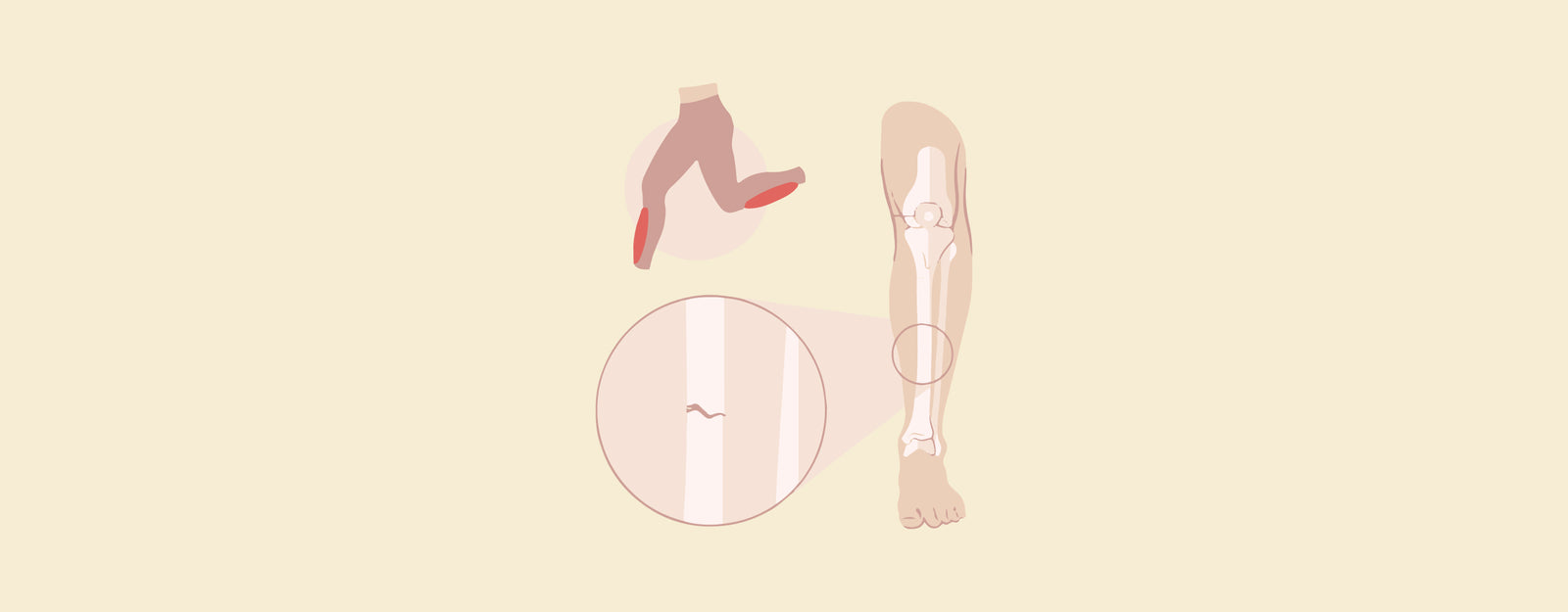
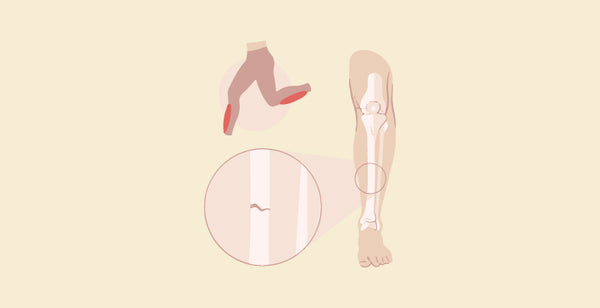
Difference Between Extensor Tendonitis and Stress Fracture: Stress fractures and Extensor Tendonitis are two different conditions that typically result from overuse or repetitive stress, although they affect different bodily components. Inflammation of the tendons that stretch or straighten a joint, known as Extensor Tendonitis, is frequently observed in the hands or feet and causes discomfort, edema, and soreness. Conversely, stress fractures, which usually affect weight-bearing bones like the foot, are microscopic breaks in the bone brought on by recurrent stress. They induce localized pain, edema, and sensitivity. Extensor Tendonitis typically affects tendons, whereas stress fractures entail bone damage, yet both disorders can cause discomfort and limited movement.
