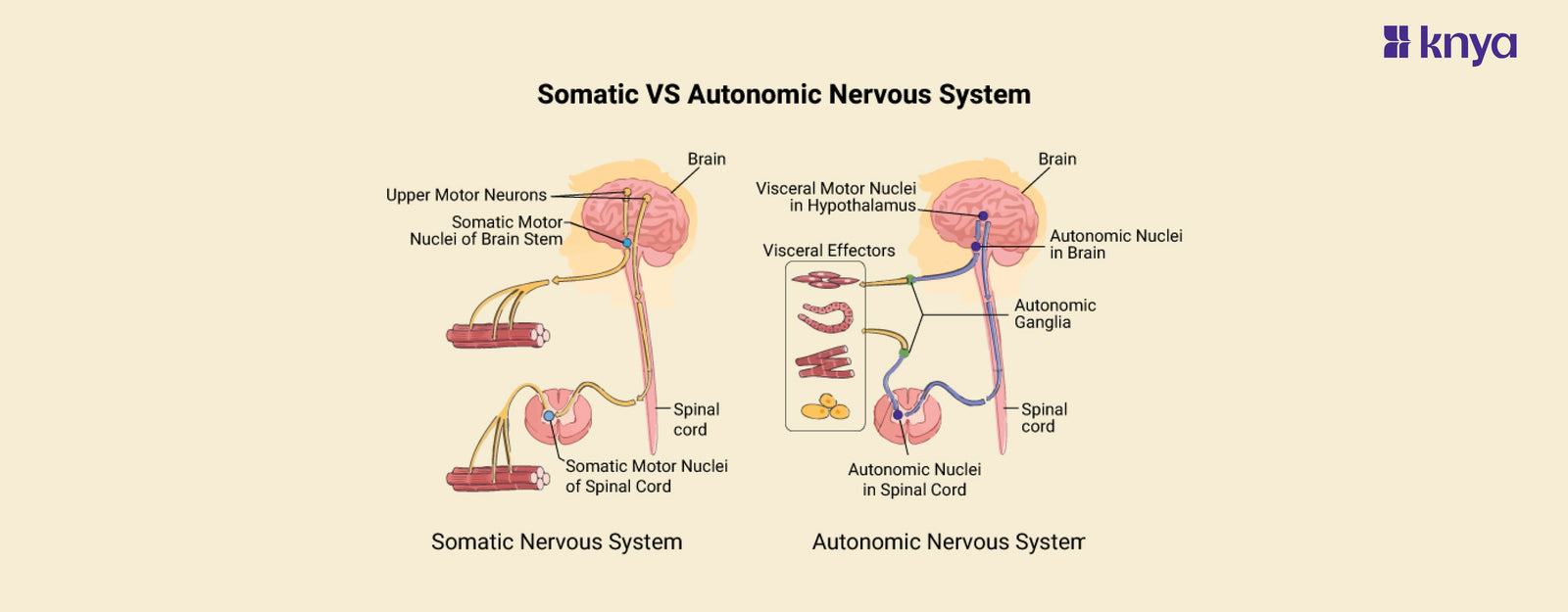
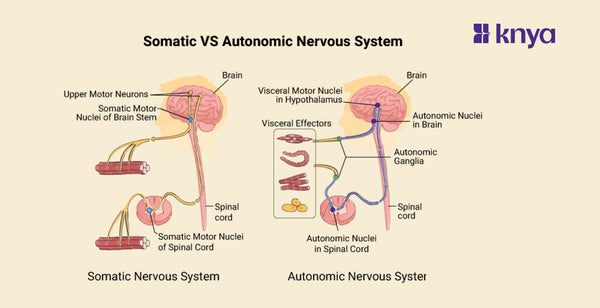
Difference Between Somatic and Autonomic Nervous System: Our nervous system is divided into two branches: somatic and autonomic. The somatic system regulates our conscious activities, such as moving our limbs and experiencing feelings from our surroundings. In contrast, the autonomic system operates automatically, controlling activities such as heart rate, digestion, and breathing without our conscious involvement. While both are important for our health, the distinction between somatic and autonomic processes is based on the degree of conscious control we have over them.
