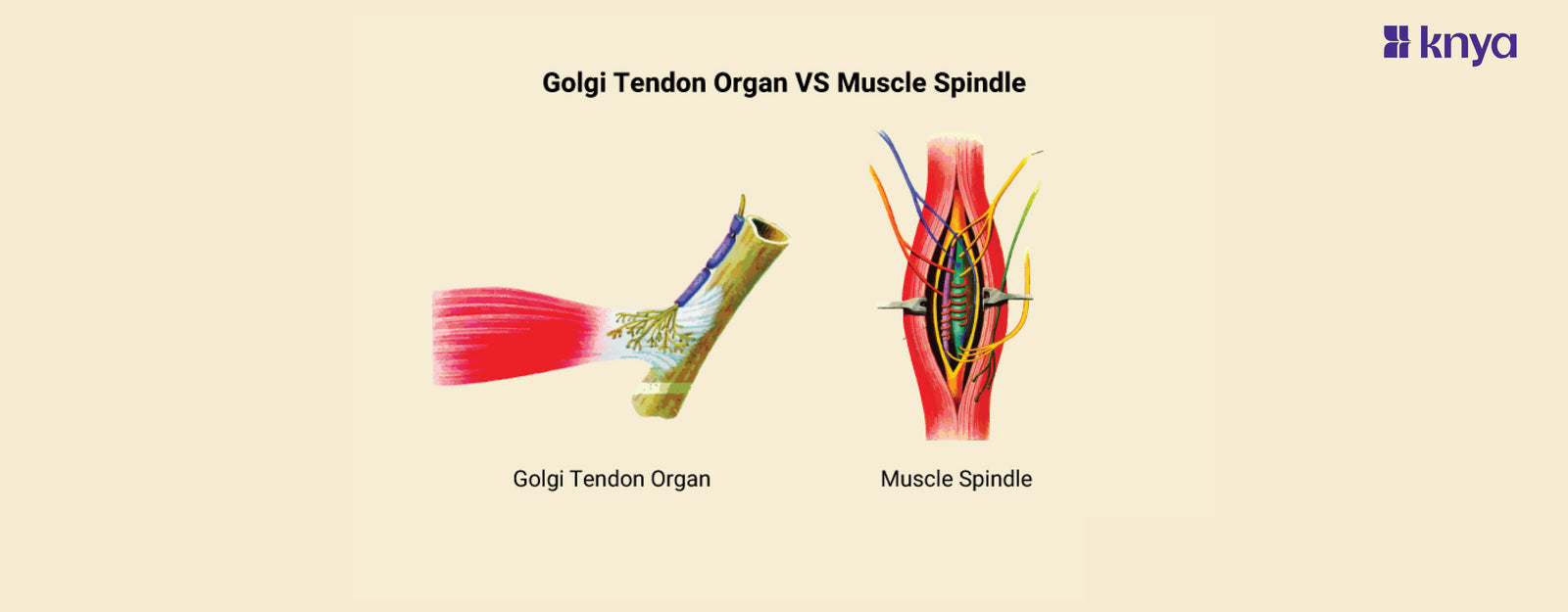
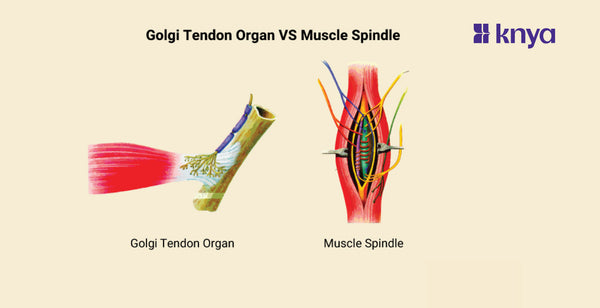
Golgi Tendon Organ Vs Muscle Spindle: Golgi Tendon Organ and Muscle Spindle are both proprioceptors, acting like tiny security guards in your muscles. While Muscle Spindles watch for muscle length (think "stretch reflex"), Golgi Tendon Organs monitor muscle tension. When a muscle stretches too far, the Spindle sends a signal to contract and protect it. Conversely, if tension gets too high, the GTO steps in and relaxes the muscle to prevent tears. Think of them as a striking duo, working together to maintain smooth, controlled movements and safeguard your muscles from injury.
