Difference Between Monopolar and Bipolar Cautery: In the realm of medical procedures, cautery is a fundamental technique employed for cutting or coagulating tissues. Two common modalities within this domain are Monopolar Cautery and Bipolar Cautery, each wielding distinct characteristics and applications. Understanding the differences between these approaches is paramount for healthcare professionals to make informed decisions in surgical settings. Here, we delve into the difference between of Monopolar and Bipolar Cautery, shedding light on their mechanisms, advantages, and clinical applications.
Difference Between Monopolar and Bipolar Cautery
Here's a concise summary of the key differences between Monopolar and Bipolar Cautery:
|
Feature |
Monopolar Cautery |
Bipolar Cautery |
|
Electrode Configuration |
Single active electrode and dispersive electrode |
Two closely spaced electrodes |
|
Tissue Effect |
Broader and potentially deeper tissue effect |
More localized tissue effect |
|
Risk of Burns |
Higher risk of burns at the dispersive electrode site |
Minimizes the risk of burns due to localized current |
|
Application Areas |
Commonly used in general surgery for larger areas |
Preferred for delicate procedures like neurosurgery, ophthalmic surgery, and endoscopic procedures |
|
Safety Considerations |
Requires careful attention to dispersive electrode placement to avoid unintended tissue damage |
Offers a higher level of safety due to localized current flow |
|
Electrode Placement |
Active electrode placed at the surgical site, and the dispersive electrode is placed remotely on the patient's body |
Both electrodes are placed directly on the target tissue |
|
Current Pathway |
Current flows from the active electrode through the patient's body to the dispersive electrode |
Current is confined to the tissue between the two electrodes |
|
Precision and Control |
Less precise due to the broader distribution of current |
More precise control as the current is localized between the two electrodes |
|
Usage in Neurosurgery |
Less commonly used in neurosurgical procedures |
Preferred for delicate neurosurgical interventions |
|
Usage in Ophthalmic Surgery |
Less common in ophthalmic surgeries |
Preferred for precision in ophthalmic surgical procedures |
|
Usage in Endoscopic Procedures |
Less common in certain endoscopic procedures |
Suitable for specific endoscopic interventions requiring precision |
|
Suitability for Large Tissue Areas |
Well-suited for procedures requiring extensive tissue coagulation or cutting |
Less suitable for procedures involving large tissue areas |
|
Examples of Instruments |
Electrosurgical pencils, diathermy machines |
Bipolar forceps, bipolar electrosurgical instruments |
What is Monopolar Cautery?
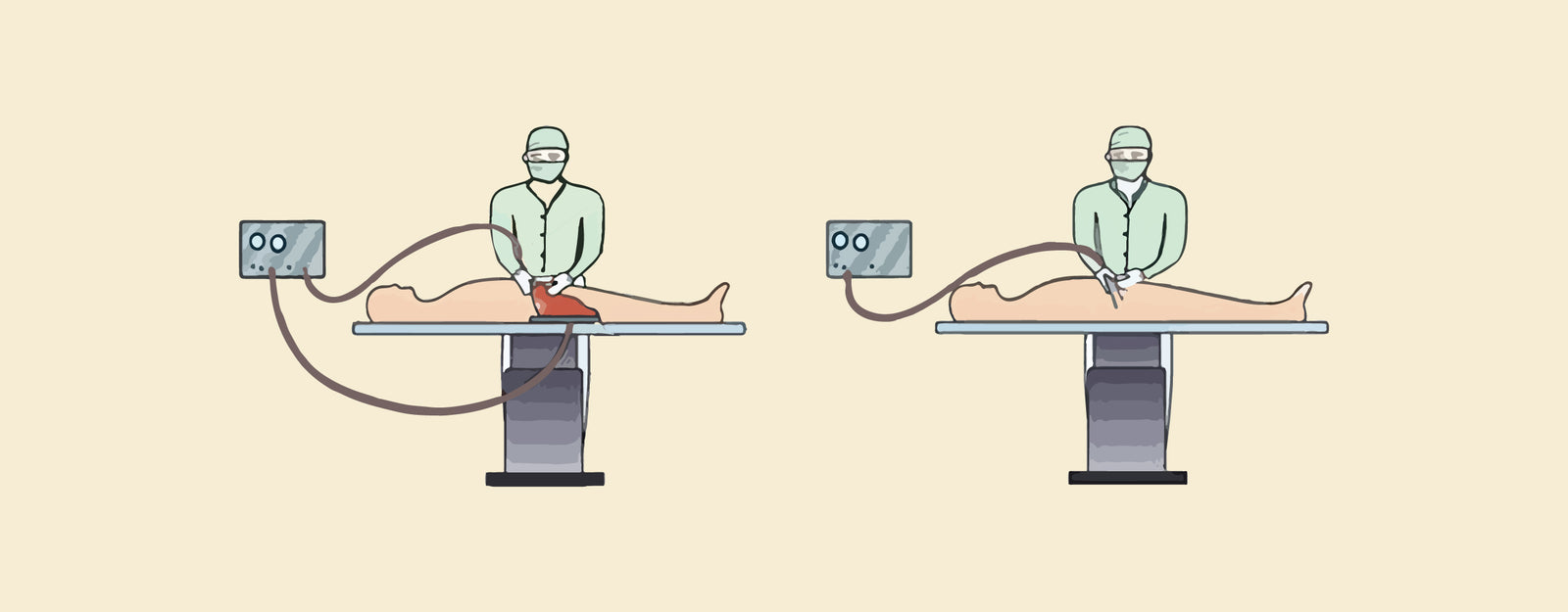
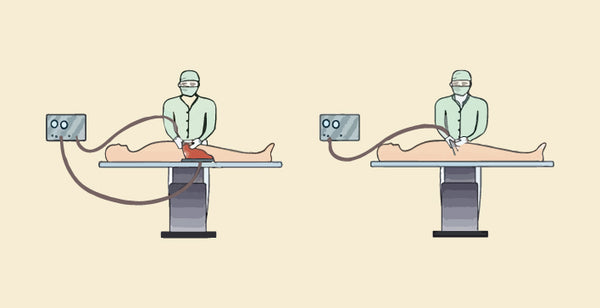
Monopolar cautery is a surgical technique used for cutting or coagulating tissues during medical procedures. It involves the application of an electrical current that flows from a single active electrode at the surgical site through the patient's body to a dispersive electrode, which is typically placed elsewhere on the patient's body. The electrical circuit is completed as the current returns through the dispersive electrode.
