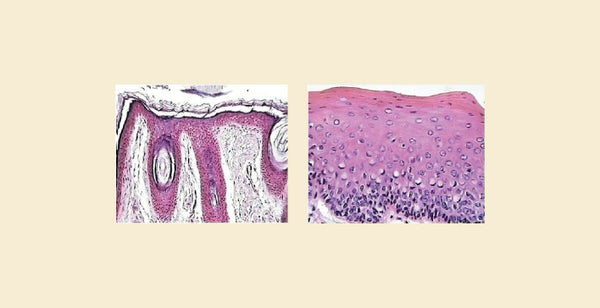
Difference Between Keratinized and Non Keratinized Epithelium: Epithelium can be categorized into Keratinized and Non-keratinized based on the presence of a protein called keratin. Keratinized epithelium, like the one found on your skin, contains a tough, waterproof layer of dead cells rich in keratin, offering strong protection. In contrast, non-keratinized epithelium, lining organs like your mouth, lacks this tough layer and is formed by living cells, allowing for functions like absorption and secretion.
Difference Between Keratinized and Non-keratinized Epithelium
Keratinized and non-keratinized epithelium are two forms of stratified squamous epithelial tissues present in the human body. They perform diverse roles and have distinct properties. What follows are the differences between the keratinized and non-keratinized epithelium.
|
Difference |
Keratinized Epithelium |
Non-Keratinized Epithelium |
|
Presence of Keratin |
Contains keratin |
Lacks keratin |
|
Water Resistance |
Highly water-resistant |
Less resistant to water |
|
Cell Nuclei |
Absent in superficial layers |
Present throughout all layers |
|
Thickness |
Generally thicker |
Thinner |
|
Location |
Found in areas subjected to mechanical stress |
Lines moist surfaces |
|
Cell Shape |
Flattened towards the surface |
Maintains cuboidal or columnar shape |
|
Protection |
Provides tough protection |
Provides lesser protection |
|
Moisture Retention |
Less moisture retention |
Better moisture retention |
|
Sensory Function |
Less sensitive to stimuli |
Contains sensory receptors |
|
Regeneration Rate |
Slower turnover rate |
Higher turnover rate |
Order the Best Jogger Scrub from Here!
What is Keratinized Epithelium?
Keratinized epithelium is a robust, waterproof layer present in places that are subjected to continual friction and require a strong barrier. It is made up of stacked, flattened cells filled with a protein called keratin. This layer serves as a barrier, protecting beneath tissues from harsh conditions, dryness, and physical harm. Examples include the epidermis (outermost layer of skin), palms, and soles of your feet.
Browse Best Scrubs Collection
Key Features of Keratinized Epithelium:
- This cell type is distinguished by the presence of keratin, a fibrous protein that forms a hard, waterproof covering on the cell surface.
- The outermost layers of keratinized epithelium are made up of dead, flattened cells loaded with keratin. These cells are regularly lost and regenerated, forming a protective barrier against wear and strain.
- Keratin forms a dry, waterproof coating that efficiently protects the underlying tissues against water loss, toxic chemicals, and bacteria.
- This dry, keratinized layer provides high abrasion resistance, shielding the body from physical injury such as friction on the palms and soles.
- Examples include skin (epidermis), palms, and soles of feet.
What is Non-keratinized Epithelium?
Non-keratinized epithelium is a wet, live cell layer that lines many internal organs and body openings. It lacks a strong keratinized outer layer. This enables for processes such as absorption, secretion, and lubrication. Examples include the lining of the mouth (except the tongue), oesophagus, vagina, and inner surface of the eyelids. These tissues must strike a balance between protection and functionality such as absorption or lubrication.
Explore All Women's Scrub
Key Features of Non-keratinized Epithelium:
- Unlike its keratinized sibling, this epithelium lacks a keratinized layer. The cells are alive and actively performing numerous activities.
- The lack of keratin provides for a moist environment, which aids in the absorption of water and other essential chemicals for the body.
- The non-keratinized epithelium is essential for the exchange of gases (such as oxygen and carbon dioxide) and other molecules between the body and its surroundings.
- This epithelium can also be specialised to secrete fluids such as mucus (lubrication and protection) or enzymes (digestion).
- Examples include the lining of the mouth, oesophagus, vagina, and urinary system.
Shop Best Lab Coats from Here!
Similarities Between Keratinized and Non-keratinized Epithelium
- Keratinized and non-keratinized epithelium are both made up of several layers of flattened cells.
- Both forms of epithelium have protective roles, functioning as barriers to mechanical damage, microbial invasion, and dehydration.
- Both forms of epithelium are connected by cell junctions such as tight junctions, adherens junctions, and desmosomes.
- Both keratinized and non-keratinized epithelium have a basal cell layer composed of actively dividing cells that replace the top layers.
- Both forms of epithelium are metabolically active, while keratinized epithelium's metabolic activity reduces as cells travel to the surface and become keratinized.
Keratinized and non-keratinized epithelium, both stratified squamous, differ greatly in composition and function. Keratinized epithelium, which contains the protein keratin, generates a dry, rough outer layer similar to that found on human skin. This layer serves as a robust, waterproof barrier, safeguarding the underlying tissues. In contrast, non-keratinized epithelium lacks keratin, leaving a wet, porous surface. This epithelium, which may be found in the mouth and eyes, facilitates absorption, secretion, and tactile sensibility. Thus, the presence of keratin is the primary distinction between keratinized and non-keratinized epithelium, resulting in contrasting characteristics and fulfilling unique functional roles in the body.
| Check out More Articles | |
| Difference Between Cartilage and Bone | |
| Difference Between Endocrine and Exocrine Glands | |
| Difference Between Cell Wall and Cell Membrane | |