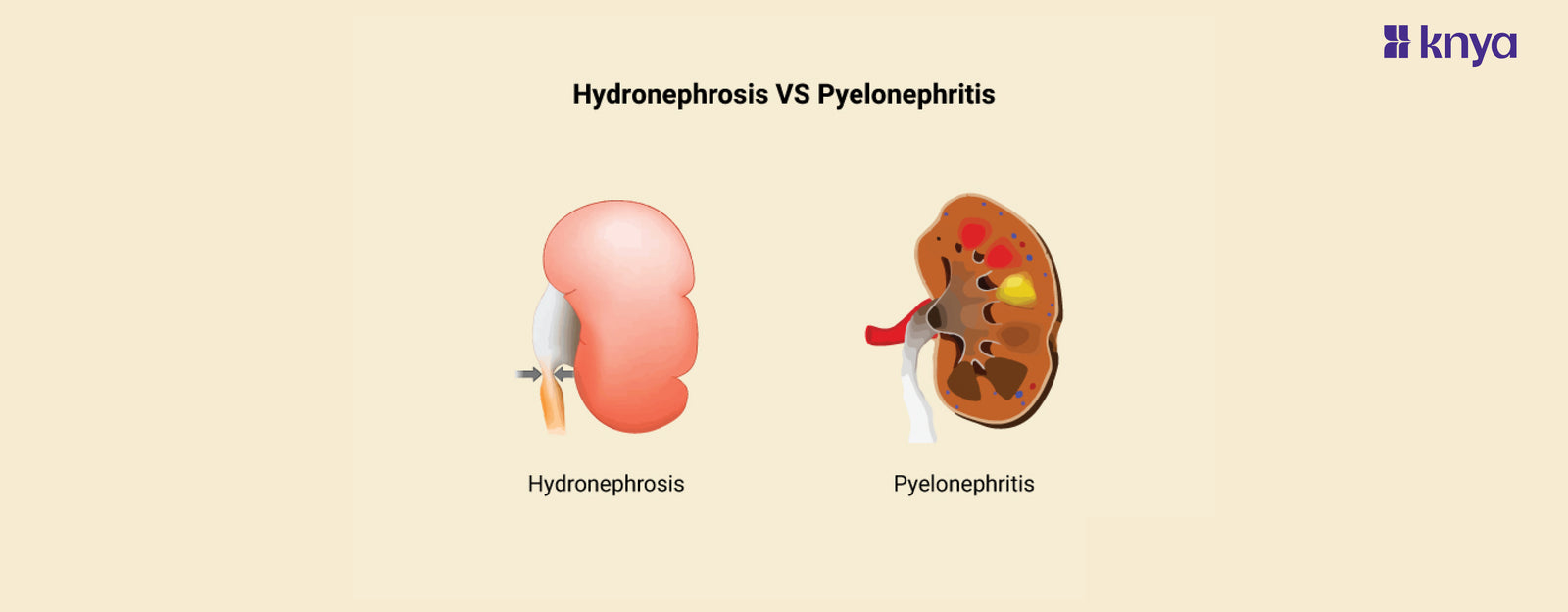
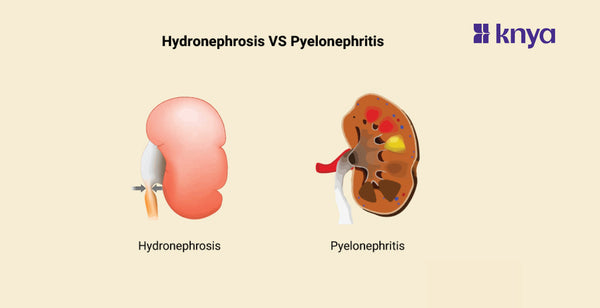
Differences between Hydronephrosis and Pyelonephritis: While Pyelonephritis is a bacterial infection of the kidneys brought on by a urinary tract infection that ascends from the bladder, Hydronephrosis is defined as the swelling or enlargement of one or both kidneys as a result of urine buildup brought on by urinary tract obstruction. Symptoms of Hydronephrosis, which include flank pain and frequent urination, can be caused by kidney stones, tumors, or congenital abnormalities. Conversely, Pyelonephritis usually presents with fever, chills, and an increased need for urination; hence, early antibiotic therapy is necessary to avoid complications such as sepsis. Although kidney function can be affected by both illnesses and medical intervention is necessary, their underlying causes, symptoms, and treatment modalities are different.
Differences Between Hydronephrosis and Pyelonephritis
Hydronephrosis is defined as kidney swelling caused by urine buildup from urinary system obstruction, whereas Pyelonephritis is a bacterial kidney infection that originates in the urinary tract. The table below provides the differences between Hydronephrosis and Pyelonephritis.