Key Aspects of Monopolar Cautery:
- Electrode Configuration: Monopolar cautery involves the use of a single active electrode at the surgical site and a dispersive electrode located elsewhere on the patient's body.
- Tissue Effect: The electrical current in monopolar cautery travels through a broad area of the patient's body, potentially leading to deeper tissue effects. It is well-suited for procedures that require larger-scale tissue coagulation or cutting.
- Risk of Burns: There is a higher risk of burns at the dispersive electrode site due to the broader distribution of electrical current.
- Application Areas: Monopolar cautery is commonly used in various surgical specialties, including general surgery, where procedures involve larger areas of tissue coagulation or cutting.
- Safety Considerations: Careful attention must be paid to the placement of the dispersive electrode to avoid unintended tissue damage and burns.
- Examples of Use: Monopolar cautery may be employed in procedures like abdominal surgeries, where extensive tissue coagulation or cutting is necessary.
Monopolar cautery is a versatile technique, but healthcare professionals must exercise caution to minimize the risk of burns and ensure safe and effective surgical outcomes.
What is Bipolar Cautery?
Bipolar cautery is a surgical technique used for cutting or coagulating tissues during medical procedures. In contrast to monopolar cautery, bipolar cautery involves the use of two closely spaced electrodes that are both placed directly on the target tissue. The electrical current flows only between these two electrodes, providing a more localized tissue effect.
Key Aspects of Bipolar Cautery:
- Electrode Configuration: Bipolar cautery utilizes two electrodes, both of which are placed directly on the target tissue. This eliminates the need for a dispersive electrode elsewhere on the patient's body.
- Tissue Effect: The electrical current in bipolar cautery is confined to the tissue between the two electrodes, resulting in a more localized effect. This makes it suitable for procedures that require precision and delicacy.
- Risk of Burns: Bipolar cautery minimizes the risk of burns, as the electrical current is limited to the immediate tissue between the electrodes.
- Application Areas: Bipolar cautery is preferred for more delicate procedures, including neurosurgery, ophthalmic surgery, and certain types of endoscopic procedures. It is well-suited for situations where a focused and precise tissue effect is essential.
- Safety Considerations: The localized current flow in bipolar cautery enhances safety by reducing the risk of collateral damage to surrounding tissues.
- Examples of Use: Bipolar cautery may be employed in procedures where precise tissue coagulation or cutting is required, such as in ophthalmic surgeries or during certain neurosurgical interventions.
Bipolar cautery offers advantages in terms of precision and safety, making it a suitable choice for specific surgical scenarios where minimizing tissue damage and ensuring accuracy are paramount.
Similarity Between Monopolar and Bipolar Cautery
Similarities Between Monopolar and Bipolar Cautery:
While Monopolar and Bipolar Cautery differ in their electrode configurations and the extent of tissue effects, there are some similarities between the two techniques:
- Electrical Current: Both techniques utilize electrical current for cutting or coagulating tissues during surgical procedures.
- Cautery Purpose: The primary purpose of both Monopolar and Bipolar Cautery is to achieve hemostasis (control bleeding) during surgery by coagulating blood vessels or tissues.
- Surgical Instruments: Both techniques involve the use of specialized surgical instruments, such as electrosurgical pencils and forceps, designed for either monopolar or bipolar applications.
- Integration in Electrosurgery: Both Monopolar and Bipolar Cautery are integral parts of electrosurgical procedures, providing surgeons with options for tissue manipulation and blood vessel control.
- Electrosurgical Generators: Both techniques require electrosurgical generators to provide the necessary electrical energy for the cautery process.
Despite their shared characteristics, healthcare professionals must understand the distinct features and applications of each technique to make informed decisions based on the specific requirements of a given surgical procedure.
|
Check out More Articles |
|