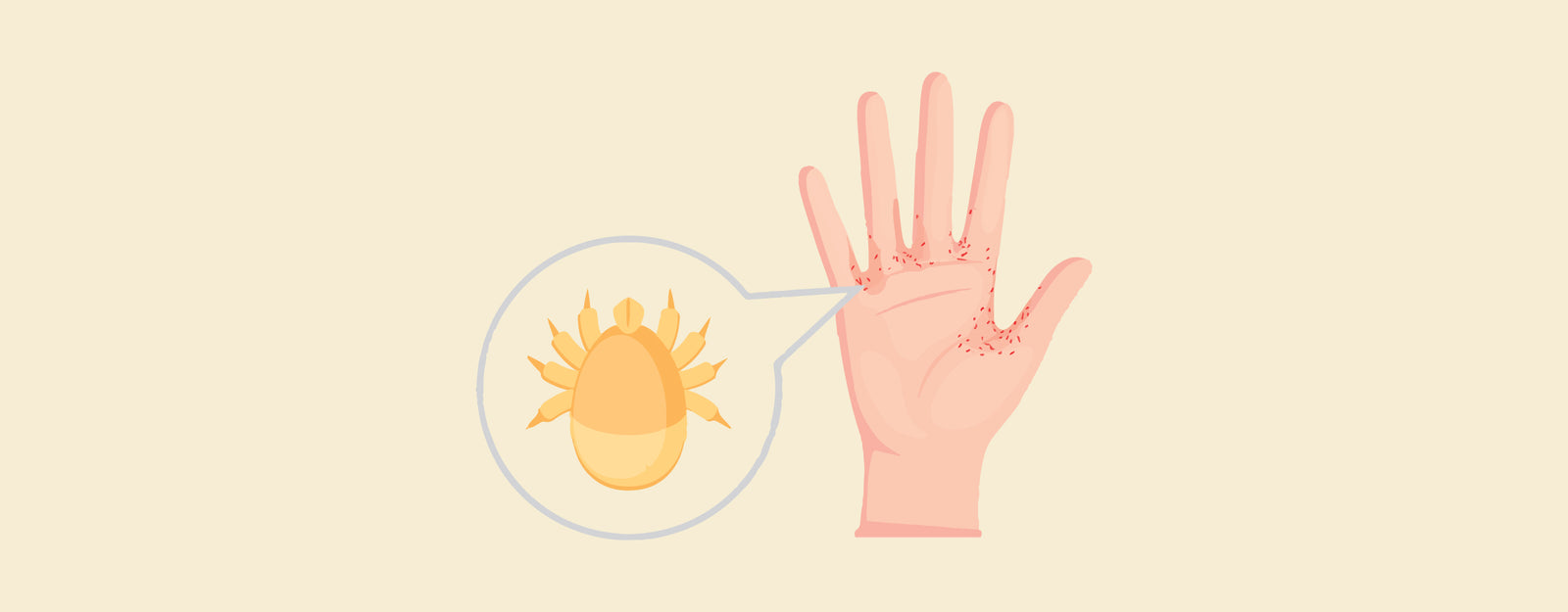
Difference between Scabies vs Syphilis: Scabies and Syphilis are two different medical conditions that affect the skin caused by different pathogens and have unique characteristics. Scabies, caused by the Sarcoptes scabies mite, spreads through close physical contact which leads to intense itching, rash, and small bumps. Whereas, Syphilis, caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum, mainly spreads through sexual contact and progresses through stages, from painless sores to severe complications if left untreated.
Difference between Scabies and Syphilis
Scabies are caused by the Sarcoptes scabies mite, which results in intense itching and a rash, while Syphilis, is caused by Treponema pallidum bacteria, whose degree increases through stages with potentially severe complications if untreated. The table below provides the differences between Scabies and Syphilis.
| Aspect | Scabies | Syphilis |
| Cause | Sarcoptes scabiei mite | Treponema pallidum bacterium |
| Transmission | Close physical contact | Sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex |
| Symptoms | Intense itching, rash, small bumps | Primary stage: painless sore (chancre); Secondary stage: rash |
| Treatment | Topical or oral medications | Antibiotics, such as penicillin |
| Complications | Secondary infections from scratching | Severe complications if untreated, affecting multiple organs |
| Prevention | Avoiding close contact with infected individuals | Safe sexual practices, regular screening, and treatment |
Browse The Best Scrubs Collection!
What are Scabies?
