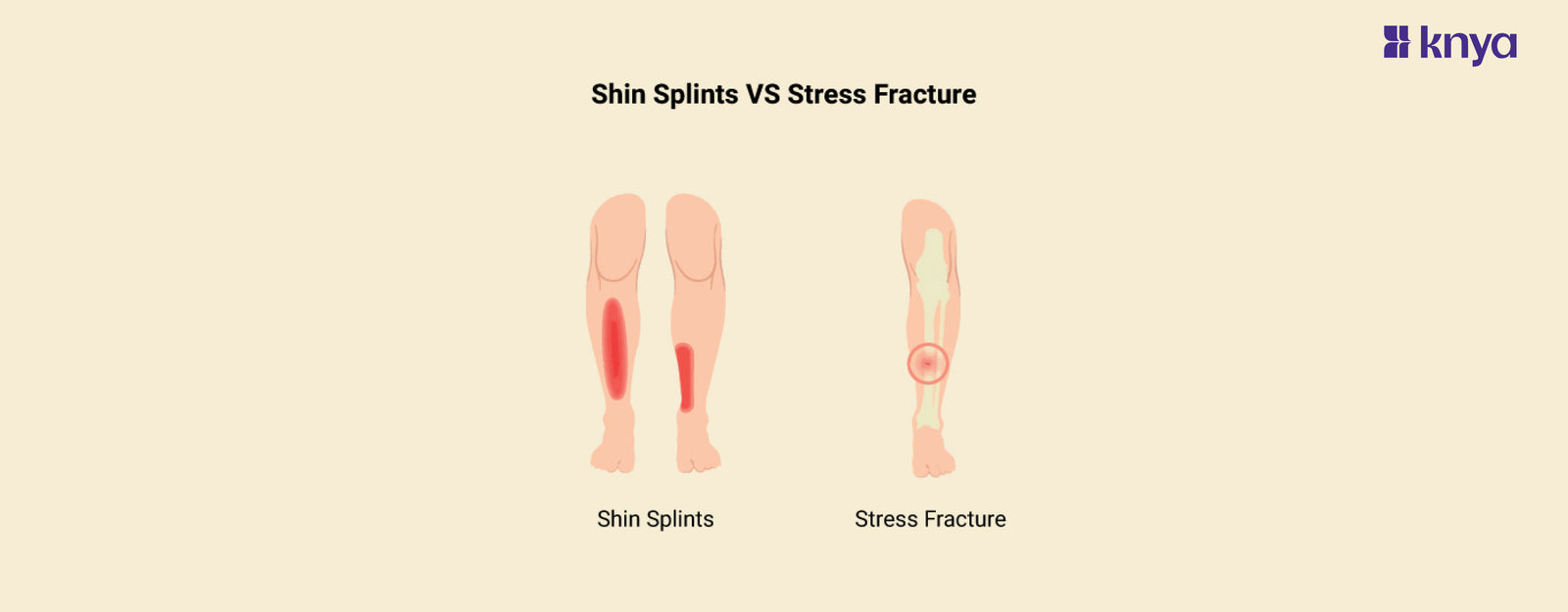
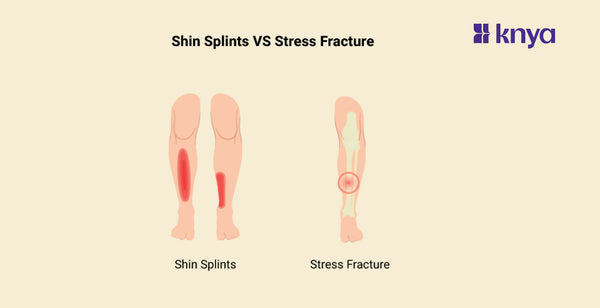
Shin Splints vs Stress Fracture: Shin Splints and Stress Fractures are injuries that target the lower leg and are commonly encountered by athletes and active individuals. Shin Splints, involves repetitive stress or pain all the way to the inner part of the shinbone. This happens particularly during physical activity. On the other hand, Stress Fractures are small cracks in the bone that happen due to a sudden increase in activity that leads to localised pain, swelling and tenderness. Proper diagnosis and treatment by a healthcare professional are very important for effective recovery and prevention of any further complications in both conditions.
