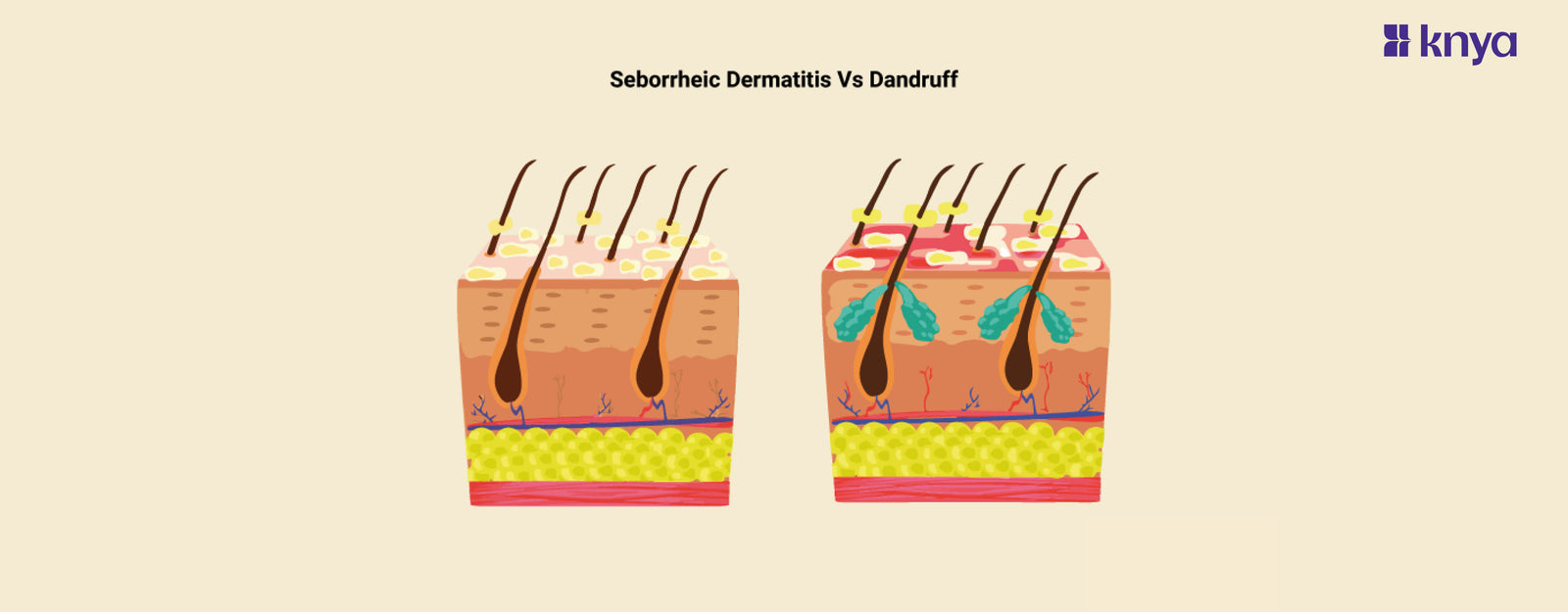
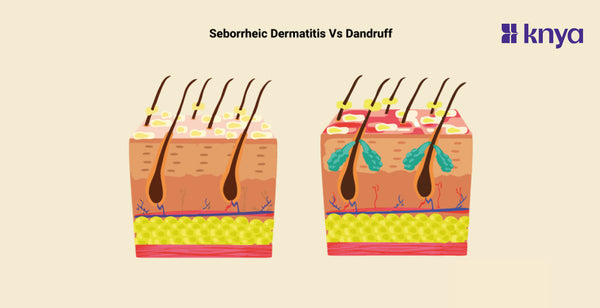
Seborrhoeic dermatitis and dandruff are both common scalp conditions that produce flaking, but there are several crucial distinctions. Dandruff is usually milder, with dry, white or yellowish flakes and occasional irritation. It is caused by increased skin cell loss as a result of Malassezia yeast proliferation. Dandruff frequently remains on the scalp. In contrast, seborrhoeic dermatitis is an inflammatory problem. It generates red, oily areas with yellow or white flakes that may be irritating or burning. It is believed to be caused by a mix of genetics, Malassezia, and excessive oil glands. Seborrhoeic dermatitis can also affect other parts of the body that contain sebaceous glands, such as the brows, beard, and chest.
