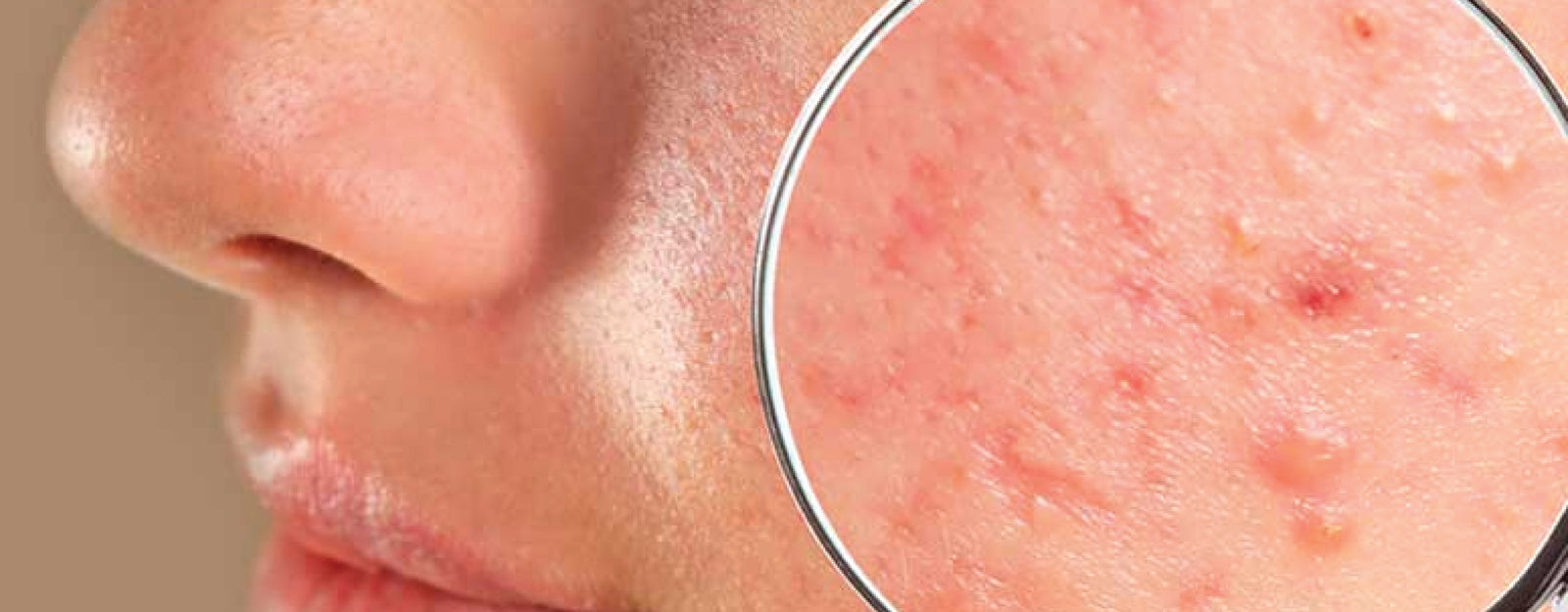
Fungal Acne Vs Closed Comedones: Fungal Acne and Closed Comedones are both frequent skin conditions that might appear as tiny lumps, but they have distinct origins and treatments. Fungal acne, also known as Malassezia folliculitis, is a yeast infection that causes an inflammatory reaction, whereas closed comedones (whiteheads) are blocked pores produced by excess oil and dead skin cells. While both can present on the face, chest, and back, fungal acne is typically more bothersome and persistent, and it may increase with perspiration or heat. It might be difficult to distinguish between Fungal Acne and Closed Comedones, thus a dermatologist should always be consulted for correct diagnosis and management.
