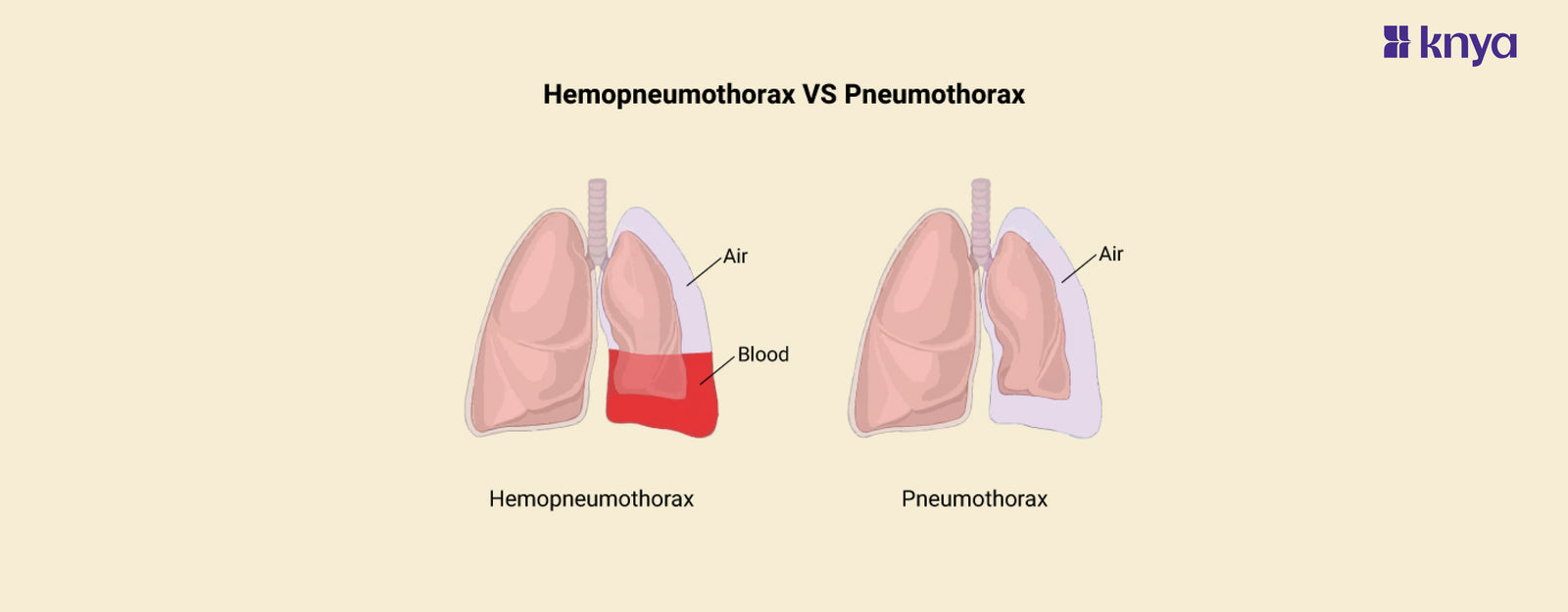
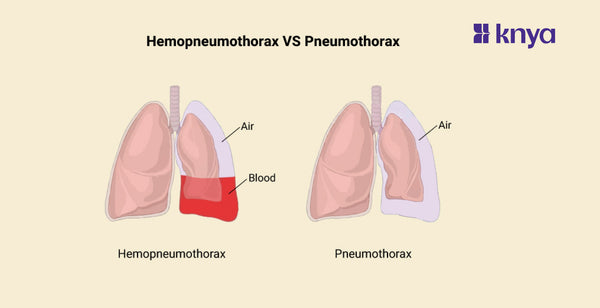
Hemopneumothorax vs Pneumothorax: Hemopneumothorax and Pneumothorax are both pleural space disorders, however, they have different compositions and causes. Pneumothorax, which can be brought on by trauma or underlying lung disease, is the accumulation of air in the pleural cavity, which frequently results in lung collapse. Breathing difficulties and abrupt chest discomfort are among the symptoms. On the other hand, Hemopneumothorax, which is usually brought on by severe trauma like piercing chest traumas, is defined by the presence of both blood and air in the pleural space. Pneumothorax symptoms and indicators of blood loss, such as low blood pressure, are evident. For these situations, prompt medical action is essential to restore lung function and avoid consequences, including the installation of a chest tube.