Difference between Shin Splints and Stress Fracture
Stress Fractures involve small cracks or breaks in the bone due to repetitive stress or sudden increases in activity, resulting in localised pain, swelling, and tenderness at the fracture site. While Shin Splints primarily affect soft tissues, Stress Fractures directly involve the bone itself. The table below provides the differences between Shin Splints and Stress Fracture.
|
Aspect |
Shin Splints |
Stress Fracture |
|
Definition |
Inflammation of the muscles, tendons, and periosteum (connective tissue covering the bone) due to overuse or repetitive stress |
Small cracks or breaks in the bone resulting from repetitive stress or sudden increases in activity |
|
Location |
Along the inner part of the shinbone |
Typically in weight-bearing bones such as the tibia or metatarsals |
|
Pain |
Dull, aching pain during or after exercise, diminishes with rest |
Localised pain worsening with activity, improving with rest |
|
Swelling |
Minimal |
May experience swelling and tenderness at the fracture site |
|
Diagnosis |
Based on symptoms and physical examination, may include imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI |
Physical examination, X-rays, MRI, or bone scans |
|
Treatment |
Rest, ice, compression, elevation, NSAIDs, gradual return to activity |
Rest, immobilisation (e.g., cast, walking boot), NSAIDs, gradual return to weight-bearing activities |
|
Recovery Time |
Shorter |
Longer |
|
Complications |
Typically less severe |
Can lead to more severe complications if untreated |
Browse The Best Scrubs Collection!
What are Shin Splints?
Shin Splints also known as medial tibial stress syndrome (MTSS), are a painful illness characterised by soreness along the inner edge of the shinbone, usually caused by overuse or repetitive stress during physical activities. Overtraining, improper footwear, and biomechanical issues can contribute to their development. Treatment usually involves Rest, ice, stretching and strengthening exercises are few treatments involved.
Causes of Shin Splints
- Overtraining: High-impact activities, like running, jumping or any other physical activity without any proper rest can lead to straining of the muscles and bones in the lower legs.
- Rapid Increase in Activity: Increasing the frequency, duration, or intensity of physical activity can overwhelm the body's ability to adapt.
- Poor Biomechanics: Flat feet, high arches, or muscle imbalances in the lower legs can cause the distribution of forces during movement which increases the risk of Shin Splints.
- Improper Footwear: Wearing worn-out shoes or shoes that do not provide the correct amount of support or cushioning contributes to excessive stress on the shinbone and surrounding tissues.
Symptoms of Shin Splints
- Pain: Pain along the inner edge of the shinbone is the main symptom of Shin Splints. The pain may be dull and achy or sharp and stabbing, and it gradually worsens after physical activities such as running or jumping.
- Tenderness: The area along the shinbone can be sore to the touch and may exacerbate the pain when pressed.
- Swelling: There may be mild swelling along the inner part of the shin in some cases though significant swelling is less common.
- Discomfort with Activity: Running, jumping, walking, or any other activity that involves repetitive stress on the lower legs may worsen the pain.
What is Stress Fracture?
A Stress Fracture is a small crack or hairline fracture in a bone which is caused by repeated stress and not a single traumatic injury. This type of fracture usually occurs in weight-bearing bones, such as the shinbone, metatarsals in the foot, or bones of the lower back. Stress Fractures are common in athletes who engage in repetitive activities like running, jumping, or dancing and among military personnel who march or run for extended periods.
Causes of Stress Fracture
- Overtraining: Involving in high-impact activities, such as running, jumping, or dancing, without proper rest or gradually increasing the intensity can strain the bones and lead to Stress Fractures.
- Sudden Increase in Activity: Rapidly increasing the frequency, duration, or intensity of physical activity can overwhelm the body's ability to adapt which causes excessive stress on the bones and increases the risk of Stress Fractures.
- Poor Biomechanics: Factors such as improper footwear, muscle imbalances, or structural abnormalities in the feet can change the distribution of forces during motion, leading to increased stress on certain bones and an elevated risk of Stress Fractures.
- Inadequate Rest: Improper rest between training sessions or failure to allow enough time for recovery can prevent the bones from repairing and therefore increase the chances of Stress Fractures.
Symptoms of Stress Fracture
- Pain: Continuous pain, which can be dull or sharp, particularly in the area of the fracture. The pain worsens with weight-bearing activities and with rest, it gets better.
- Swelling: Swelling may occur around the affected area, however it is usually mild compared to acute fractures.
- Tenderness: The area over the Stress Fracture may be tender to the touch, and pressing on it may make it worse.
- Bruising: In some cases, there can be chances for bruising around the site of the fracture, though this is less common than with acute fractures.
- Changes in Gait or Movement: People with Stress Fractures may alter their gait or movement patterns to avoid putting pressure on the damaged bone, which can cause compensatory issues in other areas.
Shop Best Lab Coats From Here!
Similarities between Shin Splints and Stress Fracture
- Location of Pain: Both Shin Splints and Stress Fractures cause pain along the inner edge of the shinbone. The pain may be localised or spread overall, depending on the degree and location of the injury.
- Activity-related Pain: Pain associated with both conditions often worsens during or after weight-bearing activities, such as running, jumping, or walking. The pain may improve with rest.
- Overuse Injuries: Shin Splints and Stress Fractures are both due to overuse injuries.
- Risk Factors: Both occur due to common factors like overtraining, sudden rise in activity, improper footwear and not getting proper rest between training or physical activity.
Order the Best Jogger Scrub From Here!
| Check out More Articles | |
| Difference Between Cartilage and Bone | |
| Difference Between Endocrine and Exocrine Glands | |
| Difference Between Cell Wall and Cell Membrane | |