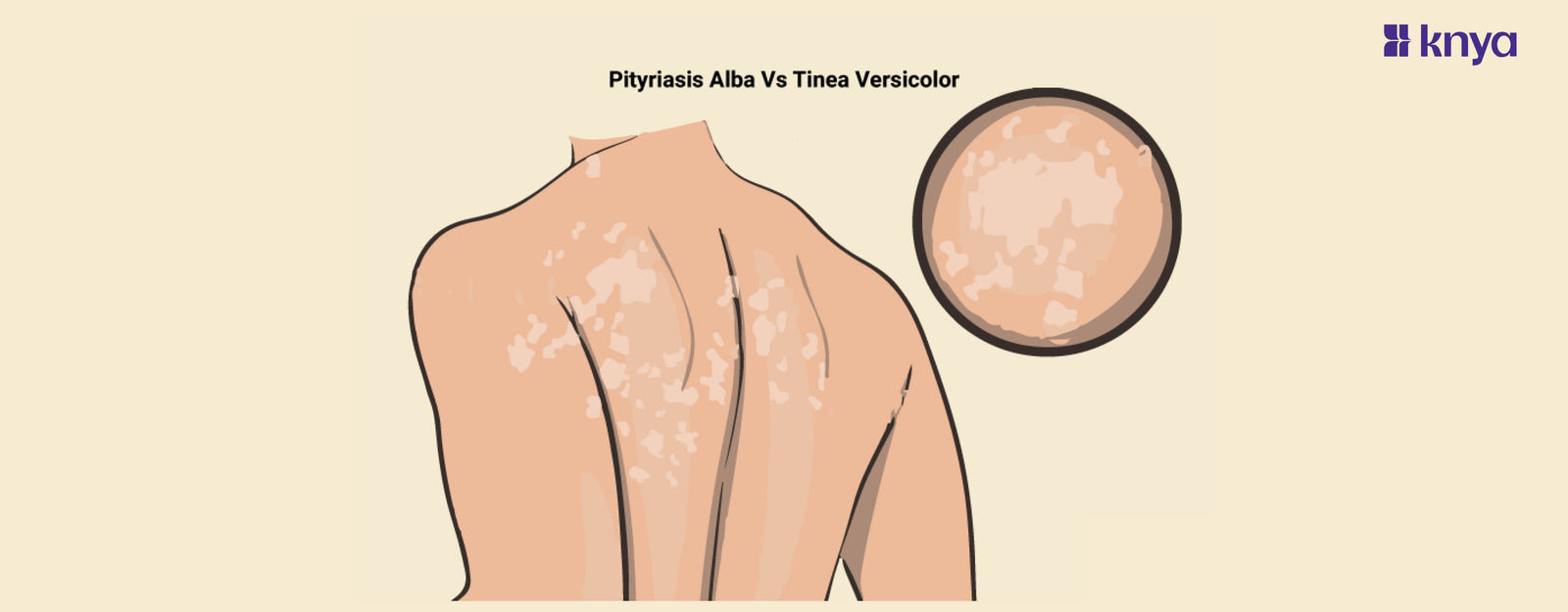
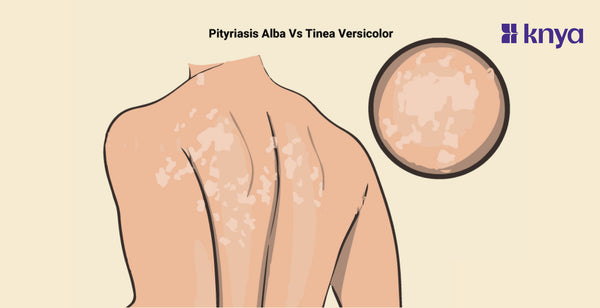
Pityriasis Alba Vs Tinea Versicolor: Navigating the realm of skin conditions can be challenging, especially when faced with similar-sounding names like Pityriasis Alba and Tinea Versicolor. While both may affect the skin's appearance, they are distinct entities with different causes and characteristics. In this exploration, we delve into the differences between Pityriasis Alba and Tinea Versicolor, shedding light on the unique features that set them apart.
