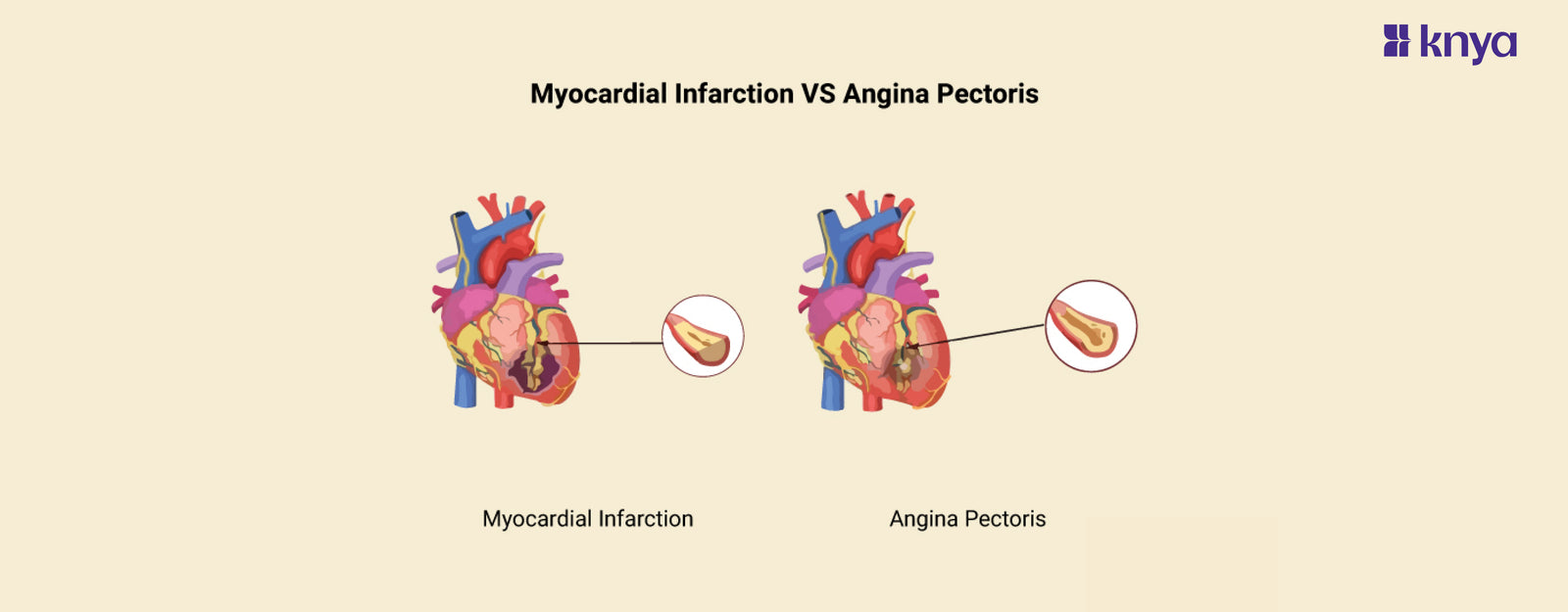
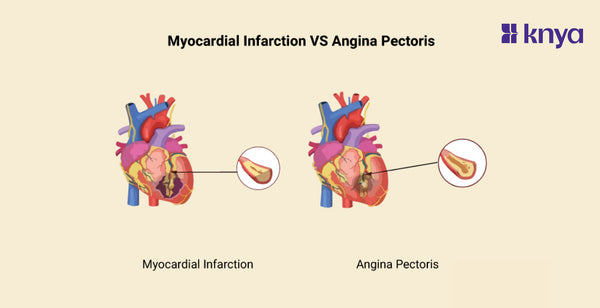
Difference Between Myocardial Infarction and Angina Pectoris: Angina Pectoris,or chest pain and Myocardial Infarction, or heart attack, are not the same thing, despite both being heart-related: A myocardial infarction happens when a blocked artery restricts blood flow to the heart, causing intense, frequently excruciating chest discomfort, shortness of breath, and sweating. This damages the heart muscle. Reduced blood flow to the heart is signalled by angina pectoris, which causes chest pain or discomfort. It is typically brought on by stress or physical activity and goes away with rest or medicine. Both can be fatal, so you should get medical help right away. Recall that this is not medical advice; for a diagnosis and course of treatment, speak with a healthcare provider.
