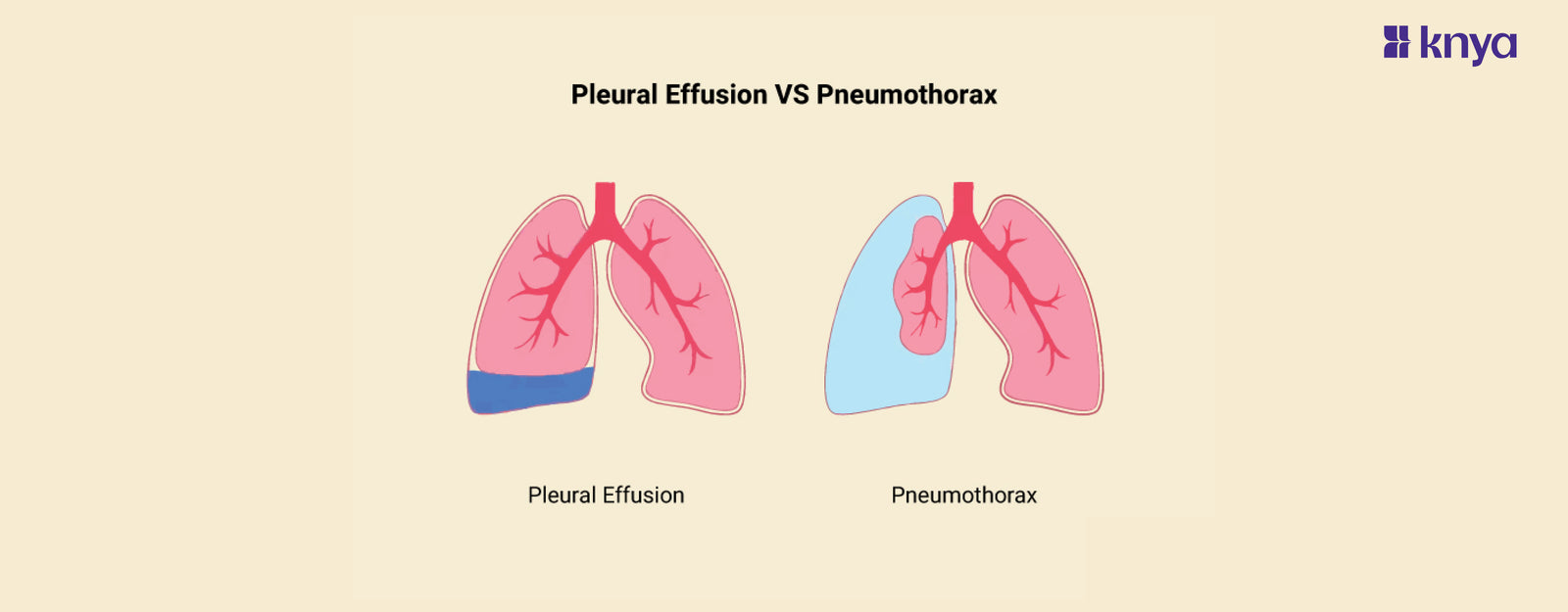
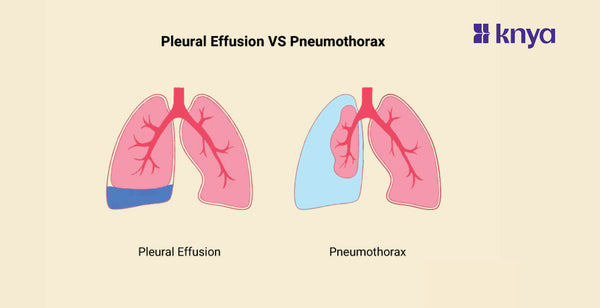
Pleural effusion and pneumothorax both impact the area around the lungs, however their contents differ, Pleural effusion is a buildup of fluid that causes difficulty breathing and, in rare cases, chest discomfort. Pneumothorax, on the other hand, is caused by trapped air, resulting in abrupt intense pain, loss of breath, and lung collapse. Pleural effusion against pneumothorax: While both can produce similar symptoms, a chest X-ray or ultrasound can distinguish between air (pneumothorax) and fluid (pleural effusion) and recommend proper therapy. Remember, expert medical guidance is essential for diagnosis and treatment.