Difference between Seborrheic Dermatitis and Dandruff
Seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff are both common scalp conditions that cause flaking and irritation, but they have some key differences.
|
Feature |
Dandruff |
Seborrheic Dermatitis |
|
1. Severity |
Generally milder with mild flaking and itchiness |
Can range from mild to severe with inflammation and scales |
|
2. Inflammation |
Mild inflammation |
More significant inflammation, red patches, and scales |
|
3. Distribution |
Primarily affects the scalp |
Extends beyond the scalp to face, ears, chest, and back |
|
4. Symptoms |
Mainly flaking and itching |
Flaking, itching, redness, swelling, and discomfort |
|
5. Underlying Causes |
Linked to overgrowth of Malassezia yeast |
Exact cause not fully understood; genetic and immune factors may play a role |
|
6. Age of Onset |
Can occur at any age |
More common in infants and adults between 30 and 60 |
|
7. Chronicity |
Generally chronic |
May also be chronic with periods of exacerbation and remission |
|
8. Associated Conditions |
Usually not associated with other conditions |
Linked to conditions like psoriasis, rosacea, and HIV |
|
9. Treatment Approach |
Over-the-counter shampoos often sufficient |
May require prescription medications, including steroids and antifungal creams |
|
10. Medical Evaluation |
Often managed with self-care measures |
Sometimes requires medical evaluation, especially for severe or persistent cases |
Browse Best Scrubs Collection
What is Seborrhoeic Dermatitis?
Dandruff is a milder condition that mostly affects the scalp. It produces dry, white, or yellowish flakes that can be irritating. Dandruff is considered to be caused by a mix of factors such as excess oil production, fungal infestation, and sensitivity to hair care treatments.
Key Features of Seborrhoeic Dermatitis:
- Seborrheic dermatitis typically presents with reddish or yellowish patches covered in oily flakes. These patches often appear on the scalp, but can also affect the face (around the nose, eyebrows, and beard), chest, and upper back.
- While not usually present, seborrhoeic dermatitis can produce itching, burning, or stinging in the afflicted regions.
- Malassezia, a yeast, is naturally found on the skin. In seborrhoeic dermatitis, this yeast overgrows, causing irritation and flaking.
- Stress, cold weather, certain drugs, and greasy skin can all cause or exacerbate seborrhoeic dermatitis.
What is Dandruff?
Seborrheic dermatitis is a more severe condition that can affect the scalp as well as other oily areas of the body, such as the face, ears, and chest. It causes red, patchy, and scaly skin that can be itchy and greasy. Seborrheic dermatitis is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic factors, hormonal changes, and stress.
Key Features of Dandruff:
- Dandruff often appears as dry, white or greyish flakes that fall across the shoulders and clothing. The scalp itself may not be red or irritated.
- Dandruff can produce mild to severe scalp itching, but it is usually less acute and extensive than that caused by seborrhoeic dermatitis.
- Dandruff is characterised by scalp dryness and irritation, both of which contribute to flaking.
- Dandruff flakes shed more faster than those from seborrhoeic dermatitis, creating a more visible "snowfall" look.
Shop Best Lab Coats from Here!
Similarities Between Seborrhoeic Dermatitis and Dandruff
- Flaking: Both disorders include the appearance of flakes or scales on the scalp.
- Itching is a typical symptom of both dandruff and seborrhoeic dermatitis.
- Treatments: Both disorders can be managed with medicated shampoos, topical steroids, and antifungal medications.
- Both may have recurrence even after effective therapy.
- Both conditions are not infectious and cannot be transmitted through human contact.
While both seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff cause pesky scalp flakes and itch, their underlying differences are as clear as day. Seborrheic dermatitis, a more intense cousin of dandruff, extends its reach beyond the scalp, colonizing oily zones like the face, eyebrows, and chest with yellowish, greasy scales. Dandruff, on the other hand, is a strictly scalp-dweller, favoring dry, white flakes. Inflammation, a hallmark of seborrheic dermatitis, amps up the itch factor and paints affected areas red. Dandruff, though itchy, lacks this inflammatory punch. So, the next time you're battling flakes, take a closer look - greasy, widespread, and inflamed? Seborrheic dermatitis. Dry, localized, and itch-without-redness? Dandruff. Knowing your foe is the first step to victory!
| Check out More Articles | |
| Difference Between Psychosis and Neurosis | |
| Dorsal Vs Ventral | |
| Difference Between Striated and Unstriated Muscles | |