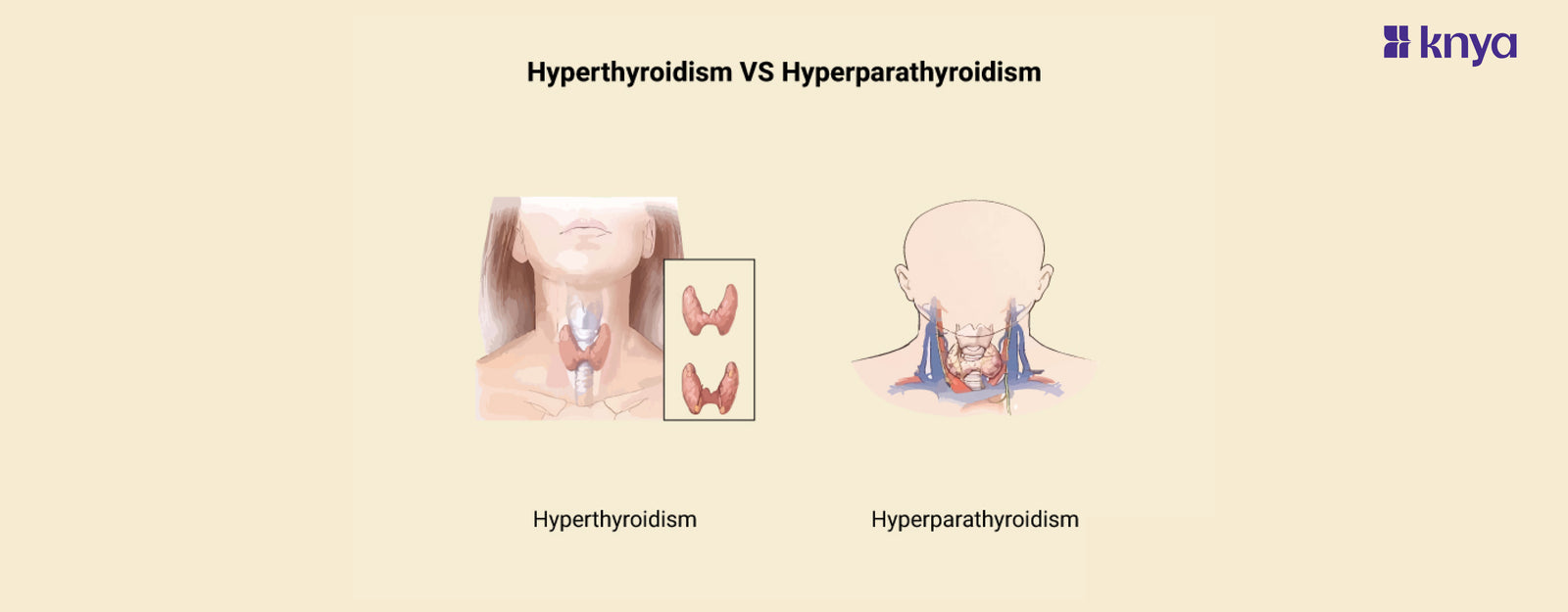
Difference Between Hyperthyroidism and Hyperparathyroidism: Hyperthyroidism and Hyperparathyroidism are two unique medical diseases that affect various glands in the body and cause distinct sets of symptoms. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland produces too many thyroid hormones, resulting in symptoms such as weight loss, rapid heartbeat, nervousness, and heat sensitivity. Hyperparathyroidism, on the other hand, is caused by the parathyroid glands secreting an excessive amount of parathyroid hormone, which causes symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, kidney stones, and osteoporosis. Despite sharing some symptoms, these conditions require distinct diagnostic and treatment approaches. Hyperthyroidism is typically managed with medications, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery, whereas Hyperparathyroidism may necessitate surgical removal of the affected glands or other interventions to restore calcium levels.
Difference Between Hyperthyroidism and Hyperparathyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is caused by the overproduction of thyroid hormones, resulting in symptoms such as weight loss and rapid heartbeat, whereas Hyperparathyroidism is caused by an excess of parathyroid hormone, which causes exhaustion and kidney stones. The table below provides the differences between Hyperthyroidism and Hyperparathyroidism.
|
Aspect |
Hyperthyroidism |
Hyperparathyroidism |
|
Gland Involved |
Thyroid |
Parathyroid |
|
Hormone Overproduction |
Excessive thyroid hormones (T3, T4) |
Excessive parathyroid hormone (PTH) |
|
Common Causes |
Graves' disease, thyroid nodules, thyroiditis |
Benign tumors of the parathyroid glands |
|
Symptoms |
Weight loss, rapid heartbeat, nervousness |
Fatigue, weakness, kidney stones, osteoporosis |
|
Diagnostic Tests |
Blood tests for thyroid hormones (T3, T4) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), imaging studies |
Blood tests for calcium and parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels |
|
Treatment Options |
Medications, radioactive iodine therapy, surgery |
Surgical removal of the affected parathyroid gland(s) |
|
Complications |
Heart problems, osteoporosis, thyroid storm |
Kidney damage, osteoporosis-related fractures, cardiovascular issues |
Browse The Best Scrubs Collection!
What is Hyperthyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism is a disorder in which the thyroid gland generates too many hormones, resulting in symptoms such as weight loss, rapid heartbeat, nervousness, and heat sensitivity. It is frequently caused by autoimmune disorders or thyroid nodules and can be identified via blood testing and imaging examinations. Medication, radioactive iodine therapy, and surgery are all possible treatment options.
Features of Hyperthyroidism
- Excess thyroid hormone production.
