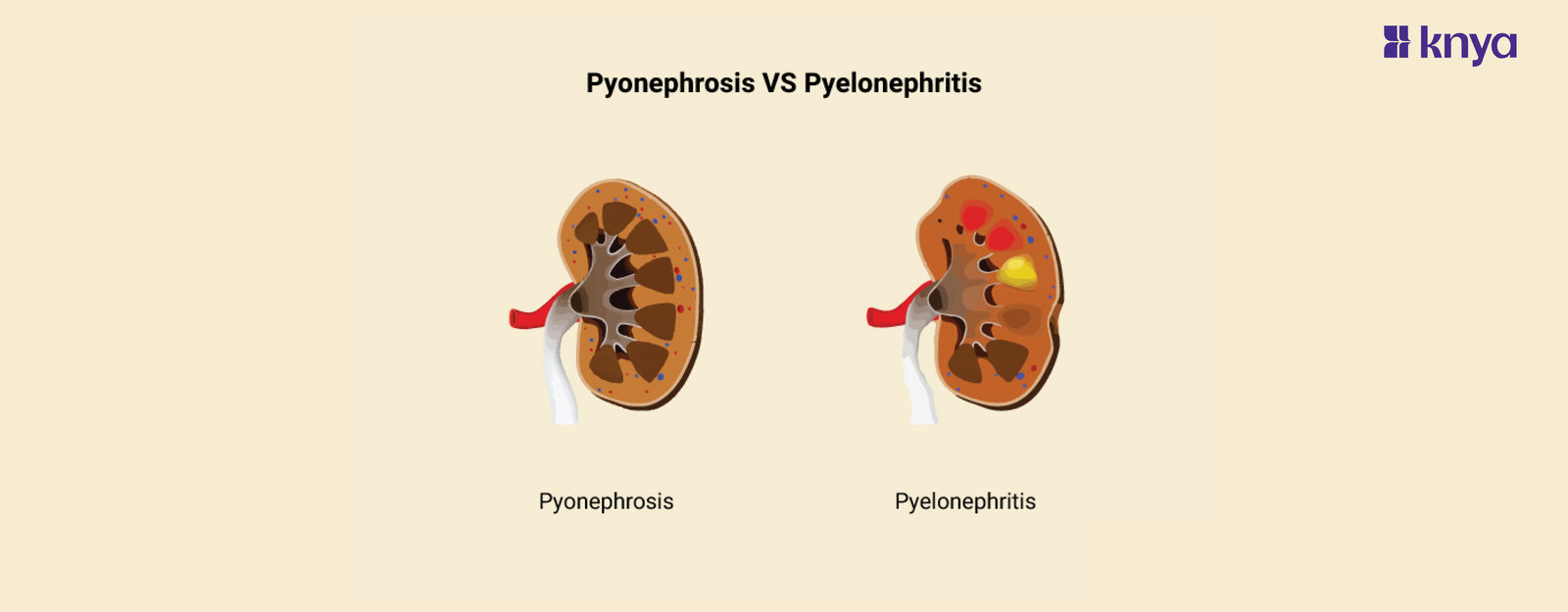
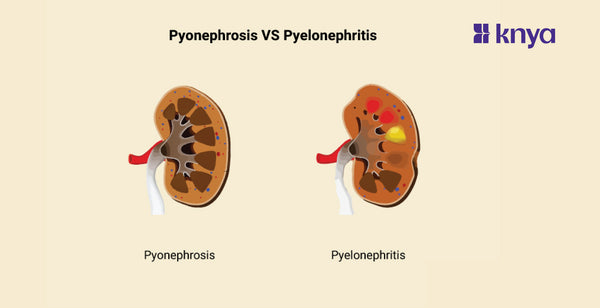
Pyonephrosis Vs Pyelonephritis: Pyelonephritis and Pyonephrosis involve kidney infections, they differ in severity and presentation. Pyelonephritis is a common bacterial infection of the kidneys, often causing fever, flank pain, and burning urination. Pyonephrosis, however, is a serious complication of untreated or recurrent pyelonephritis, marked by pus accumulation in the kidney due to blockage. This blockage traps the infection, making it harder for antibiotics to work and potentially leading to kidney damage, sepsis, and even loss of the kidney. Pyonephrosis Vs Pyelonephritis highlights the critical need for prompt treatment of the initial infection to prevent this dangerous progression.
