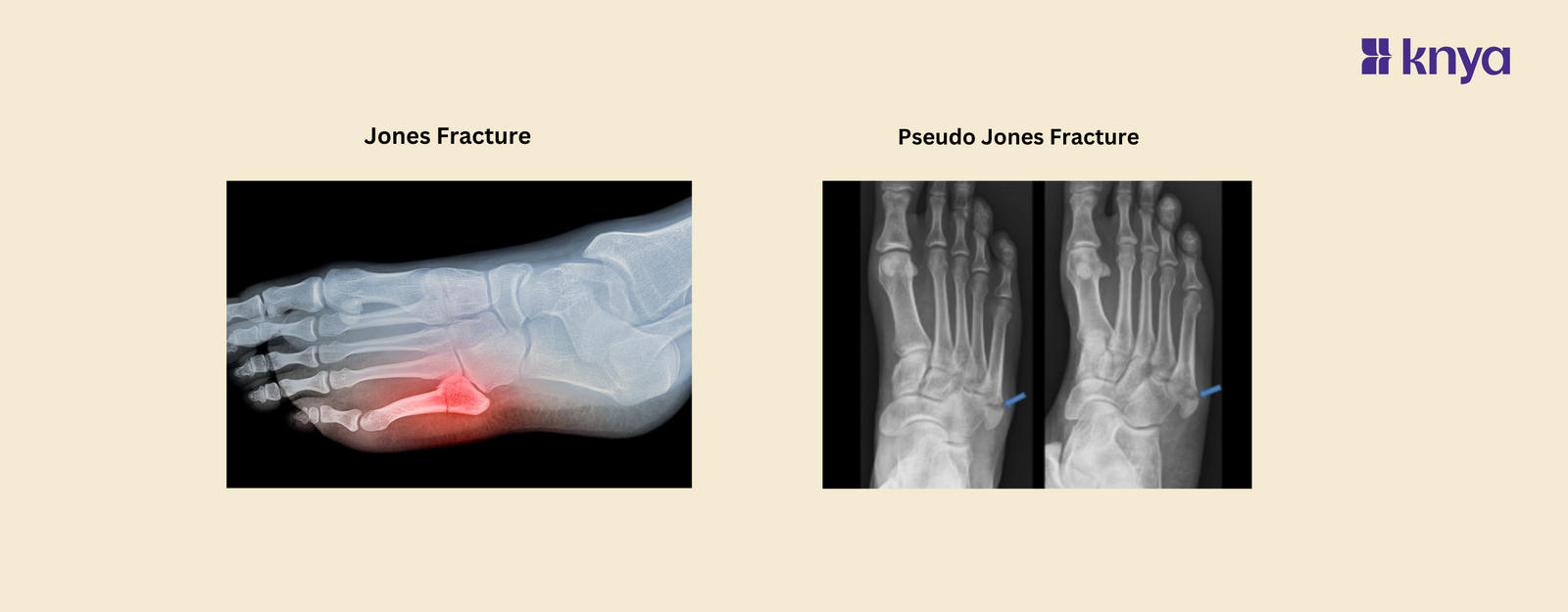
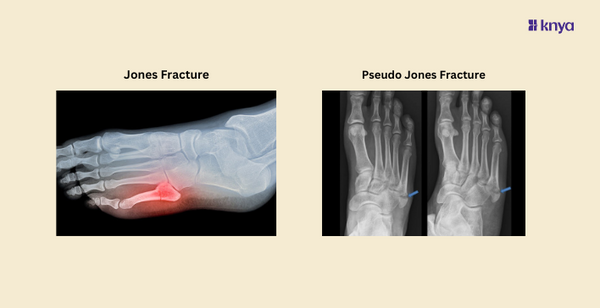
Jones fractures and pseudo Jones are two common fractures that occur in the fifth metatarsal bone of the foot which can significantly impact mobility. Jones fractures, occurring at the base of the bone, are notorious for their poor healing potential due to limited blood supply, often necessitating surgical intervention. Pseudo Jones fractures involve the tuberosity and are commonly treated conservatively, with favorable recovery outcomes and less frequent need for surgical intervention compared to Jones fractures.
