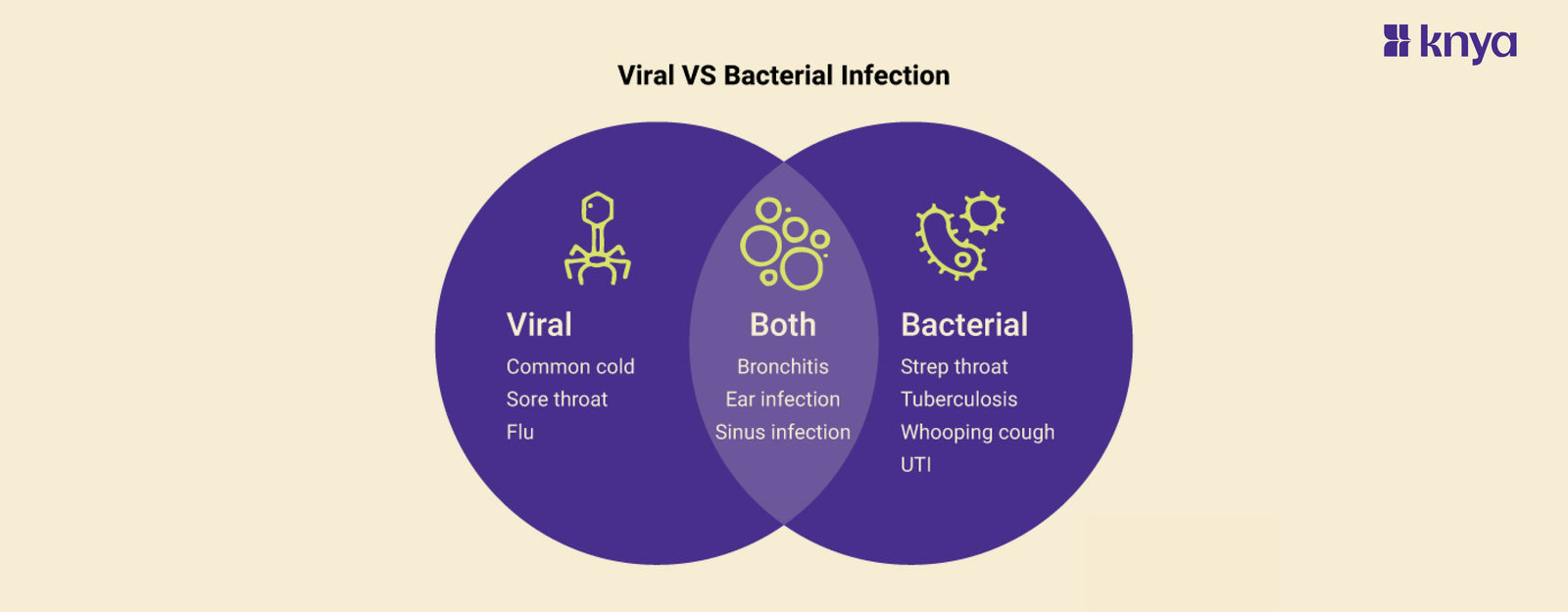
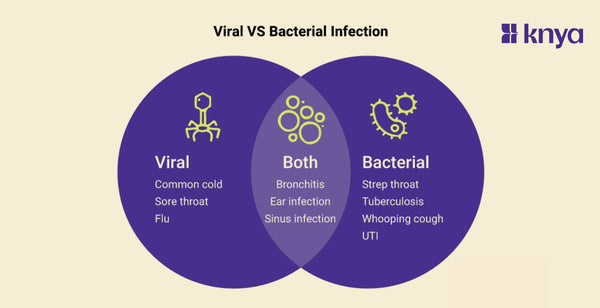
Difference Between Viral and Bacterial Infection: Viral and bacterial infections, microscopic intruders that cause anything from colds to pandemics, are both frequent but fundamentally different. Bacteria, which are single-celled creatures, live within us and can cause illnesses such as pneumonia. Viruses, which are much smaller and require us to exist, hijack our cells, causing them to produce viral copies, resulting in symptoms such as fever and exhaustion. Most bacterial adversaries are vanquished by antibiotic combinations, however viruses frequently need a lengthy war between our immune system and, for a lucky few, particular antiviral drugs. Though both can spread through coughs, sneezes, and physical contact, recognising their distinct characteristics helps us avoid and treat them properly.
