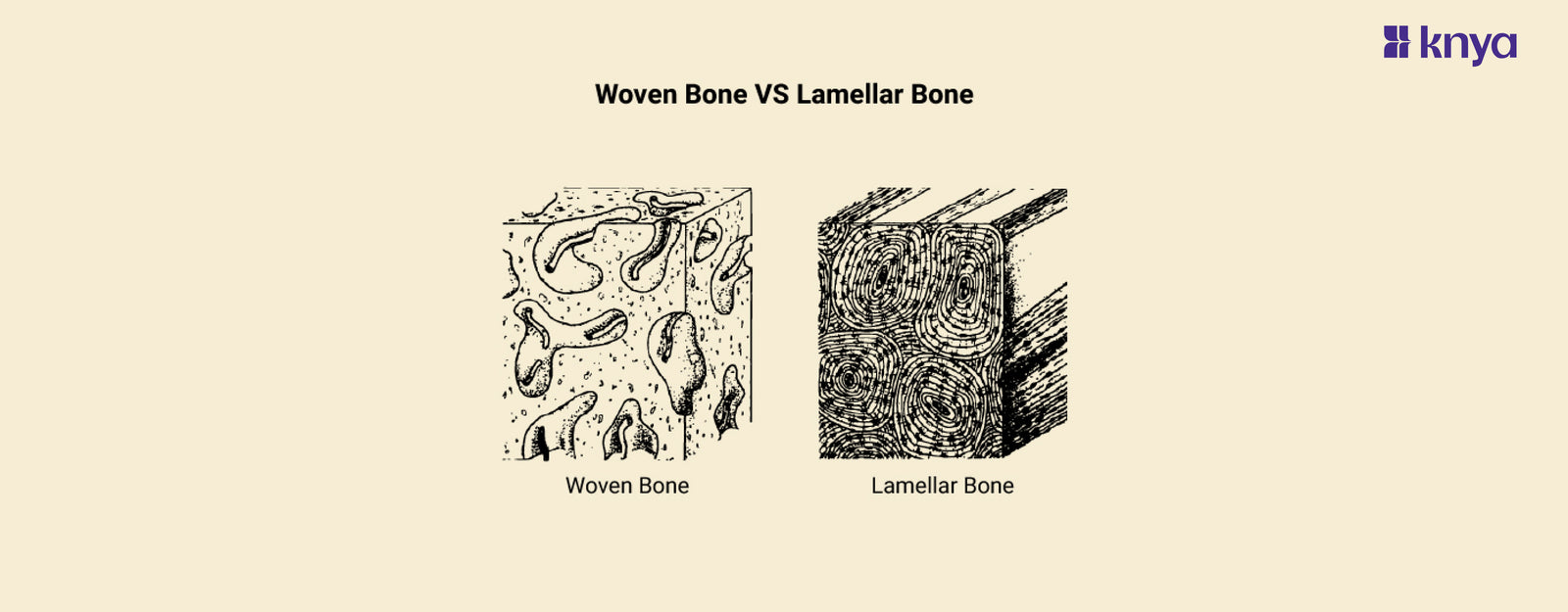
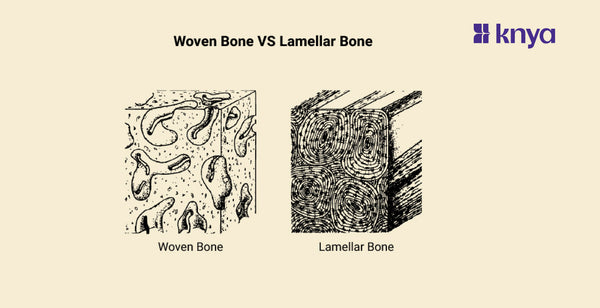
Woven Bone Vs Lamellar Bone: Woven Bone and Lamellar Bone are the two most common kinds of bone, characterised by their collagen fibre organisation. Weaving bone, also known as immature bone, has a random, weaving arrangement of collagen fibres, making it weaker but more flexible. In contrast, lamellar bone has a well-organized, layered (lamellar) collagen structure, which results in higher strength and stiffness. This distinction is analogous to comparing loosely woven fabric to tightly woven cloth; Woven Bone Vs Lamellar Bone emphasises this disparity in the building blocks of our bones.