Difference Between Somatic and Autonomic Nervous System
The nervous system is a complex network responsible for transmitting signals between different parts of the body. It can be broadly divided into the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. Listing below are the differences between the two:
|
Feature |
Somatic Nervous System |
Autonomic Nervous System |
|
Control Type |
Voluntary |
Involuntary |
|
Muscle Control |
Skeletal muscles |
Smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, glands |
|
Sensory Information Transmission |
From sensory organs to CNS |
From internal organs to CNS |
|
Motor Neurons |
CNS to skeletal muscles |
CNS to smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, glands |
|
Conscious Perception |
Yes |
No |
|
Conscious Control |
Yes |
No |
|
Neural Pathways |
Single neuron |
Two neurons (preganglionic, postganglionic) |
|
Presence of Ganglia |
No |
Yes |
|
Neurotransmitters Used at Effector Junction |
Acetylcholine |
Acetylcholine, norepinephrine |
|
Response Speed |
Rapid |
Relatively slower |
|
Examples |
Walking, talking, writing |
Heart rate regulation, digestion, pupil dilation |
Browse Best Scrubs Collection
What is a Somatic Nervous System?
The somatic nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls your voluntary actions and sensations. It's like your body's conscious control panel. When you decide to raise your arm, the somatic nervous system sends signals from your brain to your muscles, making them contract and lift your arm. It also carries sensory information back to your brain, like the feeling of the fabric of your shirt against your skin.
Key Features of Somatic Nervous System:
- The star of the show! The somatic nerve system gives you conscious control over your skeletal muscles, allowing you to walk, talk, and write.
- Action messages are sent directly from the brain stem and spinal cord to the muscles, avoiding the complications of the autonomic system.
- While the somatic system is mostly voluntary, it also manages some involuntary reactions, such as knee jerks or withdrawing your hand away from something hot.
- Unlike the autonomic system, most somatic routes use a single neuron relay between the brain and muscles to provide quicker and more accurate control.
What is an Autonomic Nervous System?
The autonomic nervous system, on the other hand, regulates all of your body's automatic activities, such as heart rate, digestion, and breathing. It works constantly behind the scenes to keep you alive and functional even when you're not aware of it. The autonomic nervous system is divided into two branches: the sympathetic nervous system, which controls the "fight-or-flight" reaction, and the parasympathetic nervous system, which controls the "rest-and-digest" response.
Key Features of Autonomic Nervous System:
- This system operates behind the scenes, regulating vital functions like heart rate, breathing, digestion, and pupil dilation, without requiring your conscious thought.
- The autonomic system has two opposing divisions:
- Sympathetic: Activates the "fight-or-flight" response, increasing heart rate, respiration, and blood pressure during times of stress or exertion.
- Parasympathetic: Promotes a "rest-and-digest" state, slowing heart rate, lowering blood pressure, and aiding digestion and relaxation.
- Unlike the direct connection in the somatic system, the autonomic system uses a complex network of neurons, involving additional ganglia (clusters of nerve cells) before reaching target organs.
- The autonomic system heavily influences your emotional state. Increased arousal and anxiety can be linked to sympathetic activation, while relaxation and calmness are associated with parasympathetic dominance.
Shop Best Lab Coats from Here!
Similarities Between Somatic and Autonomic Nervous System
- The somatic and autonomic nerve systems Both systems play critical functions in maintaining physiological equilibrium and reacting to external and internal stimuli.
- Dysfunction in either system can result in a variety of health issues and illnesses.
- Both systems work together to efficiently control body processes.
- Both systems are controlled and influenced by higher brain centres, including the cerebral cortex, hypothalamus, and brainstem.
- Both systems have plasticity, which allows them to respond to changing environmental demands and stimuli.
While both the somatic and autonomic nervous systems are essential components of the peripheral nervous system, they have quite different regulation and function mechanisms. The somatic nerve system permits conscious control of skeletal muscles, which enables voluntary acts such as walking and writing. In contrast, the autonomic nervous system regulates involuntary actions such as heart rate, digestion, and pupil dilation. The contrast between conscious and unconscious control is the primary differentiation between the somatic and autonomic nerve systems, emphasising their respective roles in sustaining our internal and external surroundings.
| Check out More Articles | |
| Difference Between Cartilage and Bone | |
| Difference Between Endocrine and Exocrine Glands | |
| Difference Between Cell Wall and Cell Membrane | |