Difference between Stress Fractures and Extensor Tendonitis
Tiny breaks in bones caused by repeated strain are known as Stress Fractures, whereas Extensor Tendonitis is the inflammation of the tendons that allows for joint extension. The table below provides the differences between Stress Fractures and Extensor Tendonitis.
|
Aspect |
Stress Fractures |
Extensor Tendonitis |
|
Definition |
Tiny cracks or hairline fractures in bones, often due to repetitive force or overuse. |
Inflammation of tendons responsible for extending or straightening a joint. |
|
Affected Structures |
Bones, commonly weight-bearing bones such as those in the feet and legs. |
Tendons, typically those on the top of the foot or hand. |
|
Cause |
Repetitive force or overuse, particularly in weight-bearing activities. |
Overuse, improper footwear, or repetitive activities straining the tendons. |
|
Location |
Commonly found in weight-bearing bones like metatarsals in the feet. |
Often affects tendons on the top of the foot or hand. |
|
Symptoms |
Localized pain, swelling, tenderness, exacerbated by weight-bearing activities. |
Pain, swelling, tenderness, often worsened with movement. |
|
Diagnosis |
Typically confirmed through imaging tests like X-rays or MRI scans. |
Diagnosis based on clinical examination, may include imaging to rule out other conditions. |
|
Treatment |
Rest, immobilization, activity modification, possibly surgical intervention for severe cases. |
Rest, ice, anti-inflammatory medications, stretching, and supportive footwear. |
|
Recovery Time |
Recovery time varies depending on severity, typically several weeks to months. |
Recovery time varies, often improves with rest and appropriate management, but may take several weeks. |
|
Prevention |
Gradual progression of activity, proper footwear, adequate nutrition to support bone health. |
Proper warm-up, stretching, strengthening exercises, supportive footwear, activity modification. |
Browse The Best Scrubs Collection!
What are Stress Fractures?
A Stress Fracture is a tiny crack or hairline fracture in a bone, typically caused by repetitive force or overuse rather than a single traumatic event. These fractures develop gradually over time due to the cumulative effect of repetitive stress on the bone, particularly in weight-bearing bones such as those in the feet and legs. Stress Fractures are common among athletes and individuals who engage in high-impact activities, such as running, jumping, or dancing. They often present with localized pain, swelling, and tenderness at the site of the fracture, which worsens with weight-bearing activities and improves with rest.
Causes of Stress Fractures
- Repetitive Stress: High-impact exercises that put repetitive strain on the bones, such as dancing, sprinting, or jumping, can progressively erode the bones and cause stress fractures.
- Increase in Activity Abruptly: Stress fractures can result from abruptly increasing the amount, frequency, or intensity of physical activity, especially if there hasn't been enough time for recovery or conditioning.
- Inadequate Biomechanics: Deviations in the way one walks, the form of the foot, or the balance of muscles can change how stresses are applied to the bones, which raises the possibility of stress fractures. This includes things like high arches, flat feet, or inappropriate footwear.
- Training Errors: People who perform too much training without enough recovery, warm up too little, or use incorrect techniques are more likely to suffer stress fractures.
- Surface or Terrain Changes: Exercising or running on concrete, uneven terrain, or hard surfaces can increase the impact forces that are transferred to the bones, which can lead to stress fractures.
Symptoms of Stress Fractures
- Localized Pain: Pain is typically experienced at the fracture site and is frequently the main sign of a Stress Fracture. Either dull or acute discomfort is possible, and weight-bearing activities usually make it worse.
