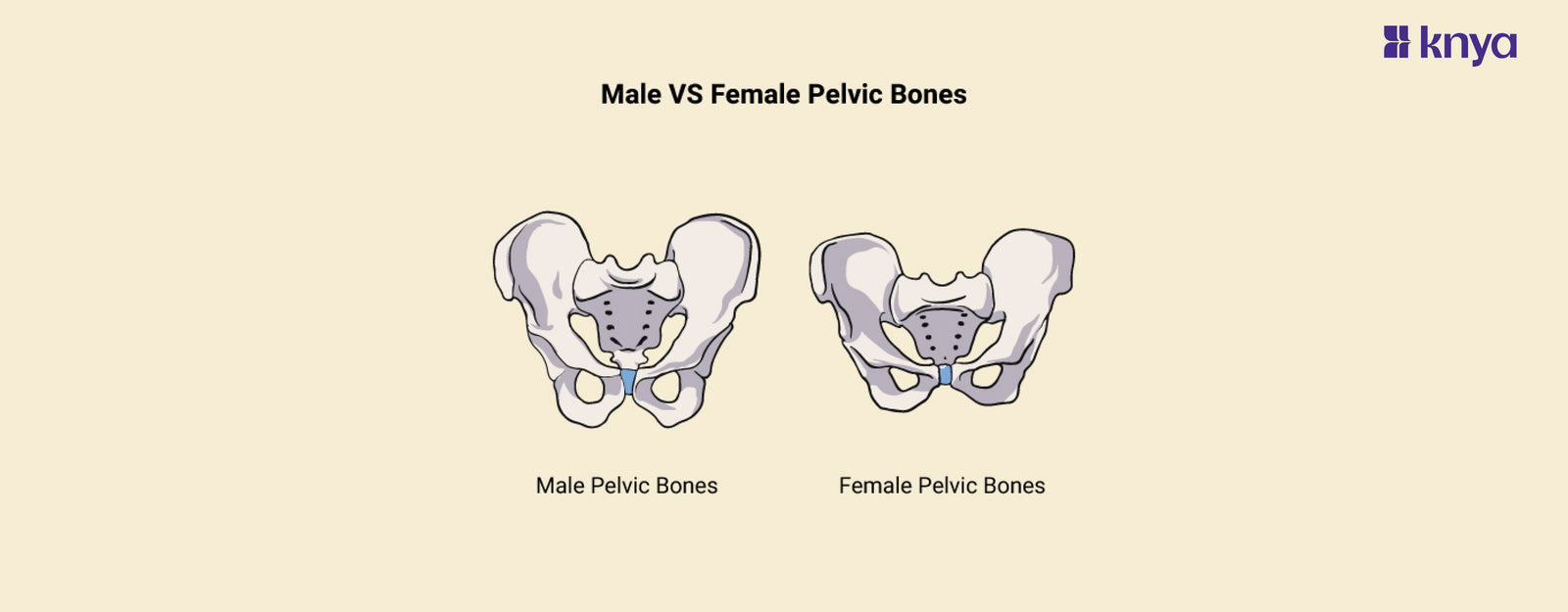
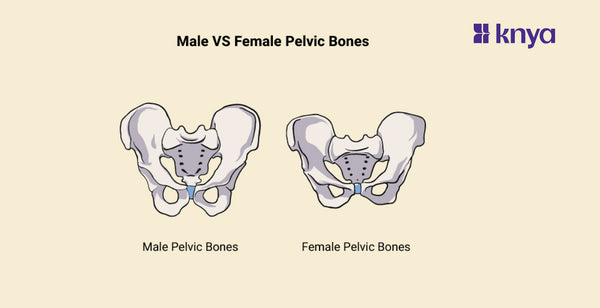
Male Vs Female Pelvic Bones: Male and Female Pelvic Bones have unique adaptations to their biological activities. To support delivery, the female pelvis is broader and rounder, with a bigger pelvic inlet (the entry of the birth canal) and a wider subpubic angle. In comparison, the male pelvis is narrower and more heart-shaped, with a smaller intake and a shallower subpubic angle. These variations contribute to the overall size and form of the pelvis, affecting everything from leg attachment to organ location.
