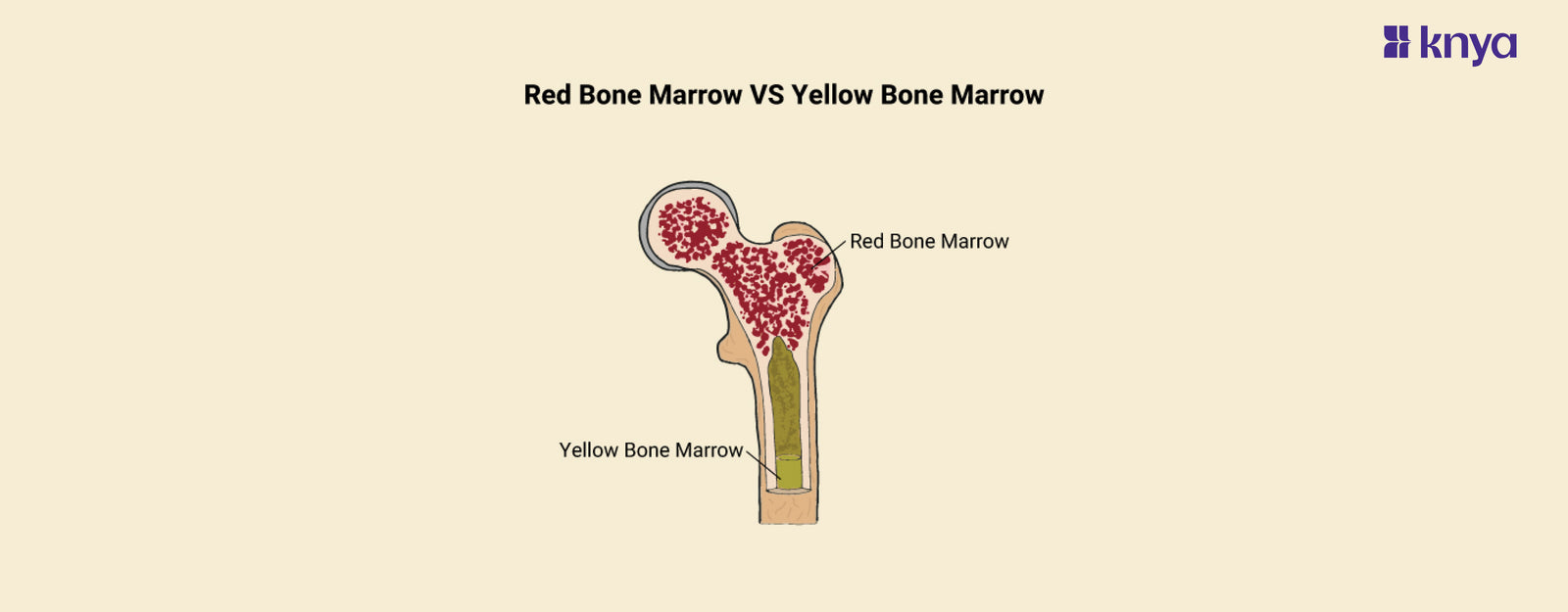
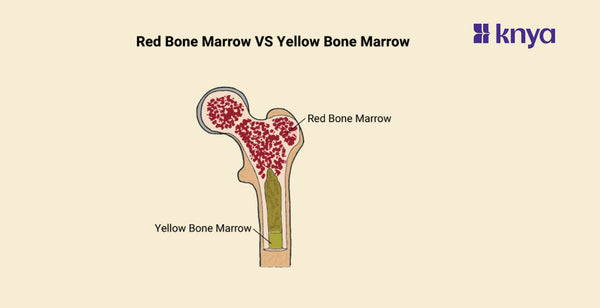
Difference Between Red Bone Marrow and Yellow Bone Marrow: Our bones contain two forms of bone marrow: red and yellow, which differ significantly. Red bone marrow, which is active in our youth, is a blood cell factory that produces red blood cells for oxygen delivery, white blood cells to combat infection, and platelets for clotting. Yellow bone marrow, which takes control as we age, stores fat for energy and contains stem cells that may form bone, cartilage, or even return to red marrow in times of dire need.