|
Characteristic |
Hydronephrosis |
Pyelonephritis |
|
Definition |
Swelling or enlargement of one or both kidneys due to urine buildup caused by urinary tract obstruction |
Bacterial infection of the kidneys, typically resulting from a urinary tract infection ascending from the bladder |
|
Causes |
Kidney stones, tumors, congenital abnormalities, strictures in the urinary tract |
Bacteria, such as Escherichia coli (E. coli), entering the urinary tract and infecting the kidneys |
|
Symptoms |
Flank pain, abdominal pain, frequent urination, urinary urgency, nausea, vomiting |
Fever, chills, flank pain, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, urinary urgency, burning sensation during urination |
|
Diagnosis |
Imaging tests (ultrasound, CT scan, MRI) to visualize kidney enlargement and urinary tract obstruction |
Physical examination, urinalysis (presence of bacteria and white blood cells), imaging tests (ultrasound, CT scan) to assess kidney involvement |
|
Complications |
Kidney damage, urinary tract infections, hydronephrosis-related pain |
Sepsis, kidney abscess, chronic kidney disease |
|
Treatment |
Addressing urinary tract obstruction surgically, relieving urinary tract blockage, managing underlying conditions |
Antibiotics to eliminate bacterial infection, supportive care for severe cases, hospitalization for intravenous antibiotics if necessary |
|
Prevention |
Treating underlying conditions promptly, maintaining hydration, following a healthy diet |
Practicing good hygiene, avoiding urinary tract infections, staying hydrated, treating underlying urinary tract abnormalities |
|
Risk Factors |
Urinary tract abnormalities, kidney stones, prostate enlargement (in males) |
Female gender, pregnancy, urinary tract abnormalities, urinary catheterization, weakened immune system, urinary retention, urinary tract obstructions |
Browse The Best Scrubs Collection!
What is Hydronephrosis?
Hydronephrosis is a medical condition characterized by swelling or enlargement of one or both kidneys as a result of urine accumulation caused by a urinary tract obstruction. Urine cannot adequately flow from the kidney due to this obstruction, which can cause pressure to build up, edema, and even damage to the kidney's tissue.
Causes of Hydronephrosis
- Kidney Stones: A blockage brought on by kidney stones that can obstruct the urine's passage from the kidneys to the bladder.
- Congenital Abnormalities: Congenital abnormalities, such as vesicoureteral reflux or obstruction of the ureteropelvic junction, in the urinary tract that result from birth problems.
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Infections that affect the urinary tract, especially when they cause inflammation or swelling that prevents the passage of urine.
- Tumors: Urinary tract tumors, such as kidney cancer or bladder tumors, can restrict urine flow and cause Hydronephrosis.
- Neurogenic Bladder: Dysfunction of the nerves that control bladder function, which can cause urine retention and Hydronephrosis.
Symptoms of Hydronephrosis
- Flank Pain: A throbbing or soreness in the back or side, usually on one side, where the kidney is damaged.
- Abdominal Pain: Pain in the lower abdomen, usually on the same side as the damaged kidney.
- Increased Urgency or Frequency of Urine: This is because the obstruction may prevent the bladder from emptying.
- Vomiting and Nausea: If the Hydronephrosis is severe or if there are additional issues, these symptoms could appear.
- Failure of Kidney: Kidney failure symptoms, including reduced urine production, edema in the legs or feet, exhaustion, and dyspnea, can arise from Hydronephrosis in extreme cases or if the condition is not addressed.
What is Pyelonephritis?
Pyelonephritis is a kind of UTI that causes inflammation and infection in one or both kidneys. It usually happens when bacteria, most frequently Escherichia coli, or E. coli., move from the bladder and other lower urinary system organs to the kidneys.
Causes of Pyelonephritis
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): If kidney infections are not treated or are treated insufficiently, they may spread to the bladder or urethra.
- Urinary Tract Obstruction: Kidney stones, tumors, and structural abnormalities are examples of obstructions in the urinary tract that can hinder urine flow and raise the risk of bacterial infection.
- Urinary Catheterization: Using a urinary catheter increases the risk of infection and can introduce bacteria into the urinary system, especially in hospitalized patients.
- Weakened Immune System: People who have diabetes, HIV/AIDS, chemotherapy, long-term corticosteroid usage, or other conditions that impair the immune system may be more vulnerable to bacterial infections, including Pyelonephritis.
Symptoms of Pyelonephritis
- Fever: Usually high-grade, with chills and perspiration.
- Flank Pain: A dull, painful pain, generally on one side, in the flanks or lower back.
- Abdominal Pain: A pain in the abdomen, especially on the side that is afflicted.
- Vomiting and Nausea: Vomiting and nausea are more likely to occur if the infection is severe.
- Fatigue: Experiencing unusually low energy or fatigue.
- Bloody or Cloudy Urine: Kidney inflammation can cause urine to appear bloody or cloudy.
Shop Best Lab Coats From Here!
Similarities Between Hydronephrosis and Pyelonephritis
- Both affect the kidneys and, if addressed, may result in problems.
- Similar symptoms, such as flank discomfort and urine symptoms like frequent urination, urgency, and a burning feeling, may be present.
- For diagnosis and therapy, immediate medical intervention is required to prevent future problems impacting kidney function.
To summarize, Pyelonephritis and Hydronephrosis both affect the kidneys and may appear with similar symptoms; however, their causes, processes, and treatment approaches differ. The main feature of Hydronephrosis is kidney enlargement brought on by urine accumulation from obstruction of the urinary tract, which is frequently brought on by kidney stones or congenital anomalies. On the other hand, Pyelonephritis, a bacterial infection of the kidneys, is brought on by bacteria that frequently ascend from the lower urinary tract. Kidney function needs to be maintained for both conditions, and complications need to be prevented by early detection and appropriate care.
Order the Best Jogger Scrub From Here!
| Check out More Articles | |
| Difference Between Tendon and Ligament | |
| Difference Between Seizure and Epilepsy | |
| Difference Between Hypothyroidism and Hyperthyroidism | |