Difference between Viral and Bacterial Infection
Viral and bacterial infections are two distinct types of infectious diseases caused by different types of microorganisms – viruses and bacteria. Following are the differences between viral and bacterial infections.
|
Feature |
Viral Infection |
Bacterial Infection |
|
Microorganism Type |
Viruses (non-living) |
Bacteria (living) |
|
Cellular Structure |
Lack cellular structure |
Have a distinct cellular structure |
|
Living or Non-Living |
Non-living |
Living |
|
Treatment |
Antiviral medications |
Antibiotics |
|
Reproduction |
Replicate within host cells |
Replicate independently through binary fission |
|
Size |
Smaller (nanometers) |
Larger (micrometers) |
|
Genetic Material |
DNA or RNA |
Typically DNA |
|
Symptoms |
Fever, fatigue, muscle aches |
Localized pain, swelling, pus formation |
|
Host Specificity |
Highly host-specific |
Broad host range |
|
Prevention |
Vaccines, antivirals |
Vaccines, antibiotics, hygiene practices |
Browse Best Scrubs Collection
What is Viral Infection?
Viral infections are caused by viruses, tiny organisms that invade and hijack healthy cells to reproduce. They spread through coughing, sneezing, contact with dirty surfaces, or bodily fluids. Common viral infections include the common cold, flu, COVID-19, and chickenpox. Symptoms vary depending on the virus, but often include fever, cough, running nose, fatigue, and muscle aches. Treatment mainly focuses on relieving symptoms and supporting the body's immune response, as antibiotics don't work against viruses. Vaccines can prevent some viral infections.
Key Features of Viral Infection:
- Viruses are far smaller than bacteria and lack complicated biological machinery. They hijack host cells to proliferate, thereby driving them to produce more viruses.
- Each virus targets a certain cell type, which explains why some viruses only cause certain illnesses (for example, the flu virus in respiratory cells). This sensitivity also makes creating broad-spectrum antiviral therapies difficult.
- Viruses change quickly, allowing them to avoid antibodies and withstand treatment. This fast adaptability exacerbates epidemics and complicates vaccine development.
- Viral infections can cause a variety of symptoms, including fever, tiredness, coughing, and rash. These symptoms indicate the body's immunological reaction to the illness.
What is Bacterial Infection?
Bacterial infections arise by single-celled organisms capable of self-reproduction. They can enter the body through skin wounds, mucosal membranes, or contaminated food or drink. Common bacterial illnesses include strep throat, urinary tract infections (UTIs), pneumonia, and skin infections. Symptoms may include fever, pus, discomfort, edoma, and redness. Antibiotics are commonly used to treat and eliminate germs.
Key Features of Bacterial Infection:
- Bacteria are self-sufficient beings that have their own cellular machinery. They can reproduce swiftly and flourish in many conditions, making them ubiquitous.
- Many bacteria create toxins that damage host cells and tissues, resulting in symptoms such as diarrhoea, vomiting, and tissue damage. This direct attack sets them apart from viruses.
- Bacterial infections can be treated with medicines that target certain bacterial functions. However, abuse and misuse of antibiotics can result in resistance, which is an increasing public health problem.
- While some bacteria target specific tissues, others can opportunistically infect several organs depending on the route of entry and the host's immunological response.
Shop Best Lab Coats from Here!
Similarities between Viral and Bacterial Infection
- Pathogenicity refers to the ability of viruses and bacteria to cause illness in their hosts.
- The immune system responds to viral and bacterial infections by activating defence systems.
- Symptoms for both types of infections include fever, inflammation, and weariness.
- Viruses and bacteria can spread by direct touch, respiratory droplets, or contaminated surfaces.
- Viruses and bacteria can change and adapt over time, resulting in new or antibiotic-resistant strains.
While both bacterial and viral infections can leave us feeling under the weather, their underlying culprits and the way they play out in our bodies are vastly different. Single-celled creatures with the ability to live independently, bacteria can enter tissues or colonise body surfaces to cause diseases like pneumonia or strep throat. Because of their propensity for multiplication and stubbornness, they must be defeated using specific medicines. Contrarily, viruses are significantly smaller and lack the independence of bacteria. They take over our own cells and force them to reproduce the virus again until the cell explodes and releases a fresh batch of viruses that can infect more people. Because of their parasitic approach, they are infamously difficult to eradicate; antiviral drugs frequently merely treat the symptoms. So, the next time you're feeling unwelll, remember, the battle behind your sniffles and sore throat might be waged by tiny, independent soldiers or resourceful cellular hijackers – and understanding the difference between viral and bacterial infections can be the first step towards finding the right weapon for a huge victory.
| Check out More Articles | |
| Difference Between Psychosis and Neurosis | |
| Dorsal Vs Ventral | |
| Difference Between Striated and Unstriated Muscles | |