Difference Between Red and Yellow Bone Marrow
Red and yellow bone marrow are two forms of bone marrow found in animals, including humans. outlined are the differences between red and yellow bone marrow.
|
Feature |
Red Bone Marrow |
Yellow Bone Marrow |
|
Color |
Appears red due to rich blood supply |
Appears yellow due to higher fat concentration |
|
Composition |
Hematopoietic tissue: blood cell production |
Primarily adipocytes: fat storage |
|
Function |
Produces blood cells |
Stores fat, does not produce blood cells |
|
Location |
Mainly in spongy bone (sternum, pelvis, etc.) |
Found in medullary cavity of long bones |
|
Cellularity |
Higher cellular density |
Lower cellular density |
|
Age-related Changes |
Converts gradually to yellow with age |
Becomes predominant as individual ages |
|
Blood Cell Production |
Continuously produces blood cells |
Does not contribute to blood cell production |
|
Nutrient Storage |
Does not store fat |
Stores triglycerides for energy metabolism |
|
Response to Anemia |
Can increase activity to produce more cells |
Remains relatively inactive |
|
Microenvironment |
Provides supportive environment for hematopoiesis |
Lacks supportive elements for blood cell production |
Order the Best Jogger Scrub from Here!
What is Red Bone Marrow?
Red bone marrow is a spongy substance that exists within parts of your bones. It produces red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, all of which are necessary components of your blood. Stem cells in red bone marrow behave like factories, continually producing new blood cells to keep your body running.
Browse Best Scrubs Collection
Key Features of Red Bone Marrow:
- Red bone marrow is a busy factory that produces all of your red blood cells (oxygen transporters), most white blood cells (immune defenders), and platelets (clotting agents).
- Red bone marrow, which is rich in hematopoietic stem cells, is the beginning place for all blood cell formation. These stem cells develop into a variety of specialised blood cells.
- During foetal development and early infancy, most bone cavities are filled with red bone marrow. It is mostly concentrated in the skull, ribs, hips, and vertebrae.
- Most bones eventually change from red bone marrow to yellow bone marrow as we become older. This change represents a decrease in the requirement for blood cell formation in healthy people.
What is Yellow Bone Marrow?
In contrast, yellow bone marrow is mostly fat. It serves as an energy store for your body and includes stem cells that may differentiate into red bone marrow in times of need, such as blood loss. Most adult bones contain yellow bone marrow.
Explore All Women's Scrub
Key Features of Yellow Bone Marrow:
- Yellow bone marrow is dominated by fat cells (adipocytes), which act as the body's energy storage. It can be turned into fuel when needed, particularly during periods of low calorie intake.
- Yellow bone marrow includes mesenchymal stem cells, which can grow into bone, cartilage, or fat cells. These cells help to preserve bone integrity and promote healing after a fracture.
- Reactivation for Blood Cell Production: In instances of severe blood loss or bone marrow illness, yellow bone marrow can be surprisingly useful. It has the ability to regenerate into red bone marrow and continue blood cell production to satisfy the body's crucial requirements.
- Most individuals develop yellow bone marrow as their predominate form. It is most commonly found in the shafts of long bones such as the femur (thigh bone) and humerus (upper arm bone).
Shop Best Lab Coats from Here!
Similarities Between Red and Yellow Bone Marrow
- Vertebrate bones contain both red and yellow bone marrow.
- During embryonic development, mesenchymal stem cells form both red and yellow bone marrow.
- Both forms of bone marrow protect and cushion the bones by absorbing stress and distributing pressures.
- Both red and yellow bone marrow receive blood flow from the surrounding bone tissue, but red bone marrow has a larger blood supply due to its increased metabolic activity.
- Both forms of bone marrow include mesenchymal stem cells, but red bone marrow also contains hematopoietic stem cells that help produce blood cells.
Our bones contain two forms of bone marrow: red bone marrow and yellow bone marrow, which serve different roles. Red bone marrow is largely active in youth and localised in certain regions such as the ribs and hips in adulthood. Stem cells produce red blood cells to deliver oxygen, white blood cells to combat infection, and platelets to clot. In contrast, yellow bone marrow takes control in lengthy bones as we age. It stores fat for energy and contains stem cells with the unusual capacity to turn into bone and cartilage cells for healing, as well as convert back to red marrow in times of blood loss, demonstrating our bone marrow's extraordinary versatility.
| Check out More Articles | |
| Difference Between Cartilage and Bone | |
| Difference Between Endocrine and Exocrine Glands | |
| Difference Between Cell Wall and Cell Membrane | |