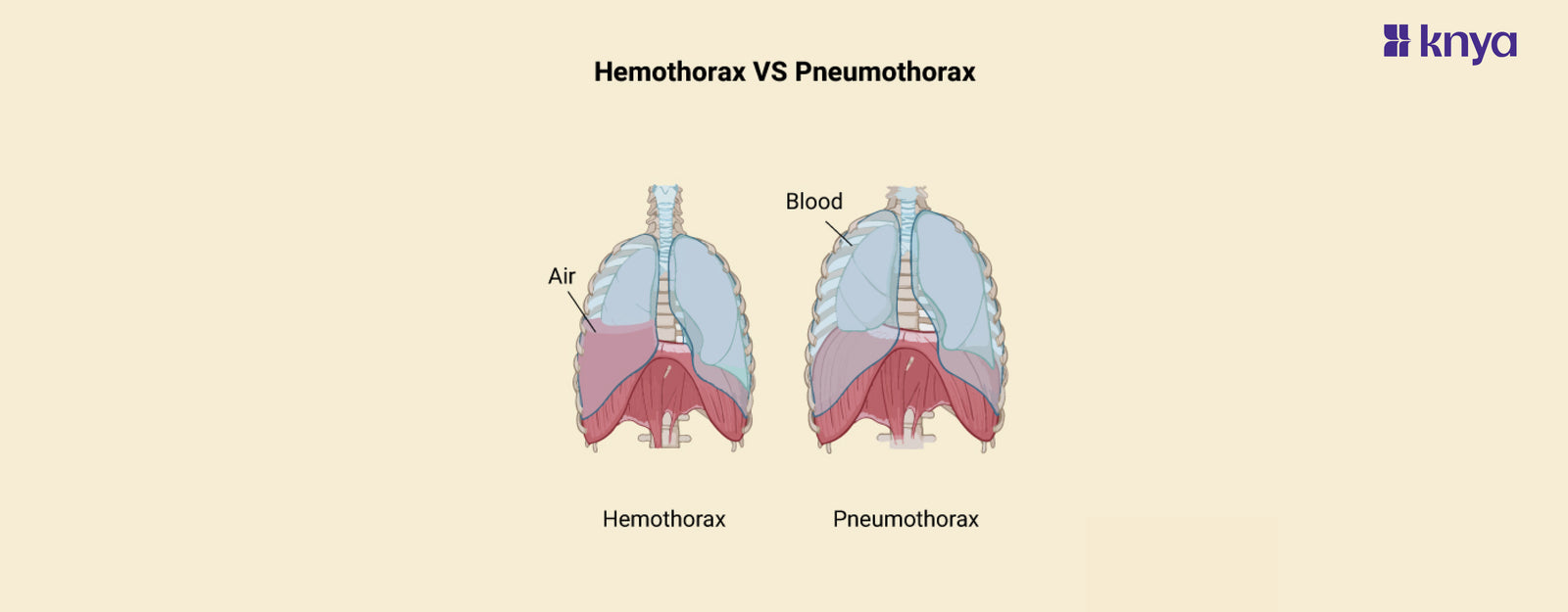
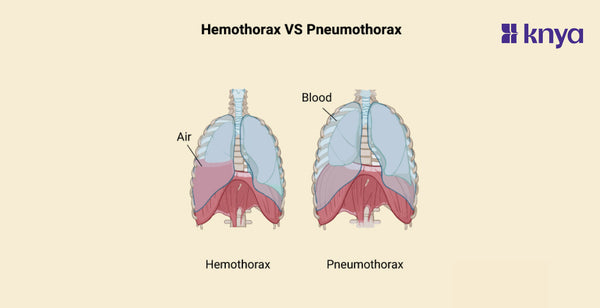
Hemothorax Vs Pneumothorax: Hemothorax and Pneumothorax are two different disorders that impact the area surrounding the lungs. Pneumothorax develops when air seeps into this region, compressing the lung and making breathing difficult. In contrast, hemothorax occurs when blood fills the same area, usually as a result of an injury, placing pressure on the lung and preventing expansion. Hemothorax vs Pneumothorax: Both can induce chest discomfort and shortness of breath, but what distinguishes them is intensity, likely causes, and treatment (chest tube drainage for air in pneumothorax, blood removal and drainage for hemothorax). Remember that both require quick medical attention.