Scabies is an extremely contagious skin infestation caused by the Sarcoptes Scabies mite. These little mites delve into the epidermis, depositing their eggs and producing a rash that is unpleasant and frequently worse at night. It frequently affects the vaginal area, armpits, wrists, elbows, and spaces between the fingers. In congested living environments, Scabies can spread quickly and are transferred by close skin-to-skin contact. Prescription drugs are usually used in treatment to eradicate the mites and their eggs, coupled with precautions against re-infestation and transmission.
Causes of Scabies
- Direct Skin-to-Skin Contact: Holding hands, sharing a bed, or any prolonged, close contact with an infected individual are the main ways that Scabies are transmitted.
- Living Conditions that are Crowded: Scabies are more likely to spread in settings like child care centres, nursing homes, and jails where individuals are frequently near one another.
- Sharing Personal Stuff: The mites can spread by sharing linens, clothes, towels, or other personal objects with an infected person.
- Weaker Immune System: Individuals receiving chemotherapy or living with HIV/AIDS are among those who have weaker immune systems and are more likely to get severe or long-lasting Scabies infections.
- Age: Scabies can strike anyone at any age, but because of their weakened immune systems and frequent contact with others, they strike youngsters and the elderly more frequently.
- Poor Hygiene: While Scabies can afflict people regardless of their level of hygiene, bad hygiene can help the infestation spread.
Symptoms of Scabies
- Severe Itching: Severe itching is the most frequent symptom of Scabies. It usually gets worse at night and can get much worse after taking a hot bath or shower.
- Rash: Tiny red pimples or blisters are the outward sign of a Scabies infestation. The rash could be found in skin folds around the waist, buttocks, elbows, wrists, fingers, and buttocks.
- Burrows and Tracks: On the skin's surface, thin, asymmetrical tracks or burrows may occasionally be visible. These result from mites entering the skin to deposit their eggs.
- Secondary Infections: By causing skin breaches from scratching, impetigo and other bacterial infections are more likely to occur.
What is Syphilis?
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. The degree of the disease increases through stages, starting with painless sores followed by symptoms similar to flu. Getting a proper treatment is very important
Causes of Syphilis
- Unprotected Sexual Activity: Engaging in sexual activity without using any protection may increase the risk of contracting Syphilis.
- Direct Contact with Syphilitic Sores: Syphilis is highly contagious in its primary and secondary stages when open sores (chancres) are present. Therefore any close contact with these sores can transmit the infection.
-
Vertical Transmission: Pregnant women with Syphilis can transmit the infection
to their unborn child during pregnancy or childbirth, leading to congenital Syphilis in infants. - Shared Needles: Sharing needles, syringes, or other drug paraphernalia with an infected person can transmit Syphilis.
- Blood Transfusions: Although rare, Syphilis can be transmitted through blood transfusions if the donated blood is infected with the bacterium.
Symptoms of Syphilis
- Primary Syphilis: Characterized by painless sores on genitals, anus, or mouth, appearing 3 weeks to 3 months after infection.
- Secondary Syphilis: Develops a few weeks to months after the chancre heals, with symptoms such as rash, fever, fatigue, sore throat, swollen lymph nodes, and patchy hair loss.
- Latent Syphilis: No symptoms, divided into early (within the past year) and late (more than a year ago).
- Tertiary Syphilis: Serious complications if untreated, including neurosyphilis (nervous system damage), cardiovascular Syphilis, and gummatous Syphilis.
Shop Best Lab Coats From Here!
Similarities between Scabies and Syphilis
- Skin Involvement: Both Scabies and Syphilis can affect the skin.
- Secondary Infections: Scratching the affected areas in both conditions can lead to secondary bacterial infections.
- Sexual Transmission: While Scabies are primarily transmitted through skin-to-skin contact, Syphilis can also be transmitted sexually.
- Rash: Both conditions may present with rashes, although the characteristics of the rashes differ. In secondary Syphilis, a rash may appear on the skin, while Scabies presents with a characteristic rash accompanied by burrow tracks and intense itching.
In summary, while both Scabies and Syphilis can affect the skin, they are caused by different pathogens (mites vs. bacteria) and have distinct modes of transmission, symptoms, and treatments. Syphilis, being a sexually transmitted infection, requires prompt medical attention and treatment to prevent serious complications and further transmission.
Order the Best Jogger Scrub From Here!
| Check out More Articles | |
| Difference Between Cartilage And Bone | |
| Difference Between Endocrine And Exocrine Glands | |
| Difference Between Cell Wall And Cell Membrane | |