Difference Between Male and Female Pelvic Bones
The human body's skeletal structure includes the male and female pelvic bones, often known as the pelvic girdle or hip bones. They differ in shape and size because men and females have structural distinctions that are mostly connected to reproductive function. Listed below are the differences between male and female pelvic bones.
|
Aspect |
Male Pelvic Bone |
Female Pelvic Bone |
|
Shape |
Narrow and more compact |
Wide and broader |
|
Pelvic Inlet |
Heart-shaped |
Oval or rounded |
|
Subpubic Angle |
< 90 degrees |
> 90 degrees |
|
Pubic Arch |
Narrow and V-shaped |
Wide and U-shaped |
|
Sacrum |
Longer and more curved |
Shorter and less curved |
|
Sacral Promontory |
More prominent |
Less prominent |
|
Coccyx |
Less movable and less curved |
More movable and more curved |
|
Pelvic Outlet |
Narrow and smaller |
Wide and larger |
|
Ischial Spines |
Protrude more prominently |
Less prominent |
|
Obturator Foramen |
Oval and smaller |
Round and larger |
|
Sacroiliac Joint |
Thicker and less mobile |
Thinner and more mobile |
|
Pubic Symphysis |
Longer and more pronounced |
Shorter and less pronounced |
|
Ilium |
Narrower wings |
Broader wings |
|
Acetabulum |
Larger and more robust |
Smaller and less robust |
|
Sciatic Notch |
Narrower and deeper |
Wider and shallower |
|
Overall Structure |
More robust and angular |
Smoother and more rounded |
|
Purpose |
Provides support for heavier body structure |
Facilitates childbirth, wider for passage of baby |
Order the Best Jogger Scrub from Here!
What is Male Pelvic Bones?
Men and women have considerably different pelvic bones, which is critical for female birth. The female pelvis is broader and shallower than the male, with a larger, rounder pelvic cavity. This bigger form is aided by a wider gap between the hip bones (iliac crest) and a pubic arch angle greater than 90 degrees. In contrast, the male pelvis is narrower and more heart-shaped, with a smaller pelvic inlet and a pubic arch angle less than 90 degrees. Furthermore, female bones are often lighter and thinner, whereas male pelvises favour strength with bigger, denser bones. These changes to the female pelvis make it simpler to accommodate a growing foetus and give birth.
Browse Best Scrubs Collection
Key Features of Male Pelvic Bones:
- The male pelvis is typically narrower and more compact than the female pelvic. This is owing to guys' narrower birth canals, which do not need to allow delivery.
- Male pelvic bones are generally bigger and more robust to support the male body's greater musculature.
- The pelvic inlet, the topmost entrance of the pelvis, is smaller in men than in females. This reflects a narrower birth canal.
- The acetabulum, the socket in the hip bone where the femur (thigh bone) joins, is wider and rounder in men, providing more stability and support for the upper body.
What are Female Pelvic Bones?
Men and women have quite distinct pelvic bones, which is crucial for female childbirth. The female pelvis is wider and shallower than the male, having a bigger, rounder pelvic cavity. This larger shape is helped by a wider space between the hip bones (iliac crest) and a pubic arch angle greater than 90°. In comparison, the male pelvis is narrower and more heart-shaped, with a smaller pelvic inlet and a pubic arch angle of less than 90 degrees. Furthermore, female bones are often lighter and thinner, whereas male pelvises encourage strength through larger, denser bones. These modifications in the female pelvis make it easier to accommodate a developing baby and deliver birth.
Explore All Women's Scrub
Key Features of Female Pelvic Bones:
- The female pelvis is wider and more basin-shaped to accommodate the larger birth canal required for birthing.
- Female pelvic bones are often smaller and lighter than their male counterparts. This provides increased flexibility and expansion during pregnancy and birthing.
- Females have a bigger pelvic inlet than men because their birth canals are broader.
- Females' acetabulums are somewhat more oval in form than men', which are rounder. This distinction is hypothesised to lead to broader hip placement in females.
Shop Best Lab Coats from Here!
Similarities Between Male and Female Pelvic Bones
- Male and female pelvic bones sustain the body's weight and act as attachment places for many muscles and ligaments.
- Both male and female pelvic bones protect the reproductive organs, bladder, and lower gastrointestinal system.
- The pelvic bones in both sexes are made up of the same bones: the ilium, ischium, and pubis, which fuse throughout development.
- The pelvic bones of both males and females comprise the pelvic girdle, which links the axial skeleton (spine) to the lower limbs.
- Both Change: During adolescence, both male and female pelvic bones change shape and size, but the differences become more obvious owing to hormonal factors.
The pelvic bones of men and women differ significantly, which is important for female birthing. The female pelvis is wider and shallower than the male pelvis, and it has a bigger, rounder pelvic cavity. This larger shape is assisted by a greater distance between the hip bones (iliac crest) and a pubic arch angle greater than 90 degrees. In comparison, the male pelvis is narrower and more heart-shaped, with a smaller pelvic inlet and a pubic arch angle of less than 90 degrees. Furthermore, female bones are often lighter and thinner, whereas male pelvis prioritises strength with larger, denser bones. These modifications in the female pelvis make it easier to accommodate a developing fetus and give delivery.