Difference Between Hemothorax and Pneumothorax
Hemothorax and pneumothorax are both medical conditions involving the chest cavity, but they involve different substances and have distinct characteristics. Here's an overview of each, followed by the difference between arterial hemothorax and pneumothorax.
|
Aspect |
Arterial Hemothorax |
Pneumothorax |
|
Substance Involved |
Blood |
Air |
|
Etiology |
Arterial injury or rupture |
Trauma, lung disease, spontaneous rupture |
|
Symptoms |
Signs of blood loss (rapid heart rate, low blood pressure) |
Chest pain, difficulty breathing |
|
Diagnostic Findings |
Bright red blood in chest drainage |
Absence of lung markings on chest X-ray |
|
Management |
May require surgical intervention to control bleeding |
Chest tube insertion to remove air and allow lung re-expansion |
|
Prognosis |
Higher risk of mortality due to potential massive blood loss |
Better prognosis if promptly treated |
|
Complications |
Hypovolemic shock, other complications of significant blood loss |
Tension pneumothorax, life-threatening complications |
|
Treatment Approach |
Surgical repair, addressing underlying arterial injury |
Removing air, preventing recurrence |
|
Thoracic Drainage Characteristics |
Dark, oxygenated blood |
Air |
|
Associated Injuries |
Often associated with other traumatic injuries |
May occur in isolation or alongside other thoracic injuries |
Browse Best Scrubs Collection
What is Hemothorax?
Hemothorax occurs when blood accumulates in the space between your lungs and chest wall, called the pleural space. This disrupts lung function by preventing it from fully expanding and taking in air. It's often caused by chest trauma like car accidents or stab wounds, but can also happen due to medical procedures or underlying conditions. Symptoms include sudden sharp chest pain, shortness of breath, and rapid breathing. It's a serious condition requiring immediate medical attention, usually involving draining the blood with a chest tube.
Key Features of Hemothorax:
- Hemothorax is the presence of blood within the pleural space, which is the hollow that surrounds the lungs. This blood can collect as a result of trauma, surgical operations, or underlying medical disorders.
- The amount of blood collected can range from tiny, presenting few symptoms, to substantial and potentially fatal, impairing lung function and causing shock.
- Smaller hemothoraces may go undetected, however bigger ones produce chest discomfort, shortness of breath, coughing (often bloody), fast breathing, and low blood pressure.
- Confirmation of the diagnosis is achieved using a chest X-ray, ultrasound, or CT scan. The treatment consists of draining the blood through a chest tube, addressing underlying problems, and giving oxygen support as needed.
What is Pneumothorax?
Pneumothorax, commonly known as a collapsed lung, happens when air enters the pleural space, collapsing the lung tissue. This also impedes lung function and causes similar symptoms to hemothorax, like chest pain and shortness of breath. It can arise from chest trauma, spontaneous lung rupture in people with underlying lung conditions like asthma, or medical procedures. Treatment generally involves inserting a chest tube to drain the air and allow the lung to re-inflate.
Key Features of Pneumothorax:
- Pneumothorax occurs when air leaks into the pleural space, collapsing the lung partially or completely. This air can come from external injuries, lung punctures, or spontaneous ruptures in lung tissue.
- Primary pneumothorax arises without known cause, often affecting young, tall, thin individuals. Secondary pneumothorax results from underlying lung conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Sharp chest pain, sudden onset of shortness of breath, rapid breathing, cough, and sometimes anxiety are common symptoms.
- Chest X-ray confirms diagnosis. Small pneumothoraces might resolve on their own, while larger ones often require needle aspiration or chest tube insertion to remove air and re-inflate the lung.
Shop Best Lab Coats from Here!
Similarities Between Hemothorax and Pneumothorax
- Both hemothorax and pneumothorax involve the pleural cavity and can result in symptoms of impaired lung function.
- Both arterial hemothorax and pneumothorax are diagnosed with comparable imaging modalities, such as chest X-rays or CT scans.
- Both disorders can cause chest discomfort, trouble breathing, and symptoms of respiratory distress.
- Both arterial hemothorax and pneumothorax may necessitate immediate treatment to stabilise the patient and avoid future problems.
- If not treated immediately and appropriately, both hemothorax and pneumothorax can lead to problems such as respiratory failure or infection.
Hemothorax and pneumothorax are abnormal collections in the pleural space around the lungs, although their contents differ greatly. Hemothorax is the buildup of blood in the thorax, which is frequently caused by trauma or medical operations. It has comparable symptoms as pneumothorax (air in the pleural space), such as difficulty breathing and chest discomfort, but it can also induce shock and hypotension owing to blood loss. While pneumothorax can be classified as open (allowing continuous air being admitted) or closed (with air trapped within), the severity of hemothorax is mostly defined by the volume of blood collected. Both illnesses need immediate medical attention, with chest tube drainage being a typical therapy. However, therapies may vary depending on the unique cause and severity of each illness.
Order the Best Jogger Scrub from Here!
| Check out More Articles | |
| Difference Between Cartilage and Bone | |
| Difference Between Endocrine and Exocrine Glands | |
| Difference Between Cell Wall and Cell Membrane | |