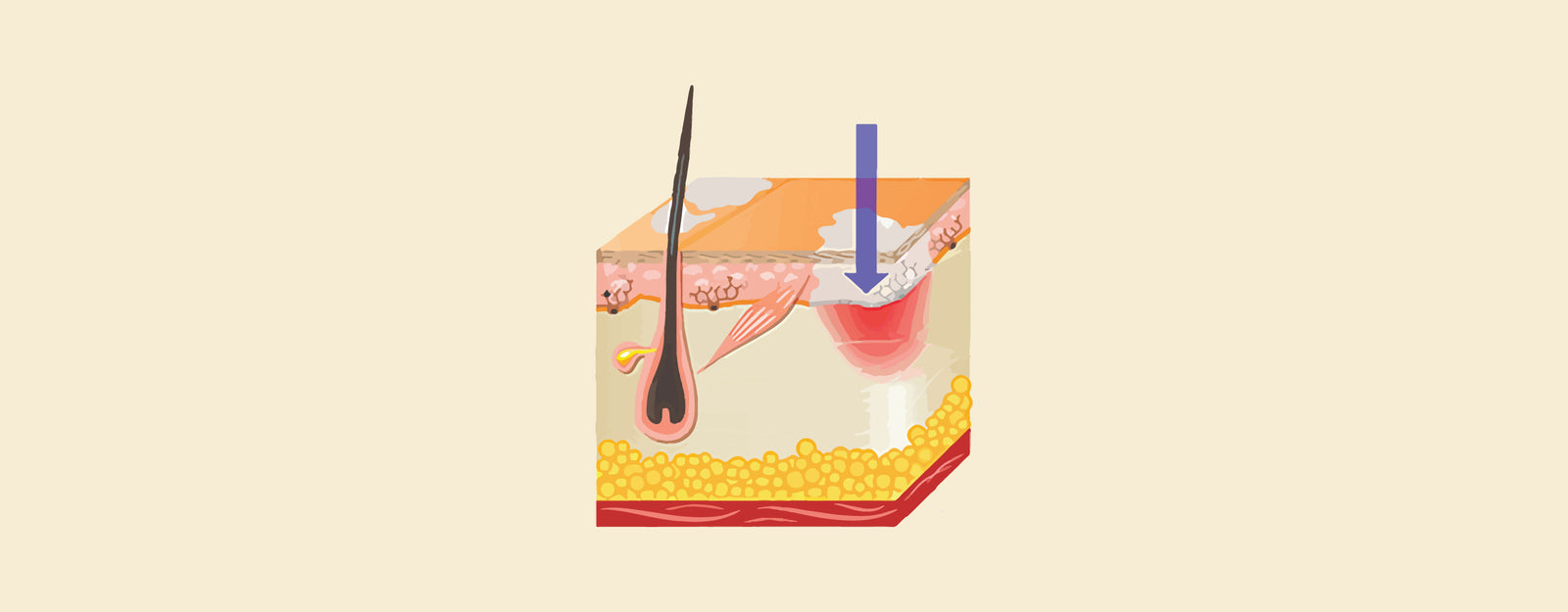
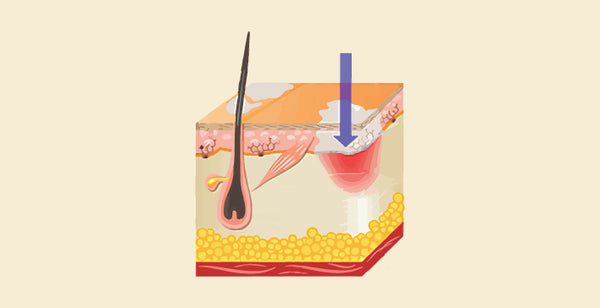
Piebaldism vs Vitiligo: Piebaldism and Vitiligo are both skin conditions that cause white patches due to a lack of pigment, but they have distinct causes and presentations. Piebaldism is a genetic condition present at birth, characterized by a white forehead patch, a white forelock (patch of white hair), and white patches on the body, often along the midline. These white patches occur because melanocytes, the pigment-producing cells, are completely absent in these areas. Vitiligo, on the other hand, is an autoimmune disorder that typically develops later in life. In Vitiligo, the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys melanocytes, leading to white patches that can appear anywhere on the body. Unlike Piebaldism, the white patches in Vitiligo can be symmetrical and may have a halo of increased pigmentation around them. Additionally, Vitiligo patches can change and grow over time, whereas Piebaldism patches typically remain stable throughout life.