Pityriasis Alba Vs Tinea Versicolor
Here's a concise comparison table highlighting the differences between Pityriasis Alba and Tinea Versicolor:
|
Aspect |
Pityriasis Alba |
Tinea Versicolor |
|
Cause |
Associated with mild eczema or atopic dermatitis. |
Caused by the yeast Malassezia, often triggered by factors like humidity and oily skin. |
|
Appearance |
Round or oval-shaped, light-colored patches with fine scaling. Patches are lighter than surrounding skin. |
Small, round or oval-shaped discolored patches that range from pink to tan or brown. May be more noticeable after sun exposure. |
|
Distribution |
Commonly affects the face, particularly the cheeks. |
Typically occurs on the trunk, shoulders, and upper arms. Can be more widespread. |
|
Scale and Itching |
Fine scale; itching is typically minimal. |
May or may not have scaling; itching can vary from mild to moderate. |
|
Age Group Affected |
Often seen in children and young adults. |
Can affect individuals of various age groups. |
|
Resolution |
Often resolves on its own without specific treatment. |
Requires antifungal treatments for effective control. |
|
Risk Factors |
Associated with atopic conditions; exact cause not fully understood. |
Associated with factors like humidity, sweating, and oily skin. |
|
Sun Exposure Impact |
No significant impact on patches with sun exposure. |
Patches may be more noticeable after sun exposure due to impaired tanning. |
Explore All Men's Scrubs Here!
What is Pityriasis Alba?
Pityriasis Alba is a common, benign skin condition that primarily affects children and adolescents. It is characterized by the presence of round or oval-shaped, light-colored patches on the skin, typically with fine scaling. The name "Pityriasis Alba" is derived from the Greek words "pityriasis," meaning scaly, and "alba," meaning white.
Key features of Pityriasis Alba include:
- Appearance: The patches are usually lighter than the surrounding skin and may range from pale pink to hypopigmented (lighter) in color. The edges of the patches are often well-defined.
- Location: Pityriasis Alba commonly appears on the face, particularly the cheeks, but it can also affect other areas of the body such as the arms and trunk.
- Scaling: The affected areas may have a fine, barely noticeable scale, and the skin texture within the patches is usually smooth.
- Itching: Itching is generally minimal or absent, distinguishing Pityriasis Alba from certain other skin conditions that may cause more significant discomfort.
- Age Group Affected: While Pityriasis Alba can occur at any age, it is most commonly seen in children and young adults. The condition often develops during childhood and may persist into adolescence.
The exact cause of Pityriasis Alba is not fully understood, but it is believed to be associated with mild eczema or atopic dermatitis. Genetic predisposition and environmental factors may also play a role in its development.
Importantly, Pityriasis Alba is a self-limiting condition, meaning it tends to improve over time without specific treatment. In many cases, the affected patches gradually fade and may eventually blend in with the surrounding skin. While moisturizers and mild topical steroids may be used to alleviate dryness or itching, the primary management approach is often supportive care.
If you suspect you or someone else has Pityriasis Alba or a similar skin condition, it is advisable to consult with a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate guidance on care and management.
Cause of Pityriasis Alba
The precise cause of Pityriasis Alba is not fully understood, but it is generally associated with a combination of genetic, environmental, and immunological factors. Here are some factors believed to contribute to the development of Pityriasis Alba:
- Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema): Pityriasis Alba is often linked to atopic dermatitis, a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by red, itchy rashes. Individuals with a history of atopic dermatitis or those with a family history of eczema may be more predisposed to developing Pityriasis Alba.
- Genetic Predisposition: There is evidence to suggest a genetic component in the development of Pityriasis Alba. Individuals with a family history of skin conditions, including eczema or Pityriasis Alba, may have a higher risk.
- Sun Exposure: While exposure to sunlight is not a direct cause of Pityriasis Alba, it is believed that the condition may become more noticeable after sun exposure. The affected skin may fail to tan as effectively as the surrounding skin, leading to a more apparent contrast.
- Skin Dryness: Dry skin is a common characteristic of Pityriasis Alba. Factors such as low humidity, harsh soaps, and inadequate moisturization may contribute to skin dryness, making the patches more noticeable.
- Immune System Response: Pityriasis Alba is thought to involve an abnormal immune response, particularly in individuals with atopic conditions. The immune system's reaction to certain triggers may contribute to the development of the characteristic light-colored patches.
Symptoms of Pityriasis Alba
Pityriasis Alba is characterized by specific symptoms that distinguish it from other skin conditions. Here are the key symptoms associated with Pityriasis Alba:
- Hypopigmented Patches:
- The hallmark symptom of Pityriasis Alba is the presence of round or oval-shaped patches on the skin.
- These patches are typically lighter than the surrounding skin and may range from pale pink to hypopigmented (lighter) in color.