Difference Between Fungal Acne and Closed Comedones
Fungal acne and closed comedones are two different skin conditions that can sometimes be confused due to their similar appearance. Highlighting the definitions and the key differences between the two:
|
Aspect |
Fungal Acne |
Closed Comedones |
|
Definition |
A type of yeast infection affecting hair follicles. |
Blocked hair follicles due to excess oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria. |
|
Cause |
Overgrowth of yeast, specifically Malassezia. |
Excess oil production, dead skin cells, and bacteria. |
|
Appearance |
Small, red or skin-colored bumps, sometimes itchy. |
Small, flesh-colored bumps with a white or yellowish center. |
|
Triggers |
Excessive sweating, tight clothing, humid environments. |
Hormonal changes, certain skincare products, genetics. |
|
Treatment |
Antifungal treatments like ketoconazole, topical antifungal creams. |
Topical treatments with salicylic acid, benzoyl peroxide. |
|
Location |
Commonly on chest, back, shoulders, sometimes face. |
Primarily on the face, especially T-zone, also chest, back. |
|
Spread |
Can spread through direct contact or contaminated items. |
Not contagious, does not spread through contact. |
|
Reoccurrence |
May recur if underlying conditions are not addressed. |
May recur if skincare/lifestyle factors persist. |
|
Diagnosis |
Requires skin scraping for microscopic examination. |
Diagnosis based on visual examination. |
|
Medical Attention |
Severe/persistent cases may require a dermatologist. |
Severe/persistent cases may require medical attention. |
Browse Best Scrubs Collection
What is Fungal Acne?
Fungal acne, also known as Malassezia folliculitis, is caused by an excess of yeast rather than bacteria on the skin. This overgrowth can result in tiny, red, itchy pimples on the chest, back, shoulders, and upper arms. Unlike typical acne, fungal acne does not generally produce blackheads or cysts.
Key Features of Fungal Acne:
- Caused by an overgrowth of Malassezia, a yeast naturally present on the skin.
- Small, itchy red pimples are frequently found on the chest, back, shoulders, and upper arms. It may also occur on the face.
- Warm, humid temperatures, perspiration, and certain drugs can aggravate fungal acne.
- Dermatologists generally prescribe antifungal lotions, shampoos, or oral drugs.
What are Closed Comedones?
Closed comedones, also known as whiteheads, are little white lumps that appear when dead skin cells and sebum (oil) become caught inside a pore. They are produced by the accumulation of dead skin cells and oil, which can be provoked by causes such as hormonal fluctuations, stress, and certain drugs. Closed comedones are typically found on the face, although they can also appear on the chest, back, and shoulders.
Key Features of Closed Comedones:
- Clogged pores are caused by excessive sebum (oil) production and dead skin cell accumulation.
- Small white lumps that persist beneath the skin's surface, commonly found on the forehead, nose, and cheeks.
- Oil-based cosmetics, harsh skincare products, hormone swings, and certain medicines can all exacerbate closed comedones.
- Over-the-counter topical retinoids, salicylic acid, or benzoyl peroxide can help clear pores and prevent new comedones from developing. In extreme situations, a dermatologist may offer prescription drugs or extraction treatments.
Shop Best Lab Coats from Here!
Similarities Between Fungal Acne and Closed Comedones
- Fungal acne and closed comedones can both appear as tiny pimples on the skin.
- They can appear on both the face and the body, however their distribution patterns vary.
- Certain skincare products can worsen fungal acne as well as closed comedones.
- Proper skincare hygiene is essential for both diseases.
- Both disorders are typically treated with topical treatments.
- Both illnesses can create pain and low self-esteem in people who are affected.
- Both fungal acne and closed comedones can benefit from focused therapies and lifestyle changes.
- Both disorders may have underlying causes, such as hormone imbalances or heredity.
- They can occasionally coexist on the same person, complicating diagnosis and therapy.
- Effective therapy frequently involves recognising and treating the root causes of the skin problem.
While both Fungal Acne and Closed Comedones can create tiny lumps on the skin, identifying the fundamental distinctions is critical for effective treatment. Fungal Acne, despite its name, is essentially a yeast overgrowth that causes itchy, red lumps on the chest, back, and upper arms. Closed comedones, also known as whiteheads, are formed by clogged pores caused by excess oil and dead skin cells and often develop in the T-zone (forehead, nose, and chin). Recognising these characteristics is critical for determining the best course of action, since Fungal Acne requires antifungal therapies, whilst Closed Comedones react well to typical acne - fighting chemicals.
| Check out More Articles | |
| Difference Between Cartilage and Bone | |
| Difference Between Endocrine and Exocrine Glands | |
| Difference Between Cell Wall and Cell Membrane | |