Difference between Hemopneumothorax and Pneumothorax
Pneumothorax is characterized by the presence of air alone in the pleural cavity, with symptoms like breathing difficulties and chest pain, whereas Hemopneumothorax involves the accumulation of both blood and air in the pleural space and is frequently the result of catastrophic chest injuries. The table below provides the differences between Hemopneumothorax and Pneumothorax.
|
Characteristic |
Hemopneumothorax |
Pneumothorax |
|
Definition |
Accumulation of both air and blood in pleural space |
Accumulation of air in pleural space |
|
Etiology |
Often results from traumatic chest injury |
Can be traumatic, spontaneous, or iatrogenic |
|
Composition |
Presence of both air and blood in pleural space |
Presence of air in pleural space |
|
Symptoms |
Chest pain, difficulty breathing, signs of blood loss |
Chest pain, difficulty breathing |
|
Additional Symptoms |
Signs of blood loss (low blood pressure, rapid heart rate, paleness) |
Breathlessness, rapid heart rate, decreased breath sounds |
|
Diagnosis |
Clinical examination, imaging (X-ray, CT scan) |
Clinical examination, imaging (X-ray, CT scan) |
|
Treatment |
Urgent medical attention, chest tube insertion, addressing associated injuries |
Chest tube insertion to remove air, observation or surgery depending on severity |
Browse The Best Scrubs Collection!
What is Hemopneumothorax?
Hemopneumothorax is a serious disorder in which both air and blood collect in the pleural area. It frequently happens as a result of trauma that damages both lung tissue and blood vessels, like a penetrating chest injury. Pneumothorax symptoms are present, along with indicators of blood loss such as paleness, low blood pressure, and an accelerated heartbeat. To treat the condition, immediate medical assistance is required. This may involve inserting a chest tube to remove blood and air from the pleural space as well as tending to any related bleeding or injuries.
Causes of Hemopneumothorax
- Trauma: Trauma to the chest, resulting from falls, auto accidents, or penetrating traumas like gunshot or stabbing wounds, is the primary cause of Hemopneumothorax. Rib fractures brought on by blunt force trauma have the potential to pierce blood vessels and lungs, accumulating blood and air in the pleural space.
- Chest Surgery: Hemopneumothorax can result from complications following thoracic procedures, especially those involving the lungs or chest wall. Damage to blood vessels or lung tissue can occur accidentally during surgical operations including lobectomies, lung biopsies, or treatments for lung disorders.
- Lung Disease: A person's risk of Hemopneumothorax may be increased by certain lung disorders or diseases. Lung cancer, TB, pneumonia, cystic fibrosis, and emphysema are a few examples. These illnesses may weaken blood vessels or lung tissue, increasing the risk of rupture and the buildup of blood and air in the pleural space.
- Spontaneous Pneumothorax: If there is concurrent bleeding into the pleural space, a spontaneous Pneumothorax may occasionally result in Hemopneumothorax. People with underlying lung diseases such as cystic fibrosis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are susceptible to spontaneous Pneumothorax.
- Thoracentesis: Hemopneumothorax is an uncommon but possible consequence of thoracentesis, a procedure in which a needle is introduced into the pleural space to drain air or fluid. During the surgery, bleeding and air leaking into the pleural cavity may result from an unintentional puncture of blood vessels or lung tissue.
Symptoms of Hemopneumothorax
- Chest Pain: One of the main signs of a Hemopneumothorax is a sharp or stabbing chest pain. The side of the damaged lung is usually where the pain is felt, and it may get worse when you breathe or cough.
- Breathlessness: Another typical symptom is dyspnea, or difficulty breathing. The accumulation of blood and/or air in the pleural cavity can compress the lung, preventing it from expanding completely, which can result in shortness of breath and reduced lung function.
- Fast Heartbeat (Tachycardia): When the body reacts to low oxygen levels and elevated stress, it can cause a fast heartbeat.
- Cyanosis: In severe situations, bluish coloring of the skin or lips may result from insufficient blood oxygenation.