Tabular Comparison of Jones fracture vs Pseudo Jones Fracture
Below is the comparision of jones fracture and pseudo jones fracture in the tabular format:
| Feature | Jones Fracture | Pseudo Jones Fracture |
| Location of Fracture | Base of the fifth metatarsal | Tuberosity or styloid process of the fifth metatarsal |
| Common Causes | Twisting or torsional forces, repetitive stress | Acute injury, traction forces by tendons/ligaments |
| Imaging Findings | Fracture at the base of the fifth metatarsal | Avulsion or fragment at the tuberosity of the fifth metatarsal |
| Treatment | Conservative (immobilization, possibly surgery) | Conservative (RICE, immobilization), rarely surgery |
| Prognosis | Prolonged recovery, risk of non-union | Generally favorable with conservative treatment |
Browse best Scrubs Collection
What is Jones Fracture?
A Jones fracture occurs at the base of the fifth metatarsal bone, typically about 1.5 to 3 centimeters from the base of the bone where it connects to the midfoot. This specific location is critical because it is known to have a relatively poor blood supply, which can impede healing and increase the risk of complications.
Causes of Jones Fracture
Jones fractures commonly result from:
- Acute trauma or repetitive stress.
- The fracture often occurs when the foot is inverted (turned inward) and pointed downward, leading to a sudden twisting or bending force on the bone.
Symptoms
Patients with a Jones fracture typically experience:
-
Acute pain and swelling on the outside of the foot, specifically at the base of the fifth metatarsal.
-
Difficulty bearing weight on the affected foot
-
Bruising around the area of injury.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing a Jones fracture involves a physical examination and imaging studies such as X-rays. On X-ray, a Jones fracture appears as a fracture line at the base of the fifth metatarsal bone, often showing signs of displacement or separation.
Treatment
Treatment options for Jones fractures vary depending on the severity of the fracture and the patient's activity level.
- Non-displaced or minimally displaced fractures may be treated conservatively with a period of immobilization in a cast or walking boot, followed by gradual weight-bearing as tolerated.
- Severe or displaced fractures often require surgical intervention. Surgery typically involves internal fixation with screws or pins to stabilize the fracture and promote healing.
What is Pseudo Jones Fracture?
A pseudo Jones fracture, also known as an avulsion fracture of the fifth metatarsal, occurs at a different location on the bone compared to a true Jones fracture. This type of fracture typically involves the tuberosity or styloid process of the fifth metatarsal, which is located more proximally (closer to the midfoot) than the base of the bone.
Causes
Pseudo Jones fractures often result from an acute injury or sudden force applied to the foot, such as during a fall or direct impact.
Symptoms
Patients with a pseudo Jones fracture may experience similar symptoms to those with a true Jones fracture, including:
- pain, swelling, and difficulty bearing weight.
- pain and tenderness may occur on the side of the foot rather than the base of the fifth metatarsal.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing a pseudo Jones fracture also involves a physical examination and imaging studies, typically X-rays. On X-ray, this type of fracture appears as a fragment or avulsion of the tuberosity of the fifth metatarsal, often with displacement or separation from the main bone.
Treatment
Treatment options for pseudo Jones fractures are generally more conservative compared to true Jones fractures.
- Non-displaced fractures may be managed with rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE protocol), along with immobilization in a cast or walking boot.
- Severe or displaced fractures may require surgical intervention, although this is less common than in true Jones fractures.
Shop the Best Lab Coats from Here!
Prognosis
- Jones Fracture: Prognosis for Jones fractures can be guarded due to the bone's poor blood supply, increasing the risk of delayed healing or non-union. Surgical intervention often yields better outcomes but may necessitate prolonged rehabilitation.
- Pseudo Jones Fracture: Prognosis for pseudo Jones fractures is generally favorable with conservative treatment, focusing on immobilization and gradual return to activity. Surgery is less frequently required, and most patients recover well with appropriate management.
| Check out More Articles | |
| Difference Between Cartilage And Bone | |
| Difference Between Endocrine And Exocrine Glands | |
| Difference Between Cell Wall And Cell Membrane | |