Difference Between Pleural effusion and Pneumothorax
Pleural effusion and pneumothorax are both conditions affecting the lungs and/or the pleural space around them, but they have distinct causes, symptoms, and treatments. Here are definitions and differences between the two:
|
Aspect |
Pleural Effusion |
Pneumothorax |
|
Definition |
Abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pleural space |
Presence of air or gas in the pleural cavity |
|
Causes |
Infections, heart failure, cancer, pulmonary embolism, liver or kidney disease |
Trauma, lung diseases (e.g., COPD), spontaneous (primary) |
|
Symptoms |
Shortness of breath, chest pain, coughing, fever |
Sudden sharp chest pain, shortness of breath, rapid heart rate, cyanosis |
|
Diagnosis |
Physical examination, imaging tests (X-rays, ultrasound), thoracentesis for fluid analysis |
Physical examination, chest X-rays, sometimes CT scans |
|
Treatment |
Drainage of fluid, treating underlying cause, medications |
Aspiration of air, chest tube insertion, surgery |
|
Key Difference |
Involves fluid accumulation |
Involves air or gas presence |
|
Origin |
Various lung or systemic conditions |
Trauma, lung diseases, or spontaneous occurrence |
|
Diagnostic Method |
Imaging and fluid analysis |
Imaging and physical examination |
|
Goal of Treatment |
Relieve symptoms, treat underlying cause |
Relieve symptoms, restore normal lung function |
|
Complications |
Respiratory failure, infection |
Respiratory failure, infection |
Browse Best Scrubs Collection
What is Pleural Effusion?
Pleural effusion is the accumulation of fluid between the lungs and the chest wall. This fluid can be caused by a number of factors, including heart failure, pneumonia, and malignancy. Pleural effusion symptoms may include chest discomfort, shortness of breath, and a cough.
Key Features of Pleural Effusion:
- Excess fluid accumulates in the pleural space between your lungs and chest wall, causing pressure on the lungs.
- Symptoms include shortness of breath, chest tightness, cough (either dry or productive), exhaustion, and fast breathing. The level of severity is determined by the amount of fluid present and the underlying reason.
- Causes include heart failure, pneumonia, liver cirrhosis, cancer, and blood clots.
- Chest X-ray, CT scan, ultrasound, and pleural fluid analysis are used to detect the kind of fluid and the underlying reason.
- Treatment aims to eliminate extra fluid while also addressing the underlying cause. Options include thoracentesis (fluid drainage), medicine, and surgery.
What is Pneumothorax?
A pneumothorax is an accumulation of air in the pleural space that can cause the lung to collapse. This might occur spontaneously or as a result of an injury or medical procedure. Symptoms of a pneumothorax include acute chest discomfort, loss of breath, and fast breathing.
Key Features of Pneumothorax:
- Air enters the pleural space, collapsing part of your lung and causing pressure on the remaining lung.
- Symptoms include sudden severe chest discomfort that worsens while breathing or coughing, shortness of breath, fast breathing, and anxiety.
- Causes include young, healthy people might get spontaneous pneumothorax (a condition that occurs without damage). Trauma, lung illness, and medical procedures can all cause secondary pneumothorax.
- Chest X-rays reveal the presence of air in the pleural space.
- Treatment is to remove the air and avoid recurrence. Optional treatments include observation, needle aspiration, chest tube implantation, and surgery (in extreme instances).
Shop Best Lab Coats from Here!
Similarities Between Pleural effusion and Pneumothorax
- Pleural effusion and pneumothorax are both conditions characterised by anomalies in the pleural area that surrounds the lung.
- Both illnesses can cause respiratory problems, including shortness of breath and chest discomfort.
- Both illnesses are commonly diagnosed using chest X-rays or CT scans.
- The objective of therapy for both illnesses is to alleviate symptoms while restoring normal lung function.
- If left untreated, these illnesses can result in problems including respiratory failure or infection.
Pleural effusion and pneumothorax both involve aberrant substances in the pleural area around the lungs; the main differences are the substance and its impact. Pleural effusion is the buildup of extra fluid, which frequently causes shortness of breath and coughing, whereas pneumothorax is the presence of air, which causes abrupt intense pain and trouble breathing. Understanding these discrepancies is critical for appropriate diagnosis and therapy, because their management tactics differ greatly.
| Check out More Articles | |
| Difference Between Cartilage and Bone | |
| Difference Between Endocrine and Exocrine Glands | |
| Difference Between Cell Wall and Cell Membrane | |