- Fine Scaling:
- The affected areas may exhibit a fine, barely noticeable scale.
- The scaling is generally mild and contributes to the slightly rough texture of the patches.
- Smooth Skin Texture:
- Despite the presence of scaling, the skin texture within the patches is usually smooth.
- Unlike conditions with more pronounced roughness or irregularities, Pityriasis Alba patches often feel relatively smooth to the touch.
- Facial Predominance:
- Pityriasis Alba commonly affects the face, particularly the cheeks. However, it can also occur on other areas of the body, such as the arms and trunk.
- Age Group Affected:
- While Pityriasis Alba can occur at any age, it is most commonly seen in children and young adults.
- The condition often develops during childhood and may persist into adolescence.
- Minimal or Absent Itching:
- Itching associated with Pityriasis Alba is typically minimal or absent.
- Unlike certain other skin conditions that may cause significant discomfort, Pityriasis Alba is generally not intensely itchy.
- Sun Exposure Impact:
- While not a symptom per se, the appearance of Pityriasis Alba patches may become more noticeable after sun exposure.
- The affected skin may not tan as effectively as the surrounding skin, leading to a more apparent contrast.
What is Tinea Versicolor?
Tinea Versicolor, also known as pityriasis versicolor, is a common fungal infection of the skin. This condition is caused by the overgrowth of a yeast-like fungus called Malassezia, which is naturally present on the skin. While Malassezia is a normal component of the skin flora, factors such as humidity, sweating, and oily skin can create an environment conducive to its proliferation, leading to Tinea Versicolor.
Key features of Tinea Versicolor include:
- Discolored Patches:
- Tinea Versicolor manifests as small, round or oval-shaped patches on the skin.
- The color of these patches can vary and may range from pink to tan or brown. In some cases, the patches may appear lighter or darker than the surrounding skin.
- Scaling and Texture:
- The affected areas often exhibit fine scaling, giving the skin a somewhat scaly or powdery appearance.
- Despite the scaling, the skin texture within the patches is generally smooth, and the patches may feel dry.
- Distribution:
- Tinea Versicolor commonly occurs on the trunk, shoulders, and upper arms. However, it can also affect the neck, face, and other areas of the body.
- Sun Exposure Impact:
- The patches may become more noticeable after sun exposure. This is because the fungus interferes with the normal tanning response of the skin, leading to a contrast between the affected and unaffected areas.
- Itching:
- Itching associated with Tinea Versicolor is usually mild. While some individuals may experience slight discomfort, intense itching is not a prominent feature of this condition.
- Common in Adolescents and Young Adults:
- Tinea Versicolor is most commonly seen in adolescents and young adults. Hormonal changes during puberty may contribute to its development.
- Recurrence:
- Tinea Versicolor has a tendency to recur, especially in warm and humid climates. Recurrences may be more common in individuals with predisposing factors such as oily skin.
Tinea Versicolor is generally a benign condition and does not lead to serious health problems. However, its appearance on the skin can be cosmetically bothersome for some individuals. Treatment options include antifungal medications, such as topical creams or shampoos, which are effective in controlling the overgrowth of the fungus.
If you suspect you have Tinea Versicolor or if you are experiencing skin changes, consulting with a healthcare professional or dermatologist is recommended for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Cause of Tinea Versicolor
The cause of Tinea Versicolor is the overgrowth of a yeast-like fungus called Malassezia on the skin. Malassezia is a normal part of the skin flora and is usually present in small amounts without causing any issues. However, certain factors can create an environment that promotes the proliferation of this fungus, leading to the development of Tinea Versicolor. The key contributing factors include:
- Humidity and Warmth:
- Malassezia thrives in warm and humid environments. Areas with high temperatures and increased humidity create favorable conditions for the overgrowth of the fungus.
- Oily Skin:
- Malassezia feeds on the natural oils (sebum) produced by the skin. Individuals with oily skin provide an ideal environment for the fungus to multiply.
- Sweating:
- Excessive sweating can contribute to the growth of Malassezia. The combination of moisture and warmth from sweat creates an environment conducive to fungal overgrowth.
- Hormonal Changes:
- Hormonal changes, particularly during adolescence, pregnancy, or while using hormonal contraceptives, may influence the development of Tinea Versicolor. The condition is more common in adolescents and young adults.
- Weakened Immune System:
- Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with certain medical conditions or undergoing immunosuppressive therapy, may be more susceptible to fungal infections, including Tinea Versicolor.