Differences Between Woven Bone and Lamellar Bone
The human body has two forms of bone tissue: woven bone and lamellar bone. They vary in structure, function, and features. The following are the differences between woven bone and lamellar bone:
|
Feature |
Woven Bone |
Lamellar Bone |
|
Structure |
Disorganized arrangement of collagen fibers |
Layered and organized collagen fiber arrangement |
|
Fiber orientation |
Randomly oriented collagen fibers |
Collagen fibers arranged parallel to each other |
|
Strength |
Less strong |
Stronger |
|
Formation rate |
Rapid |
Slower |
|
Presence in development |
Found during fetal development and fracture repair |
Predominant in mature skeletons |
|
Vascularization |
More highly vascularized |
Less vascularized |
|
Cellular composition |
More osteocytes, fewer lamellae |
Fewer osteocytes, more lamellae |
|
Appearance under microscope |
Woven or fibrous appearance |
Organized with distinct layers |
|
Function |
Temporary scaffold during bone formation or repair |
Long-term structural support and stability |
|
Location |
Found in developing fetal skeleton and areas of bone fracture healing |
Found in mature bone tissue |
Order the Best Jogger Scrub from Here!
What is Woven Bone?
Woven bone is a kind of juvenile bone tissue that forms during embryonic development and after a fracture. It is distinguished by a disorganised and random arrangement of collagen fibres, giving it a woven texture. Woven bone is weaker and less rigid than lamellar bone, but the body can lay it down more quickly. As healing develops, the woven bone is progressively replaced by the stronger lamellar bone.
Browse Best Scrubs Collection
Key Features of Woven Bone:
- Woven bone is the body's champion at fast bone creation. During fracture healing or bone development surges in infancy, braided bone swiftly forms a primitive bone matrix. Consider it a temporary framework to get the project started.
- Unlike the stronger lamellar bone, woven bone has a more disorganised and random arrangement of collagen fibres. Consider a tangled jumble of wires vs carefully organised cables. This quick building weakens it but enables for faster bone development.
- Woven bone begins mineralizing as it is being created, giving it a woven and infantile look under a microscope. In contrast to the more phased procedure used with lamellar bone, this is a contemporaneous process.
- Woven bone is a temporary player. The body progressively replaces it with the stronger and more organised lamellar bone through a process known as remodelling. Woven bone is analogous to the rough draft that is corrected before becoming the final polished form.
What is Lamellar Bone?
Lamellar bone, also known as secondary or mature bone, is the most prevalent form of bone tissue in the adult skeleton. Its collagen fibres are finely organised and stacked, making it significantly stronger and more stiff than woven bone. Osteoblasts deposit these layers, known as lamellae, in a parallel pattern, resulting in a plywood-like structure capable of withstanding substantial stresses. Lamellar bone is regularly remodelled during life to retain strength and respond to mechanical demands.
Explore All Women's Scrub
Key Features of Lamellar Bone:
- Lamellar bone has a well-organized and stratified arrangement of collagen fibres. Consider perfectly built and aligned bricks, resulting in a considerably stronger and more solid material than braided bone.
- Lamellar bone has a more methodical approach. Collagen fibres are put down first, and subsequently mineralized, resulting in hardness and strength. This tiered method creates a stronger framework.
- Lamellar bone is named from its lamellae, which are tiny layers of mineralized bone matrix with collagen fibres. These layers are layered in a precise and organised manner, adding to the bone's strength.
- The adult skeleton is primarily made up of lamellar bone. It's intended for strength, stability, and long-term function, supplying the body's structure and support.
Shop Best Lab Coats from Here!
Similarities Between Woven Bone and Lamellar Bone
- Woven bone and lamellar bone are two forms of osseous tissue that comprise the skeletal system.
- Both forms of bone tissue contain collagen fibres that have been mineralized with calcium and other minerals, resulting in strength and stiffness.
- Osteoblasts, specialised bone-forming cells, generate both woven and lamellar bone.
- Both forms of bone tissue provide structural support and protection for numerous organs and tissues in the body.
- Throughout life, both woven and lamellar bone undergo remodelling, which is a continual bone resorption and production process mediated by osteoclasts and osteoblasts.
Woven bone and lamellar bone are two separate forms of bone tissue distinguished by their collagen structure and overall strength. Woven bone, also known as basic bone, has a random arrangement of collagen fibres, like a woven basket. This disorganised structure makes it less strong than lamellar bone, yet it allows for faster production during development, repair, or under certain pathological situations. In contrast, lamellar bone, also known as secondary bone, has a highly organised structure with collagen fibres carefully aligned in parallel sheets. Lamellar bone is the predominant bone tissue in the adult skeleton due to its extensive layering, which provides better strength and stability. In essence, woven bone vs. lamellar bone is a trade-off between fast creation and structural strength.
| Check out More Articles | |
| Difference Between Cartilage and Bone | |
| Difference Between Endocrine and Exocrine Glands | |
| Difference Between Cell Wall and Cell Membrane | |