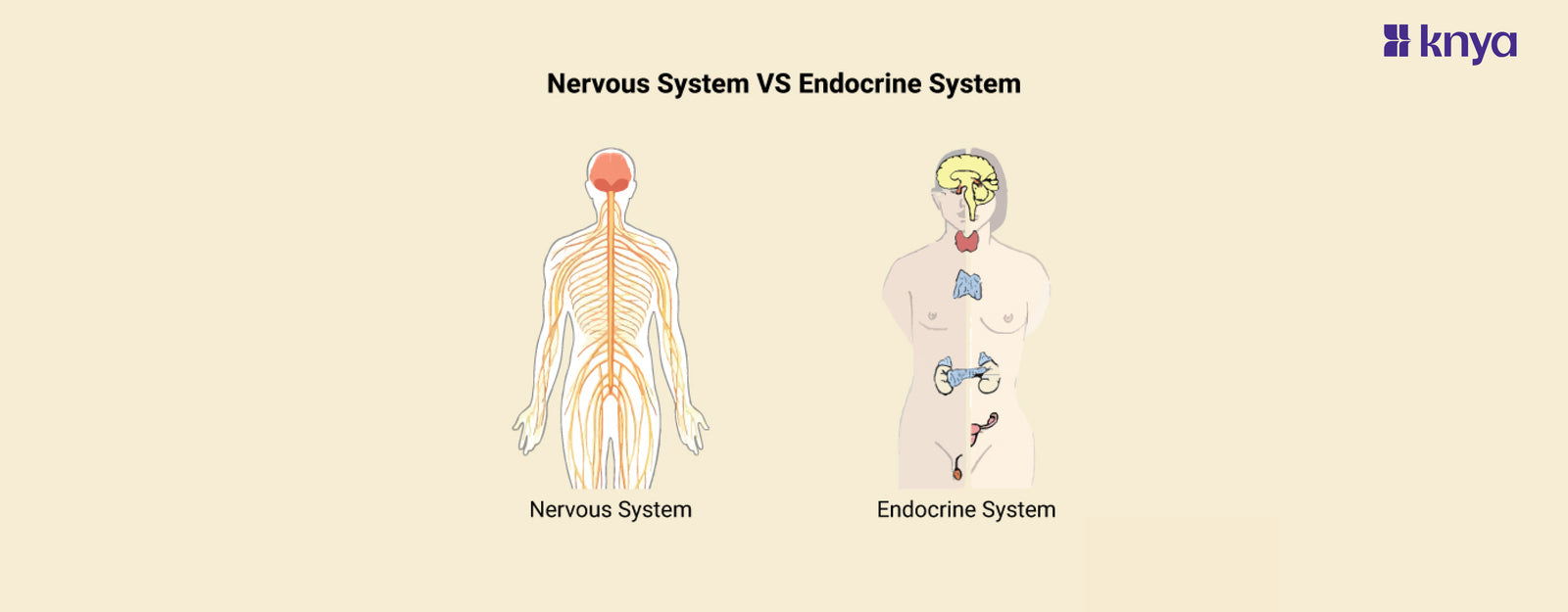
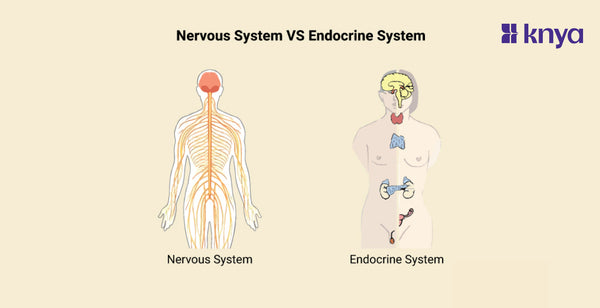
Difference Between Nervous System and Endocrine System: Our body's two communication networks, the nervous and endocrine systems, work together to keep us alive. The nervous system, like a rapid messenger, employs electrical impulses and neurotransmitters to transfer information between the brain and the body, directing instantaneous movements such as muscle contraction. The endocrine system, a slower but more comprehensive broadcaster, employs chemical messengers called hormones released by glands to govern long-term processes like development, metabolism, and mood, regulating everything from digestion to reproduction. While the nervous system functions as a fast reaction team, the endocrine system regulates the body's general tone, guaranteeing internal equilibrium.