- Malassezia Species:
- Different species of Malassezia can contribute to Tinea Versicolor. Malassezia globosa and Malassezia furfur are two species commonly associated with this condition.
- Geographical Location:
- Tinea Versicolor is more prevalent in regions with warm and humid climates. The environmental conditions in such areas facilitate the growth of Malassezia.
While Malassezia is a natural part of the skin microbiota, the factors mentioned above can disrupt the balance, leading to an overgrowth and the characteristic skin changes associated with Tinea Versicolor. It's important to note that Tinea Versicolor is not a contagious condition, and it does not result from poor hygiene.
Symptoms of Tinea Versicolor
Tinea Versicolor is characterized by specific skin symptoms that set it apart from other skin conditions. Here are the key symptoms associated with Tinea Versicolor:
- Discolored Patches:
- Tinea Versicolor typically presents as small, round or oval-shaped patches on the skin.
- The color of these patches can vary and may range from pink to tan or brown. In some cases, the patches may appear lighter or darker than the surrounding skin.
- Fine Scaling:
- The affected areas often exhibit fine scaling, giving the skin a slightly scaly or powdery appearance.
- Despite the scaling, the skin texture within the patches is generally smooth.
- Smooth Skin Texture:
- Unlike some other skin conditions that may cause rough or irritated skin, Tinea Versicolor patches usually have a smooth texture.
- Distribution:
- Tinea Versicolor commonly occurs on the trunk, shoulders, and upper arms. However, it can also affect the neck, face, and other areas of the body.
- Sun Exposure Impact:
- The patches may become more noticeable after sun exposure. This is because the fungus interferes with the normal tanning response of the skin, leading to a contrast between the affected and unaffected areas.
- Mild Itching:
- Itching associated with Tinea Versicolor is generally mild. While some individuals may experience slight discomfort, intense itching is not a prominent feature of this condition.
- Color Variations:
- The color of the patches may vary based on the individual's skin tone and the degree of pigmentation. Patches may appear more noticeable in individuals with darker skin.
- Common in Adolescents and Young Adults:
- Tinea Versicolor is most commonly seen in adolescents and young adults. Hormonal changes during puberty may contribute to its development.
- Recurrence:
- Tinea Versicolor has a tendency to recur, especially in warm and humid climates. Recurrences may be more common in individuals with predisposing factors such as oily skin.
If you suspect you have Tinea Versicolor or if you are experiencing skin changes, consulting with a healthcare professional or dermatologist is recommended for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Similarity Between Pityriasis Alba Vs Tinea Versicolor
While Pityriasis Alba and Tinea Versicolor are distinct skin conditions with different causes, there are some similarities between them, primarily related to their appearance and certain characteristics. Here are some similarities:
- Hypopigmented Patches:
- Both conditions present with patches on the skin that are lighter in color compared to the surrounding skin. Pityriasis Alba patches are typically pale, while Tinea Versicolor patches can range from pink to tan or brown.
- Scaling:
- Both Pityriasis Alba and Tinea Versicolor may exhibit fine scaling on the affected areas. The scaling in both conditions contributes to a slightly rough texture on the skin.
- Smooth Skin Texture:
- Despite the presence of scaling, the skin texture within the patches for both conditions is generally smooth. Unlike some skin conditions that may cause roughness or irritation, the affected areas feel relatively smooth to the touch.
- More Common in Adolescents and Young Adults:
- Both Pityriasis Alba and Tinea Versicolor are often observed in adolescents and young adults. Hormonal changes during puberty may contribute to the development of these conditions.
- Benign Nature:
- Neither condition is associated with serious health problems. Both Pityriasis Alba and Tinea Versicolor are generally considered benign and do not lead to significant medical complications.
- Sun Exposure Impact:
- The appearance of patches in both conditions may be more noticeable after sun exposure. In Tinea Versicolor, the patches may contrast with the surrounding skin due to the interference with normal tanning.
Despite these similarities, it's crucial to recognize the differences between Pityriasis Alba and Tinea Versicolor, as their causes, risk factors, and treatment approaches differ. Pityriasis Alba is often associated with mild eczema or atopic dermatitis, while Tinea Versicolor is caused by an overgrowth of the yeast-like fungus Malassezia. If there is uncertainty about the diagnosis or if you are experiencing skin changes, consulting with a healthcare professional or dermatologist is recommended for accurate identification and appropriate management.
|
Check out More Articles |
|