Difference Between Pyelonephritis and Pyonephrosis
Pyonephrosis and pyelonephritis are both medical conditions that affect the kidneys, specifically involving infections. However, they differ in several aspects. Listed below are the differences between pyonephrosis and pyelonephritis:
|
Aspect |
Pyonephrosis |
Pyelonephritis |
|
Definition |
Collection of pus within the renal pelvis due to an obstructed urinary tract. |
Infection of renal parenchyma and pelvis, usually bacterial ascending from lower urinary tract. |
|
Pathophysiology |
Obstruction leading to stasis and infection. |
Bacterial ascension from bladder or urethra. |
|
Presentation |
Severe flank pain, fever, chills, systemic signs of infection. |
Fever, flank pain, dysuria, urinary frequency. |
|
Imaging findings |
Dilation of renal pelvis with purulent material. |
Enlargement of kidney, inflammation, abscess. |
|
Obstruction |
Obstruction of urinary tract (e.g., kidney stone, tumor). |
May or may not involve obstruction. |
|
Treatment approach |
Urgent decompression, drainage, surgical intervention. |
Antibiotics, supportive care (hydration, pain management). |
|
Complications |
Renal abscess, sepsis, renal failure. |
Septic shock, renal scarring, recurrent infections. |
|
Prognosis |
Depends on prompt intervention. |
Generally favorable with appropriate treatment. |
|
Risk factors |
Urinary tract obstructions, congenital abnormalities. |
Female gender, urinary tract abnormalities. |
|
Chronicity |
Can lead to chronic kidney damage. |
Chronic pyelonephritis from recurrent infections. |
Browse Best Scrubs Collection
What is Pyelonephritis?
Pyelonephritis is an inflammation of the kidney's tubules and interstitium, the tissue between the tubules. It's a common type of UTI that can cause fever, chills, flank pain, and burning urination. If left untreated, pyelonephritis can lead to serious complications, including kidney damage and sepsis.
Key Features of Pyelonephritis:
- It's a severe complication of unresolved or untreated pyelonephritis, resulting in a pus-filled, swollen kidney. Imagine a balloon inflating with pus inside your kidney.
- Symptoms: Often presents with chills, fever, severe flank pain, nausea, vomiting, and urinary urgency or frequency. Pain might radiate to the groin or lower abdomen. Urine may appear cloudy or bloody.
- Diagnosis: Requires imaging tests like ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to visualize the swollen kidney and confirm the presence of pus. Urine tests may show infection markers.
- Treatment: Immediate drainage of pus is crucial, usually through catheters inserted into the kidney or percutaneously, followed by long-term antibiotics to clear the infection. Surgery might be necessary in severe cases.
What is Pyonephrosis?
A far more dangerous illness known as pyonephrosis arises when pus builds up in the kidney's renal pelvis, which serves as a collection location. Usually, it is brought on by an obstruction in the ureter, the tube that carries urine from the kidney to the bladder, which harbours and feeds germs. Similar symptoms to those of pyelonephritis are caused by pyonephrosis, but they are frequently more severe and can include vomiting, nausea, and a high temperature. In order to avoid irreversible kidney damage or perhaps renal failure, prompt antibiotic therapy and pus drainage are essential.
Key Features of Pyonephrosis:
- An acute bacterial infection of the kidney usually originating in the bladder or lower urinary tract and ascending upwards. Think of bacteria climbing up the urinary tract and setting up camp in your kidney.
- Symptoms: Similar to pyonephrosis but often less severe. Fever, chills, flank pain, burning urination, frequent urination, and urgency are common. Urine may be cloudy or bloody, with a foul odor.
- Diagnosis: Urine tests typically reveal infection markers like white blood cells and bacteria. Imaging tests like ultrasound might be used to assess kidney involvement and rule out complications.
- Treatment: Prompt antibiotic therapy is the mainstay of treatment. Choosing the right antibiotic based on the identified bacteria is crucial. Oral antibiotics are usually sufficient, but severe cases might require hospitalization and intravenous antibiotics.
Shop Best Lab Coats from Here!
Similarities Between Pyelonephritis and Pyonephrosis
- The kidney tissue is infected with bacteria in pyonephrosis and pyelonephritis.
- Frequent symptoms of both illnesses include fever, flank discomfort, and systemic sickness indicators including malaise and chills.
- Both disorders are often diagnosed using a combination of imaging investigations (MRI, CT scan, or ultrasound), laboratory testing (blood and urine), and clinical examination to determine abnormalities and measure kidney function.
- Bacterial pathogens are the main cause of pyonephrosis and pyelonephritis, with Escherichia coli being the most frequent offender.
Given that kidney infections are a common feature of both pyonephrosis and pyelonephritis, their severity and urgency are very different. A bacterial illness limited to the kidney tissue, pyelonephritis frequently results in fever, flank discomfort, and urgency in urinating. On the other hand, a far more serious consequence known as pyonephrosis occurs when blockage causes pus to build up inside the kidney's collecting system. The infection is trapped by this obstruction, which impairs immune function and appropriate drainage and increases the risk of sepsis and renal damage. Pyonephrosis is the inferno, while pyelonephritis is essentially the fire. Antibiotics are frequently used to treat pyelonephritis, but early detection and action are critical for pyonephrosis, which frequently requires urgent draining treatments. Recall that untreated pyelonephritis can progress to pyonephrosis, emphasising the significance of promptly obtaining medical assistance if you suspect a kidney infection.
| Check out More Articles | |
| Difference Between Tendon and Ligament | |
| Difference Between Seizure and Epilepsy | |
| Difference Between Hypothyroidism and Hyperthyroidism | |