Difference Between Nervous System and Endocrine System
The nervous system and the endocrine system are two major regulatory systems in the human body that work together to maintain homeostasis and coordinate various physiological processes. Listed below are the differences between Nervous and Endocrine System:
|
Feature |
Nervous System |
Endocrine System |
|
Mode of Communication |
Electrical impulses and neurotransmitters |
Hormones released into the bloodstream |
|
Speed of Response |
Rapid (milliseconds) |
Slower (seconds to minutes) |
|
Duration of Action |
Short-term, brief and rapid responses |
Long-term, sustained and prolonged responses |
|
Target Cells |
Specific target cells at synapses |
Target cells throughout the body via bloodstream |
|
Control |
Precise, immediate control |
Regulates activities requiring gradual adjustments |
|
Pathway of Communication |
Neural pathways and synapses |
Release of hormones directly into the bloodstream |
|
Adaptation to Stimuli |
Rapid adaptation to stimuli |
Slower adaptation, maintains longer-term responses |
|
Type of Signal |
Point-to-point signaling |
Systemic signaling affecting multiple tissues |
|
Response to Stimulus |
Immediate, short-lived responses |
Slower but more prolonged responses |
|
Transmission Medium |
Neurons and nerve fibers |
Bloodstream |
Browse Best Scrubs Collection
What is the Nervous System?
The nervous system is your body's electrical highway, delivering quick messages through neurons to govern immediate responses. It's like a lightning-fast decision-maker that syncs your muscles, reflexes, and senses in real time. Imagine walking on a sharp item; your neural system immediately instructs your foot to withdraw, eliminating additional harm.
Key Features of Nervous System:
- The nervous system uses electrical impulses and neurotransmitters to send messages across the body at lightning speed. Imagine a complex network of wires and neurons firing signals, coordinating your every movement and response.
- Sight, hearing, touch, taste, and smell: the nervous system collects information from the environment via sense organs and sends it to the brain for processing. It's like a massive network of antennae continually detecting your surroundings.
- The neurological system regulates all muscle movements in your body, from the smallest twitch to the most forceful leap. It's as if a master puppeteer is manipulating your actions and emotions.
- The nervous system maintains internal equilibrium (homeostasis) using reflexes such as blinking and breathing. It also regulates fight-or-flight reactions, which ensures your survival in dangerous situations.
What is the Endocrine System?
The endocrine system functions as your body's chemical orchestra, influencing long-term processes through hormones delivered in the circulation. It acts like a slow but consistent conductor, controlling growth, metabolism, mood, and sleep. Consider puberty: the endocrine system releases hormones that gradually modify your body and thinking.
Key Features of Endocrine System:
- The endocrine system uses chemical messengers called hormones, released into the bloodstream, to regulate numerous bodily functions. Think of it as a network of glands acting like factories, producing and releasing different hormones to control various procedures.
- Hormones such as growth hormone and insulin play critical roles in growth, development and metabolism. They're like little molecular architects who create and maintain your body's structure and function.
- Sex hormones such as oestrogen and testosterone control sexual development, menstrual periods, and sperm production. They act as conductors for your reproductive system, coordinating its operations.
- Hormones such as cortisol and oxytocin affect mood, stress, and social behaviour. They're like chemical musicians, performing songs that influence your emotional state and relationships with others.
Shop Best Lab Coats from Here!
Similarities Between Nervous and Endocrine
- Both Nervous and Endocrine systems collaborate to coordinate physiological activities in the body.
- Homeostasis involves both systems working together to preserve internal stability.
- Both systems use feedback mechanisms to adapt and regulate body functioning.
- Some tasks, including metabolic regulation, require both systems to act together.
- The neurological and endocrine systems frequently integrate, resulting in hormone release in response to brain impulses
Though both orchestrate our internal harmony, the nervous system and endocrine system employ contrasting tactics. The nervous system acts like a rapid-fire telegraph, sending precise electrical signals through neurons to trigger immediate responses. Think dodging a speeding car – your nerves relay the danger, sparking instant reflexes. In contrast, the endocrine system operates like a slow, but potent messenger. It releases chemical messengers called hormones into the bloodstream, subtly influencing long-term processes like growth, metabolism, and mood. While one delivers urgent commands, the other orchestrates gradual adjustments, both working in concert to maintain the delicate balance of our inner world.
| Check out More Articles | |
| Difference Between Cartilage and Bone | |
| Difference Between Endocrine and Exocrine Glands | |
| Difference Between Cell Wall and Cell Membrane |