Difference Between Angina Pectoris and Myocardial Infarction
Angina Pectoris and Myocardial Infarction (MI) are both cardiovascular disorders affecting the heart, although they have unique features, symptoms, causes, and prognosis. Outlined are the differences between angina pectoris and myocardial infarction.
|
Aspect |
Angina Pectoris |
Myocardial Infarction (MI) |
|
Definition |
Chest pain or discomfort due to temporary ischemia of the heart muscle |
Prolonged insufficient blood supply leading to damage or death of heart muscle tissue |
|
Cause |
Temporary ischemia from narrowed coronary arteries, often from coronary artery disease |
Complete blockage of coronary arteries, typically from plaque rupture |
|
Duration of Symptoms |
Temporary, usually resolves within minutes |
Longer duration, often more than 20 minutes, may not completely resolve with rest or medication |
|
Severity |
Milder symptoms, pressure, squeezing, burning, tightness in chest |
More severe symptoms, intense chest pain, sweating, nausea, shortness of breath |
|
Damage to Heart Muscle |
Does not cause permanent damage |
Results in death or irreversible damage to heart muscle |
|
ECG Changes |
Transient ST-segment depression or T-wave inversion |
Pronounced and persistent ST-segment elevation |
|
Enzyme Levels |
Normal or minimally elevated cardiac enzyme levels |
Significant elevation in cardiac enzyme levels, especially troponins |
|
Complications |
Few complications, generally not severe |
Can lead to severe complications like arrhythmias, heart failure, cardiogenic shock |
|
Treatment |
Lifestyle modifications, medications, possibly interventions like angioplasty or bypass surgery |
Emergency treatment to restore blood flow, medications, PCI, CABG |
|
Prognosis |
Generally good with appropriate management |
Prognosis varies depending on extent of damage and complications, higher risk of mortality and long-term complications |
Browse Best Scrubs Collection
What is Angina Pectoris?
Angina pectoris, often known as angina, is a chest pain caused by decreased blood supply to the heart muscle. It usually manifests as a sensation of chest tightness, pressure, or squeezing, which is frequently induced by effort, mental stress, or cold weather. Angina symptoms, unlike those of a heart attack, are typically transitory and can be eased with rest or medicine. Angina is a warning indication of underlying coronary artery disease and requires medical attention to control the condition and avoid future consequences.
Key Features of Angina Pectoris:
- Angina typically presents as chest pain or discomfort, often described as tightness, squeezing, or pressure. It may radiate to the jaw, neck, back, or arms.
- Episodes are often triggered by exertion, emotional stress, cold weather, or heavy meals. Rest or medication usually relieves the pain within minutes.
- Reduced blood flow to the heart muscle due to narrowed coronary arteries (atherosclerosis), but no permanent tissue damage.
- Focuses on managing symptoms and preventing future episodes. Strategies include lifestyle changes, medications (nitrates, beta-blockers, etc.), and sometimes procedures like angioplasty or bypass surgery.
What is Myocardial Infarction?
Myocardial infarction, often known as a heart attack, happens when a blocked artery prevents blood flow to a portion of the heart muscle. This causes oxygen starvation and damage to the cardiac tissue. Symptoms usually include crushing chest pain that spreads to the arm, jaw, or back, as well as shortness of breath, nausea, and perspiration. It's a medical emergency that needs quick medical intervention to limit harm and maximise healing.
Key Features of Myocardial Infarction:
- Similar to angina, but more acute, persistent, and uncompromising. Sweating, nausea, exhaustion, and shortness of breath are some possible symptoms.
- Similar to angina, however it can occur at rest or with minimum exercise.
- A full blockage of a coronary artery causes tissue death in the afflicted heart muscle region.
- Immediate medical intervention is critical to minimising harm. Treatment consists of drugs, surgeries (angioplasty, stents, bypass surgery), and rehabilitation to aid in recovery and avoid future episodes.
Shop Best Lab Coats from Here!
Similarities Between Angina Pectoris and Myocardial Infarction
- Angina and myocardial infarction are both cardiac conditions caused by coronary artery disease.
- Both illnesses can cause chest discomfort or pain, although the intensity and duration may vary.
- Both disorders are associated with hypertension, high cholesterol, diabetes, smoking, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, and a family history of heart disease.
- Both disorders are commonly diagnosed using a combination of clinical examination, ECG, cardiac enzymes, stress testing, echocardiography, and coronary angiography.
- Both disorders may necessitate lifestyle modifications, drugs (such as antiplatelets, statins, and beta-blockers), and therapies targeted at increasing blood flow to the heart and lowering the risk of future complications.
While both Angina Pectoris and Myocardial Infarction (heart attack) are caused by coronary artery disease, the degree and long-term effects of heart injury vary significantly. Angina Pectoris is characterised by brief limited blood flow to the heart, resulting in chest pain that is usually eased by rest or medications. A heart attack, on the other hand, implies a full blockage, resulting in long-term heart muscle damage and the need for rapid medical attention. Understanding the difference between Angina Pectoris and Myocardial Infarction is critical, as the latter is a life-threatening emergency. If you are experiencing chest discomfort, get medical help right once to ensure an accurate diagnosis and quick treatment. Remember that taking early action can have a major influence on your outcome.
Order the Best Jogger Scrub from Here!
| Check out More Articles | |
| Difference Between Cartilage and Bone | |
| Difference Between Endocrine and Exocrine Glands | |
| Difference Between Cell Wall and Cell Membrane | |