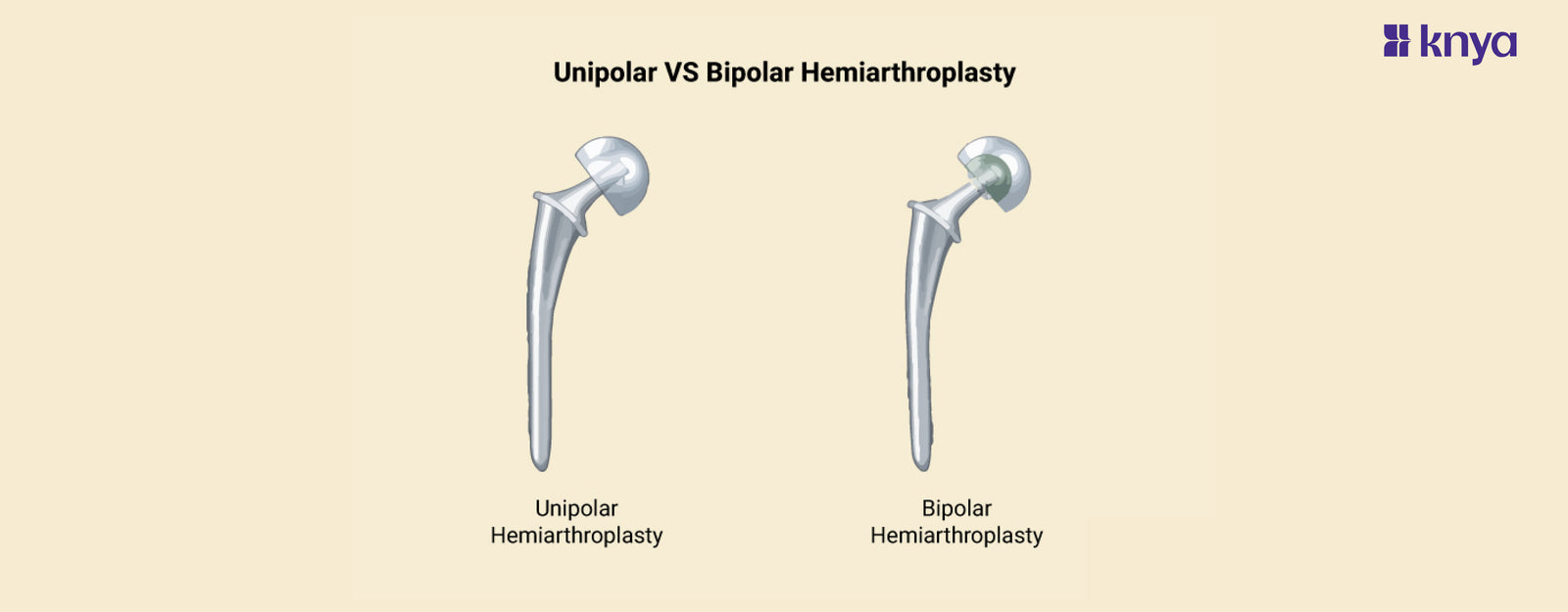
Unipolar Vs Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty: Joint replacement surgeries have become increasingly prevalent, offering relief and enhanced mobility to individuals grappling with hip joint issues. Unipolar and bipolar hemiarthroplasty are two surgical approaches that address specific concerns related to the hip joint. While both procedures aim to reduce pain and restore function, they differ in their design and application. Let's delve into the nuances of unipolar versus bipolar hemiarthroplasty, exploring the difference between that define each technique.
Unipolar Vs Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty
Here's a summary highlighting the key differences between Unipolar and Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty:
|
Feature |
Unipolar Hemiarthroplasty |
Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty |
|
Articular Surface Configuration |
Replaces only the femoral head |
Replaces both the femoral head and acetabulum |
|
Movement Mechanism |
Femoral head rotates within the acetabulum |
Both femoral head and acetabulum can move independently |
|
Indications and Considerations |
Fractures of the femoral neck, especially in the elderly |
Arthritis or conditions where preserving the acetabulum is beneficial |
|
Stability and Range of Motion |
Generally stable but may have limitations in range of motion |
Increased stability and broader range of motion due to dual articulation |
|
Surgical Complexity |
Simpler procedure compared to bipolar |
Can be more complex due to the dual articulation system |
|
Wear and Tear |
Potentially lower wear due to unipolar design |
Wear distributed between the femoral head and acetabulum, potentially affecting longevity |
|
Revision Surgery |
Easier to revise if needed |
Revision can be more challenging due to dual components |
|
Patient Age |
Commonly used in elderly patients with femoral neck fractures |
Suitable for a broader range of age groups and conditions |
|
Prosthetic Longevity |
May have a longer lifespan in certain cases |
Longevity influenced by factors such as patient activity and implant materials |
What is Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty?
Bipolar hemiarthroplasty is a surgical procedure commonly employed in orthopedics, specifically for the treatment of hip joint conditions, such as fractures, arthritis, or degenerative disorders. This procedure involves the replacement of both the femoral head (the ball-shaped top of the thigh bone) and the acetabulum (the socket in the pelvic bone where the femoral head fits) with prosthetic components.
Key features of bipolar hemiarthroplasty include:
- Dual Articulation: Unlike unipolar hemiarthroplasty, which replaces only the femoral head, bipolar hemiarthroplasty involves the use of a dual articulation system. This means that both the femoral head and the acetabulum are replaced, allowing for movement at both articulating surfaces.
- Increased Stability: The dual articulation design contributes to increased stability in the hip joint. This stability can be beneficial, especially in cases where the patient has conditions such as arthritis or where preservation of the acetabulum is desired.
