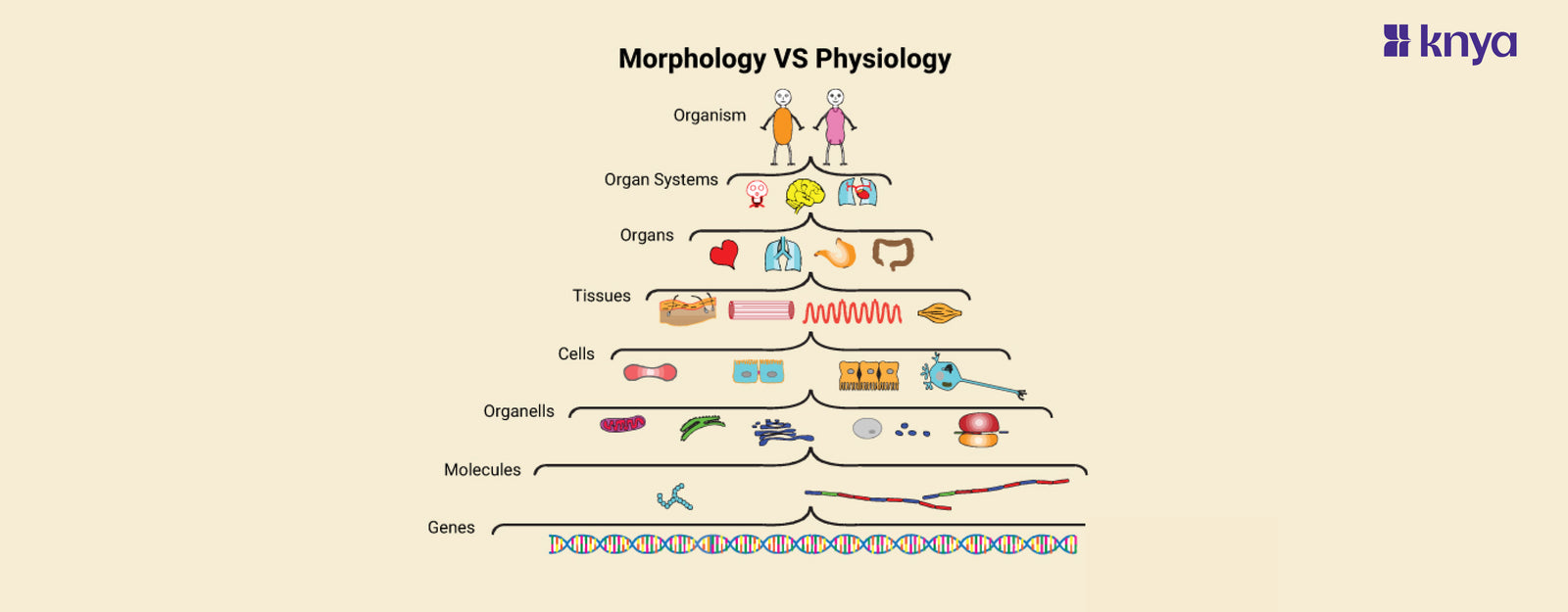
Difference Between Morphology and Physiology: Morphology and physiology are foundational concepts in the realms of biology and anatomy, providing distinct perspectives on the structure and function of living organisms. While morphology delves into the study of form and structure, physiology explores the intricate mechanisms and processes that underlie the functioning of these structures. Together, they offer a comprehensive understanding of the complexities of life. Here are the key difference between morphology and physiology:
Difference Between Morphology and Physiology
|
Feature |
Morphology |
Physiology |
|
Focus |
Study of form, structure, and arrangement of organisms |
Study of the functioning of living organisms and their components |
|
Emphasis |
Structures and their observable characteristics |
Dynamic processes and mechanisms underlying functions |
|
Perspective |
Observational and analytical |
Investigative and dynamic |
|
Nature |
Static snapshot of structures at a specific point in time |
Examines dynamic processes over time |
|
Disciplinary Overlap |
Overlaps with anatomy, taxonomy, and classification |
Intersects with biochemistry, pharmacology, and systems biology |
|
Approach |
Holistic, considering the entire structure |
Reductionist, breaking down processes into fundamental components |
|
Examples |
Identifying and classifying organisms based on structural characteristics |
Understanding biochemical and physiological mechanisms that govern life processes |
|
Questions Addressed |
"What does it look like?" |
"How does it work, and what processes are involved?" |
|
Research Methods |
Observation, microscopy, classification |
Experimentation, molecular analysis, physiological testing |
|
Application |
Taxonomy, evolutionary studies, classification |
Medicine, pharmacology, understanding disease mechanisms |
|
Temporal Scale |
Focuses on the immediate and static aspects of structures |
Examines processes on various timescales, from milliseconds to years |
|
Spatial Scale |
Emphasizes the spatial arrangement and organization of structures |
Considers spatial relationships during physiological processes |
|
Influence of Environment |
Structural features may be influenced by the external environment |
Physiological processes are often responsive to and influenced by the environment |
|
Adaptation and Evolution |
Contributes to the understanding of adaptive structures and evolutionary patterns |
Provides insights into adaptive physiological responses and evolutionary changes |
|
Technological Tools |
Relies on imaging technologies such as microscopes and CT scans |
Utilizes tools like electrophysiology, molecular biology techniques, and imaging methods |
|
Interconnectedness |
Structures often interconnected within an organism |
Processes are interconnected, forming complex regulatory networks |
|
Ethical Considerations |
Involves ethical concerns related to specimen collection and preservation |
Raises ethical questions regarding experimentation on living organisms and human subjects |
What is Morphology?