- Shallow Breathing: To make up for diminished lung function, patients may breathe quickly or shallowly.
- Cough: While a dry cough is less common than chest pain and shortness of breath, some patients with Hemopneumothorax may develop one.
- Hypotension: Because bleeding into the pleural cavity reduces blood volume, severe Hemopneumothorax instances might result in low blood pressure.
What is Pneumothorax?
Pneumothorax occurs when air enters the pleural space and causes the afflicted lung to collapse partially or completely. There are several reasons why air can enter the pleural space, including lung diseases, trauma, and spontaneous Pneumothorax, which occurs when air enters the area without any obvious reason. Abrupt chest discomfort, dyspnea, elevated heart rate, and diminished breath sounds on the afflicted side are among the symptoms. As part of treatment, a chest tube is frequently inserted to drain air and permit lung tissue to expand again.
Causes of Pneumothorax
- Trauma: A rib fracture or other penetrating injury that permits air to enter the pleural space is one of the most frequent causes of Pneumothorax.
- Spontaneous Pneumothorax:
Primary Spontaneous Pneumothorax (PSP): This happens when there is no underlying lung illness. It is believed to be connected to the development of tiny, ruptured air-filled sacs (blebs) on the lung surface, which frequently occur in tall, thin people.
Secondary Spontaneous Pneumothorax (SSP): People who already have lung diseases such as pneumonia, cystic fibrosis, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) may experience this. A Pneumothorax is more likely when there is an underlying lung illness because it weakens the lung tissue.
- Iatrogenic Pneumothorax: This kind is brought on by medical treatments or procedures that have the potential to inadvertently puncture the lung and let air into the pleural space, such as central line implantation, mechanical ventilation, or lung biopsies.
- Catamenial Pneumothorax: Endometriosis is linked to this uncommon kind of Pneumothorax. Endometrial tissue may invade the pleural space during menstruation, causing irritation and air collection.
- Connective Tissue Disorders: Certain connective tissue disorders, such as Marfan syndrome or Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, can predispose people to Pneumothorax due to structural abnormalities in lung tissue.
Symptoms of Pneumothorax
- Sudden Chest Pain: Usually felt on one side of the chest, this pain is frequently described as sharp or stabbing. Coughing or breathing may cause the pain to get worse.
- Breathing Difficulties: Breathing problems are frequently experienced, particularly when the Pneumothorax gets worse and the afflicted lung is more compressed. In extreme situations, it may cause cyanosis, which is a blue staining of the skin brought on by a shortage of oxygen, or fast breathing.
- Fast Heartbeat (Tachycardia): The body may quicken its heartbeat to make up for a drop in oxygen saturation.
- Chest Tightness: Some people may feel as though their chest is constricted or pressing against them.
Shop Best Lab Coats From Here!
Similarities between Hemopneumothorax and Pneumothorax
- Pleural Space Involvement: Blood and/or air are present in the pleural space in Hemopneumothorax and Pneumothorax, respectively. In Hemopneumothorax, both blood and air are present in the pleural cavity, whereas in Pneumothorax, only air collects there.
- Potential Causes: Both disorders are frequently brought on by trauma. They may be brought on by trauma to the chest that breaks blood vessels or lung tissue, such as rib fractures or penetrating wounds.
- Clinical Presentation: Hemopneumothorax and Pneumothorax symptoms may coexist. Sudden onset chest discomfort, dyspnea, reduced breath sounds on the affected side, and maybe indicators of shock in the event of Hemopneumothorax are the common symptoms of both disorders.
- Diagnostic Evaluation: To view the pleural space and determine the extent of the abnormalities, imaging procedures like chest X-rays or CT scans are frequently used in the diagnosis process for both disorders. There may be similarities between the two instances' physical examination results, such as diminished breath sounds and indications of respiratory distress.
In conclusion, Hemopneumothorax, which is typically caused by traumatic injury, involves both air and blood buildup in the pleural space, whereas Pneumothorax only involves the accumulation of air. To avoid complications and restore lung function, these disorders require immediate medical examination and management.
Order the Best Jogger Scrub From Here!
| Check out More Articles | |
| Difference Between Cartilage and Bone | |
| Difference Between Endocrine and Exocrine Glands | |
| Difference Between Cell Wall and Cell Membrane | |