Difference Between Piebaldism and Vitiligo
Piebaldism and Vitiligo are both skin conditions characterized by patches of depigmented skin, but they have distinct differences in terms of their causes, presentation, and inheritance patterns. Here are the differences between Piebaldism and Vitiligo:
|
Feature |
Piebaldism |
Vitiligo |
|
Cause |
Genetic mutation in KIT gene |
Autoimmune reaction against melanocytes |
|
Inheritance |
Autosomal dominant |
No clear-cut inheritance pattern |
|
Onset |
Present at birth or shortly thereafter |
Can develop at any age |
|
Pattern of Depigmentation |
Symmetrical, localized |
Asymmetrical, generalized or localized |
|
Hair and Eye Involvement |
Depigmented hair, iris irregularities |
Typically no hair or eye involvement |
|
Associated Conditions |
Deafness, colobomas, skeletal abnormalities |
Other autoimmune diseases, e.g., thyroid disorders |
|
Progression |
Typically stable |
Can be progressive |
|
Treatment Response |
Poor response to repigmentation treatments |
May respond to various treatments |
|
Depigmented Macules |
Well-defined, sharply demarcated |
Less well-defined borders |
|
Histopathology |
Reduced or absent melanocytes |
Absence of melanocytes, inflammatory infiltrates |
Order the Best Jogger Scrub from Here!
What is Piebaldism?
Piebaldism is a hereditary disorder that causes patches of white skin and hair in locations where pigment-producing cells do not exist. These patches frequently have a distinct distribution, such as a white forehead patch and a white midline belly stripe.
Browse Best Scrubs Collection
Key Features of Piebaldism:
- Piebaldism is distinguished by patches of lighter skin colour (hypopigmentation) spread over the body, sometimes with well-defined borders. These patches vary in size and form, resulting in a distinct "piebald" pattern.
- Unlike vitiligo, piebaldism frequently affects the face, notably the forehead (with a white forelock) and midface. This facial involvement is a distinguishing feature of pibaldism.
- Piebaldism can sometimes impact hair colour, resulting in a white forelock (a patch of white hair near the hairline). Patches of lighter-colored hair may also occur on other areas of the body.
- Piebaldism is a hereditary disorder caused by mutations in either the KIT or SIP1 genes. These genes contribute to the synthesis and migration of melanocytes, the cells that produce skin and hair pigment (melanin).
What is Vitiligo?
Vitiligo, on the other hand, appears later in life and is not hereditary for everyone. It is caused by the immune system attacking melanocytes, or pigment cells, which results in uneven white patches that can occur anywhere and alter over time.
Explore All Women's Scrub
Key Features of Vitiligo:
- Unlike piebaldism, which has clear demarcation lines, vitiligo causes a progressive loss of skin pigment, resulting in lighter patches that appear over time. The boundaries of these patches are usually ill-defined and uneven.
- Vitiligo can occur anywhere on the body, however it is more frequent on the face, hands, feet, and around bodily openings (eyes, mouth, genitals). Unlike piebaldism, it often does not affect the scalp or mucous membranes.
- Vitiligo frequently has a symmetrical pattern, with patches forming on both sides of the body in mirrored areas. This symmetrical distribution is a feature of vitiligo.
- Vitiligo is thought to be an autoimmune condition in which the immune system erroneously assaults melanocytes, resulting in a decrease of pigment synthesis in certain regions. The specific cause of this autoimmune reaction remains unknown.
Shop Best Lab Coats from Here!
Similarities Between Piebaldism and Vitiligo
- Piebaldism and vitiligo are characterised by patches of depigmented skin caused by the absence or decrease of melanocytes.
- Because of their obvious character and the possibility of stigma or social discomfort, both diseases can have a substantial psychological impact on those who suffer.
- While treatment methods vary, both disorders can benefit from psychological assistance and counselling to assist patients in dealing with the emotional impact of their skin condition.
- Individuals with Piebaldism and Vitiligo are frequently advised to avoid excessive sun exposure since depigmented skin is more prone to sunburn and injury.
- Despite the availability of many therapeutic options, both illnesses can be difficult to treat, and treatment outcomes may differ between individuals.
Piebaldism and Vitiligo may look similar due to the appearance of light or white spots on the skin, but they have different causes. Piebaldism is a congenital disorder caused by mutations that prevent pigment-producing cells (melanocytes) from developing in certain locations. These patches frequently have a distinct pattern and may be accompanied with a white forelock. Vitiligo is an autoimmune condition that appears later in life. The body destroys healthy melanocytes, resulting in unexpected patches that spread and alter over time. While neither ailment is life-threatening, knowing the difference between Piebaldism and Vitiligo aids in diagnosis and treatment.
| Check out More Articles | |
| Difference Between Cartilage And Bone | |
| Difference Between Endocrine And Exocrine Glands | |
| Difference Between Cell Wall And Cell Membrane | |