- Range of Motion: Bipolar hemiarthroplasty provides a broader range of motion compared to unipolar procedures. This is due to the dual articulation, allowing for more natural movement between the femoral head and the acetabulum.
- Indications: Bipolar hemiarthroplasty is often recommended for patients with conditions beyond femoral neck fractures, such as those with arthritis affecting the hip joint. The procedure is versatile and can be applied to various hip joint disorders.
- Surgical Considerations: While offering advantages in terms of stability and range of motion, bipolar hemiarthroplasty can be a more complex surgical procedure compared to unipolar alternatives. Surgeons need to carefully assess each patient's condition to determine the most appropriate surgical approach.
- Implant Longevity: The longevity of the prosthetic components in bipolar hemiarthroplasty may be influenced by factors such as patient activity level, the quality of the surgical technique, and the materials used in the implants.
Bipolar hemiarthroplasty aims to improve joint function, alleviate pain, and enhance the overall quality of life for individuals suffering from hip joint conditions. Surgeons evaluate the patient's specific condition and medical history to determine whether bipolar hemiarthroplasty is the most suitable option for their needs.
What is Unipolar Hemiarthroplasty?
Unipolar hemiarthroplasty is a surgical procedure commonly used in orthopedics to address certain hip joint conditions, particularly fractures of the femoral neck. The term "unipolar" refers to the fact that only one component of the hip joint is replaced during the surgery. Specifically, unipolar hemiarthroplasty involves the replacement of the femoral head (the ball-shaped top of the thigh bone) with a prosthetic implant, while the acetabulum (the socket in the pelvic bone) remains untouched.
Here are key characteristics and considerations associated with unipolar hemiarthroplasty:
- Femoral Head Replacement: The primary focus of unipolar hemiarthroplasty is to replace the damaged or fractured femoral head with a prosthetic implant. This implant typically consists of a metal stem that is inserted into the femur and a ball-shaped component that mimics the natural shape of the femoral head.
- Surgical Simplicity: Unipolar hemiarthroplasty is often considered a simpler surgical procedure compared to its bipolar counterpart. This simplicity can be advantageous, especially in cases where a less invasive approach is preferred or in situations where the patient's overall health may limit the complexity of the surgery.
- Indications: This procedure is commonly recommended for elderly patients who have sustained a fracture of the femoral neck. Femoral neck fractures are relatively common in this demographic and can significantly impact mobility and quality of life.
- Stability: While unipolar hemiarthroplasty can provide stability by replacing the damaged femoral head, it may have limitations in terms of rotational stability and range of motion compared to bipolar procedures.
- Limitations in Arthritis Cases: Unipolar hemiarthroplasty may not be the preferred choice for individuals with pre-existing arthritis or conditions that affect the acetabulum. In such cases, bipolar or total hip arthroplasty may be considered.
- Revision Surgery: If the need for revision surgery arises, unipolar hemiarthroplasty is generally considered more straightforward compared to revision procedures involving both the femoral head and the acetabulum.
The decision to perform unipolar hemiarthroplasty is based on careful evaluation by orthopedic surgeons, taking into consideration the patient's age, overall health, the nature of the hip joint condition, and the desired outcomes. The goal of unipolar hemiarthroplasty is to alleviate pain, restore function, and improve the patient's ability to bear weight on the affected hip.
Shop best Lab Coats from Here!
Similarity Between Unipolar and Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty
While unipolar and bipolar hemiarthroplasty are distinct surgical approaches used to address hip joint conditions, they share certain similarities, particularly in their overarching goal of improving the functionality and quality of life for patients with hip issues. Here are some commonalities between unipolar and bipolar hemiarthroplasty:
- Hip Joint Pain Relief: Both unipolar and bipolar hemiarthroplasty are performed with the primary objective of alleviating pain in the hip joint. Whether caused by fractures, arthritis, or other degenerative conditions, these procedures aim to reduce discomfort and improve the patient's overall quality of life.
- Improved Mobility: Both procedures contribute to enhanced mobility for patients. By addressing the underlying issues in the hip joint, individuals undergoing either unipolar or bipolar hemiarthroplasty can experience an increased range of motion and a restored ability to perform daily activities.
- Orthopedic Reconstruction: Unipolar and bipolar hemiarthroplasty involves the reconstruction of the hip joint using prosthetic components. These implants are designed to mimic the natural anatomy of the hip, providing stability and facilitating normal joint function.
- Focus on Femoral Head: In both procedures, attention is directed toward the femoral head—the ball-shaped portion of the thigh bone. Whether replacing just the femoral head in unipolar hemiarthroplasty or both the femoral head and acetabulum in bipolar hemiarthroplasty, the aim is to address issues affecting this crucial hip joint component.
- Postoperative Rehabilitation: Patients undergoing either type of hemiarthroplasty typically undergo postoperative rehabilitation to regain strength, improve joint function, and maximize the benefits of the surgery. Rehabilitation programs often include exercises and physical therapy tailored to the specific procedure performed.
- Orthopedic Evaluation: Both procedures require a thorough orthopedic evaluation to determine the most appropriate surgical approach based on the patient's condition, age, overall health, and individual needs. Surgeons consider factors such as the nature of the hip pathology, the patient's activity level, and the potential for long-term success.
While these procedures share common goals, it's important to note that the choice between unipolar and bipolar hemiarthroplasty depends on various factors, including the specific condition being treated and the patient's unique circumstances. Orthopedic surgeons carefully assess each case to determine the most suitable surgical approach for optimal outcomes.
|
Check out More Articles |
|