Morphology is a branch of biology that focuses on the study of the form, structure, and organization of living organisms and their parts. It involves the examination and analysis of the external and internal features of organisms, ranging from the macroscopic level of entire organisms to the microscopic level of cells and tissues. Morphologists aim to understand the physical characteristics, shape, size, color, and arrangement of structures within organisms, as well as the variations that exist among different species.
Key aspects of morphology include:
- Taxonomy and Classification: Morphological characteristics are often used in taxonomy to classify and identify different species. Scientists examine features such as body shape, presence or absence of certain organs, and external markings to categorize organisms into groups.
- Evolutionary Studies: Morphological studies contribute to our understanding of evolutionary relationships among species. Comparisons of anatomical structures across different organisms help elucidate common ancestry and evolutionary adaptations.
- Structural Adaptations: Morphology provides insights into how organisms are structurally adapted to their environments. This includes adaptations for locomotion, feeding, reproduction, and defense mechanisms.
- Microscopic Morphology: At the cellular and subcellular levels, morphology involves the study of cell structures, organelles, and other microscopic features. This is crucial for understanding cellular functions and processes.
- Paleontology: In paleontology, the study of fossilized remains involves morphological analysis to reconstruct the anatomy and appearance of extinct species.
- Botanical Morphology: In plants, morphology includes the study of plant structures such as leaves, stems, roots, and reproductive organs. This is essential for plant identification and classification.
What is Physiology?
Physiology is a branch of biology that deals with the study of the normal functions and processes of living organisms and their parts. It explores the mechanisms and activities that enable organisms to function, survive, and thrive in their environments. Physiologists investigate the integrated functions of various organs, tissues, cells, and biochemical processes within the body, aiming to understand how these components work together to maintain homeostasis and sustain life.
Key aspects of physiology include:
- Cellular Physiology: Examining the functions of cells and how they contribute to the overall function of tissues and organs. This includes cellular processes such as metabolism, energy production, and signal transduction.
- Organ System Physiology: Investigating the coordinated activities of organs and organ systems. For example, the cardiovascular system, respiratory system, and nervous system all have specific functions that contribute to the overall physiological balance of the organism.
- Homeostasis: Physiology is concerned with the maintenance of internal stability and balance, known as homeostasis. This involves the regulation of variables such as temperature, pH, and nutrient levels to ensure optimal conditions for cellular and organismal function.
- Integration of Functions: Understanding how different physiological systems integrate and communicate with each other. For instance, the endocrine system releases hormones that regulate various physiological processes, coordinating responses to internal and external stimuli.
- Adaptation and Response: Physiological processes often involve adaptive responses to changes in the environment. This can include responses to stress, changes in temperature, or alterations in nutrient availability.
- Pathophysiology: Investigating the abnormal functioning of the body that occurs in disease states. Physiologists study how disruptions in normal physiological processes lead to pathological conditions and work towards understanding and treating these conditions.
- Exercise Physiology: Examining how the body responds to physical activity and exercise. This includes studying the cardiovascular, respiratory, and musculoskeletal systems during exercise and training.
- Comparative Physiology: Comparing physiological processes across different species to understand the diversity of adaptive strategies in living organisms.
Similarity Between Morphology and Physiology
While morphology and physiology are distinct branches of biology that focus on different aspects of living organisms, there are areas of overlap and connection between the two fields. Here are some similarities:
- Holistic Understanding: Both morphology and physiology contribute to a holistic understanding of living organisms. Morphology provides insights into the physical structures and forms, while physiology delves into the dynamic functions and mechanisms underlying those structures.
- Interconnected Nature: The structures studied in morphology are often interconnected and contribute to the overall function of the organism. Physiology explores how these structures work together, emphasizing the interconnectedness of different organ systems and processes.
- Adaptations: Both fields involve the study of adaptations. Morphological adaptations refer to structural features that help organisms survive and thrive in their environments. Physiological adaptations involve functional changes that contribute to the organism's ability to cope with environmental challenges.
- Evolutionary Relationships: Morphology is used to identify and classify organisms based on their physical characteristics, and these morphological features often reflect evolutionary relationships. Physiology also provides insights into evolutionary adaptations by studying the functional changes that have occurred over time.
- Organismic Perspective: Together, morphology and physiology contribute to an organismic perspective, considering both the form and function of living entities. This integrative approach is essential for a comprehensive understanding of biological systems.
- Role in Taxonomy: Morphological characteristics play a crucial role in taxonomy, helping classify and identify different species. Physiology, while not directly involved in taxonomy, contributes to our understanding of species by revealing functional differences and adaptations.
- Research Methodologies: Both fields utilize a variety of research methodologies, including observation, experimentation, and advanced imaging techniques. Researchers in both morphology and physiology employ these tools to explore the structures and functions of living organisms.
|
Check out More Articles |
|