- Swelling: Inflammation and fluid buildup at the Stress Fracture site may cause swelling. The afflicted region might feel sensitive to the touch or show obvious signs of swelling
- Tenderness: The area around the Stress Fracture site frequently feels tender. Applying pressure to the region could cause pain or discomfort.
- Pain with Activity: When engaging in weight-bearing exercises like walking, running, or jumping, the pain from a Stress Fracture frequently gets worse. While at rest, the pain may go away, but it frequently comes back as you start up again.
- Localized Bruising: Sometimes bleeding into the surrounding tissues causes bruising to appear around the Stress Fracture site.
What is Extensor Tendonitis?
Extensor Tendonitis is characterized by inflammation of the tendons that extend or straighten a joint. It typically affects the tendons in the hands or feet, resulting in localized discomfort, edema, and tenderness. Overuse, inappropriate footwear, or repetitive activities that put a strain on the tendons—like typing, playing an instrument, or engaging in sports that require sprinting or jumping—are common causes of this problem. To reduce pain and speed up recovery, treatment usually consists of rest, ice, anti-inflammatory drugs, and stretching exercises.
Causes of Extensor Tendonitis
- Overuse: Extensor tendons can become strained and inflamed by repeatedly performing actions that require extending or straightening a joint, such as typing, playing an instrument, or engaging in specific sports movements.
- Inappropriate Footwear: While engaging in activities that require a lot of impact or pressure on the feet, Extensor Tendonitis is more likely to occur while wearing shoes that do not offer enough support or cushioning for the feet.
- Muscle Imbalance: Abnormal stress and pressure on the tendons can result in tendonitis and inflammation by weakening or tightening the surrounding muscles.
- Inadequate Form or Technique: When engaging in physical activities or sports, using poor form or technique can place an undue amount of strain on the tendons and cause tendonitis.
- Trauma: Sudden impact or vigorous activity are examples of direct trauma or injury to the extensor tendons that can result in inflammation and irritation and eventually lead to tendonitis.
Symptoms of Extensor Tendonitis
- Pain: The main sign of Extensor Tendonitis is frequently pain. It could only be present at the apex of the afflicted joint or through the tendon.
- Swelling: Inflammation can cause swelling around the injured tendon or joint. The region can feel sensitive to touch or show obvious signs of swelling.
- Tenderness: Commonly, the afflicted tendon or joint will feel tender. Applying pressure to the region could cause pain or discomfort.
- Stiffness: The afflicted joint may feel stiff or have a limited range of motion, particularly during rest periods or first thing in the morning.
- Weakness: Activities involving stretching or straightening the joint may become challenging due to weakness in the affected area.
Shop Best Lab Coats From Here!
Similarities Between Stress Fractures and Extensor Tendonitis
- Overuse Injury: Repetitive stress or overuse in the affected area can lead to Stress Fractures as well as Extensor Tendonitis. Both disorders can develop as a result of repetitive activities, especially ones that involve high-impact or repetitive motion.
- Localized Pain: At the site of the injury, these disorders commonly cause localized pain. Whereas Extensor Tendonitis causes pain mostly around the affected tendon or joint, Stress Fractures typically cause discomfort centered on the bone close to the fracture site.
- Aggravation with Activity: Pain in the affected area usually gets worse with movement or activity, which is common with both Stress Fractures and Extensor Tendonitis. Running or other weight-bearing exercises may make either condition's pain worse.
In summary, there are similarities between Stress Fractures and Extensor Tendonitis in terms of symptoms, etiology, and preventive measures, even though they affect different bodily parts. Both disorders can cause localized discomfort, swelling, and tenderness that is especially aggravated by exercise. They are frequently brought on by overuse or recurrent stress. Effective therapy requires accurate diagnosis and management, with strategies ranging from immobilization and rest to activity moderation and supporting measures.
Order the Best Jogger Scrub From Here!
| Check out More Articles | |
| Difference Between Tendon and Ligament | |
| Difference Between Seizure and Epilepsy | |
| Difference Between Hypothyroidism and Hyperthyroidism | |