- Symptoms include weight loss, rapid heartbeat, nervousness, tremors, excessive sweating, heat intolerance, weariness, and muscle weakness.
- Autoimmune disorders such as Graves' disease, thyroid nodules, and thyroiditis are possible causes.
- Blood tests to evaluate thyroid hormone levels (T3, T4) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) are part of the diagnostic process, as are imaging scans.
- Medication, radioactive iodine therapy, and surgical intervention are all possible treatment options.
Causes of Hyperthyroidism
- Graves' Illness: An autoimmune condition in which the body creates antibodies that cause the thyroid gland to overproduce hormones.
- Thyroid Nodules: Abnormal growths on the thyroid gland that can manufacture thyroid hormones independently, leading to Hyperthyroidism.
- Thyroiditis: Inflammation of the thyroid gland that may result in an overabundance of thyroid hormones being released.
- Excessive Iodine Intake: Taking too much iodine, either through diet or prescription, can cause Hyperthyroidism.
- Overactive Thyroid Medication: Certain drugs intended to treat Hypothyroidism or other diseases might produce Hyperthyroidism if the dosage is excessive.
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
- Weight Loss Without Reason: People with Hyperthyroidism may lose weight despite having a normal or increased appetite.
- Increased Heart Rate: Tachycardia, or a raised heart rate, can cause palpitations, a rapid heartbeat, or abnormal heart rhythms.
- Heat Intolerance: Even in cooler weather, people may feel overheated or sweat more than normal.
- Nervousness and Irritability: Hyperthyroidism might make you feel anxious, nervous, or irritable. Some people may have mood swings or problems concentrating.
- Tremors: Increased metabolic activity can cause fine tremors, especially in the hands and fingers.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Despite the increased metabolic rate, people may feel weary or weak, including muscle weakness.
What is Hyperparathyroidism?
Hyperparathyroidism is a medical disorder characterized by overactivity of the parathyroid glands, which causes excessive synthesis of Parathyroid Hormone (PTH). This hormone serves to control calcium levels in the blood and bone metabolism. Hyperparathyroidism is characterized by excessive PTH levels in the blood, which can induce fatigue, weakness, kidney stones, osteoporosis, and gastrointestinal problems.
Features of Hyperparathyroidism
- Increased levels of parathyroid hormone (PTH).
- Increased blood calcium levels (hypercalcemia).
- Symptoms include weariness, weakness, bone pain, kidney stones, and digestive difficulties.
- Age, gender (more common in women), and certain medical problems, such as kidney disease, all contribute to the risk.
- Blood tests to detect calcium and PTH levels, as well as imaging procedures such as an ultrasound or sestamibi scan, are often used to make the diagnosis.
- Treatment options include surgical removal of the damaged parathyroid gland(s), calcium-lowering medicines, and lifestyle changes.
Causes of Hyperparathyroidism
- Benign Tumors (Adenomas): The most common cause of Hyperparathyroidism is a benign tumor on one of the parathyroid glands, called a parathyroid adenoma. This tumor causes the afflicted gland to create excessive PTH.
- Hyperplasia: Hyperplasia occurs when more than one parathyroid gland becomes swollen and hyperactive. This can result in an excessive generation of PTH.
- Parathyroid Cancer: Although rare, malignant growths on the parathyroid glands can induce increased PTH production, resulting in Hyperparathyroidism.
- Genetic Factors: Certain rare genetic abnormalities, such as multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) and type 2A (MEN2A), can predispose people to developing Hyperparathyroidism.
- Radiation Therapy: Previous radiation treatment to the head and neck might damage the parathyroid glands, resulting in PTH overproduction and Hyperparathyroidism.
Symptoms of Hyperparathyroidism
- Joint Pain: Chronic discomfort in the bones and joints, primarily affecting the back, hips, and wrists. This pain may be caused by calcium being pulled out of the bones, resulting in decreased bone structure.
- Kidney Stones: Elevated calcium levels in the blood can cause kidney stones to form, resulting in symptoms such as severe back or abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and bloody urine.
- Muscle Weakness: Excess PTH can cause muscle weakness, tiredness, and overall weakness.
- Exhaustion and Weakness: Individuals may have general weakness and exhaustion, which might disrupt everyday activities.
- Frequent Urination: Elevated calcium levels in the blood can cause higher urine output, resulting in frequent urination.
Similarities between Hyperthyroidism and Hyperparathyroidism
- Symptoms: While the specific symptoms of Hyperthyroidism and Hyperparathyroidism differ due to the distinct glands involved, there may be some overlap, such as fatigue, weakness, and muscle discomfort.
- Bone Health: Although the effects are distinct, both illnesses can have an impact on bone health. Hyperthyroidism can result in bone loss (osteoporosis) due to increased bone turnover, whereas Hyperparathyroidism can induce bone discomfort and raise the risk of fractures due to excessive calcium release from bones.
- Cardiovascular Effects: Both disorders have the potential to damage the cardiovascular system. Hyperthyroidism can produce palpitations, fast heart rate, and hypertension, but Hyperparathyroidism can lead to hypertension and cardiovascular problems by disrupting calcium metabolism.
- Potential consequences: If left untreated, both Hyperthyroidism and Hyperparathyroidism can result in serious consequences. Hyperthyroidism can cause cardiac problems like atrial fibrillation and osteoporosis, but Hyperparathyroidism can lead to kidney stones, osteoporosis, and kidney damage.
| Check out More Articles | |
| Difference Between Tendon and Ligament | |
| Difference Between Seizure and Epilepsy | |
| Difference Between Hypothyroidism and Hyperthyroidism | |