Difference Between Golgi Tendon Organ and Muscle Spindle
Proprioceptors are sensory receptors that convey information to the central nervous system regarding the position and movement of muscles and joints. The Golgi tendon organ and the muscle spindle are two examples. However, they serve various purposes and have separate structures and reactions. Below are the differences between the Golgi tendon organ and the muscle spindle.
|
Characteristic |
Golgi Tendon Organ (GTO) |
Muscle Spindle |
|
Location |
Located in the tendon-muscle junction |
Found parallel to muscle fibers within the muscle belly |
|
Sensory Receptors |
Consist of type Ib sensory nerve endings |
Consist of type Ia and type II sensory nerve endings |
|
Function |
Monitors tension within the muscle-tendon complex |
Monitors muscle length and changes in muscle length |
|
Response |
Activated by tension/stretch in the tendon |
Activated by changes in muscle length and velocity |
|
Sensitivity |
Highly sensitive to changes in muscle tension |
Sensitive to changes in muscle length and velocity |
|
Feedback |
Provides negative feedback to prevent excessive force |
Provides feedback for muscle length and proprioception |
|
Reflex Involvement |
Involved in the inverse myotatic reflex |
Involved in the stretch (myotatic) reflex |
|
Neural Pathways |
Signals primarily travel via type Ib afferent fibers |
Signals primarily travel via type Ia afferent fibers |
|
Adaptation |
Adapt slowly to sustained tension |
Adapt quickly to changes in muscle length |
|
Role in Movement |
Contributes to fine motor control and coordination |
Essential for maintaining posture and executing movements |
Browse Best Scrubs Collection
What is Golgi Tendon Organ?
Located within tendons, these receptors sense muscle tension. When a muscle contracts too forcefully, the Golgi tendon organ sends signals to the spinal cord to relax the muscle, preventing it from being overloaded and potentially damaged. consider it as a safety button for your muscles.
Key Features of Golgi Tendon Organ:
- Situated within tendons, near the junction with muscle fibers.
- Acts as a "tension sensor", detecting excessive muscle force and triggering relaxation.
- When muscle tension increases, the Golgi tendon organ sends signals to the spinal cord, prompting the muscle to relax (autogenic inhibition). This reflex helps maintain muscle tone and prevents damage during forceful contractions.
- Golgi tendon organ dysfunction can contribute to muscle imbalances and movement disorders. Understanding their role is crucial for physical therapy and rehabilitation interventions.
What is Muscle Spindle?
These receptors, located within muscle fibers, detect changes in muscle length. If a muscle is stretched too rapidly, the muscle spindle activates, causing a reflex contraction to protect the muscle from further strain. Call it a built-in ruler for your muscles.
Key Features of Muscle Spindle:
- Embedded in muscle bellies and surrounded by muscular fibers.
- Acts as a "stretch sensor," detecting changes in muscle length and causing muscular contraction (the stretch response).
- When a muscle is stretched, the spindle transmits signals to the spinal cord, which causes the muscle to contract and oppose the strain. This reaction helps to maintain posture and balance, as well as smooth coordinated movements.
- muscular spindle dysfunction can cause muscular weakness, incoordination, and stiffness. Understanding their involvement is critical for detecting and treating neurological conditions.
Shop Best Lab Coats from Here!
Similarities Between Golgi Tendon Organ and Muscle Spindle
- Proprioceptors include the Golgi tendon organs and muscle spindles.
- They send sensory signals to the central nervous system concerning muscle length and tension.
- They serve critical functions in reflex systems that help to maintain posture, balance, and coordination.
- Both Golgi tendon organs and muscle spindles help in motor control and coordination during voluntary movements.
- They are both engaged in protective reflexes that help to avoid muscle injury caused by excessive tension or stretching.
While both Golgi tendon organs (GTOs) and muscle spindles are important proprioceptors, their functions differ dramatically. Muscle spindles, which are implanted within muscles, detect length and stretch, activating the stretch reflex to prevent overextension. Imagine them as little guards who constrict the muscle if it lengthens too much. In contrast, GTOs are found at the muscle-tendon junction and assess muscular tension. They function as safety brakes, transmitting inhibitory impulses to relax the muscle when the force exceeds acceptable limits. Think of them as stress detectors that avoid undue strain. This GTO vs Muscle Spindle dynamic promotes smooth, regulated motions and protects against damage, with both working together to maintain optimal muscle function.
| Check out More Articles | |
| Difference Between Tendon and Ligament | |
| Difference Between Seizure and Epilepsy | |
| Difference Between Hypothyroidism and Hyperthyroidism | |