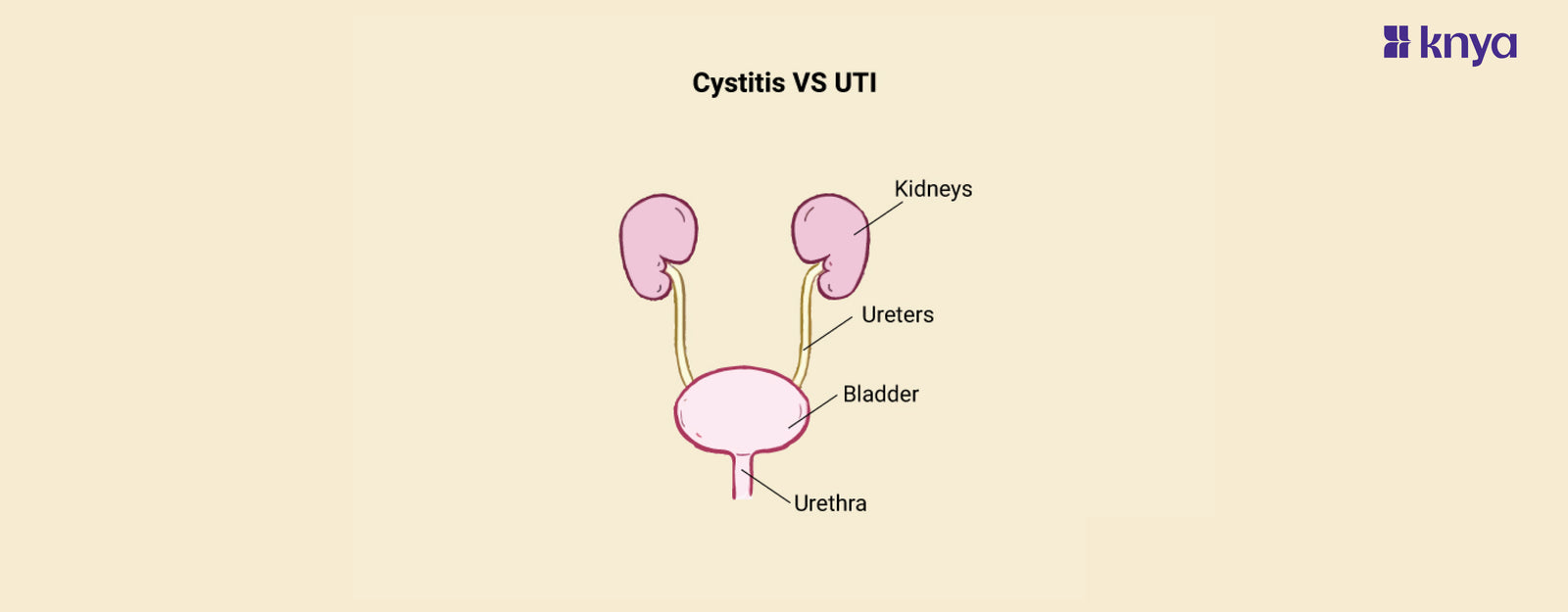
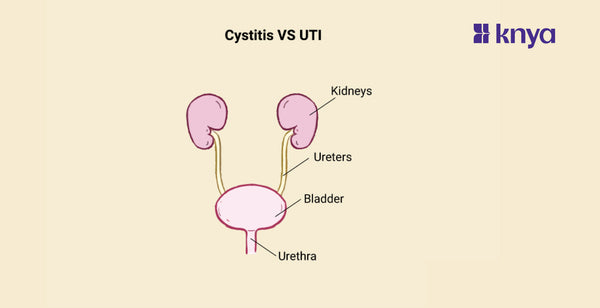
Cystitis and UTIs cause urinary discomfort, they're not identical twins. Cystitis specifically targets the bladder, inflaming it due to infection (bacterial UTI) or other reasons. UTIs, on the other hand, invade any part of your urinary tract, from the urethra to the kidneys, with bacteria being the usual culprit. Distinguishing them hinges on the cause and location of inflammation. If it's just the bladder and involves bacteria, it's likely a UTI manifesting as Cystitis. But Cystitis can also arise from non-infectious causes, making a doctor's visit crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Order the Best Jogger Scrub from Here!
Difference Between Cystitis and UTIs
Cystitis and UTI (Urinary Tract Infection) are both conditions related to the urinary system, but they have some key differences, Highlighting the key differences between the two:
|
Feature |
Cystitis |
UTI |
|
Location |
Inflammation limited to the bladder |
Infections can occur anywhere in the urinary tract |
|
Extent of Infection |
Limited to the bladder |
Can affect bladder, urethra, ureters, kidneys |
|
Symptoms |
Pelvic pressure, localized discomfort |
Similar symptoms including frequent urination, urgency |
|
Severity |
Generally milder |
Can range from mild to severe, potentially life-threatening |
|
Risk Factors |
Bladder irritation, medications |
Sexual activity, urinary catheterization, underlying medical conditions |
|
Treatment |
Oral antibiotics |
May require stronger antibiotics or hospitalization for severe cases |
|
Complications |
Generally mild, if treated promptly |
Can lead to kidney damage, sepsis if untreated |
|
Frequency |
Recurrent due to bladder abnormalities |
Recurrent due to anatomical abnormalities, immune function |
|
Diagnostic Tests |
Urinalysis for signs of inflammation, infection |
Urinalysis, urine cultures for bacterial identification |
|
Underlying Causes |
Bacterial infection, irritation, underlying conditions |
Primarily bacterial infection, E. coli most common |
Browse Best Scrubs Collection
What is Cystitis?
Cystitis is a bladder inflammation caused most commonly by a bacterial infection. It's a common urinary tract infection (UTI), particularly in women, that causes a constant, urgent need to urinate even after emptying your bladder. While most instances are treatable with medications or home treatments, left untreated, they can progress to catastrophic kidney infections.
Key Features of Cystitis:
- Location: Inflammation and irritation of the bladder, the pouch that stores urine.
- Symptoms:
- Frequent urination, often with urgency and pain.
- Burning sensation during urination.
- Lower abdominal pain or pressure.
- Urine may be cloudy, bloody, or foul-smelling.
- Causes: Most commonly caused by E. coli bacteria entering the bladder through the urethra. Other bacteria and even fungi can also be culprits.
- Treatment: Antibiotics are the mainstay of treatment, along with pain relievers and increased fluid intake.
Explore All Women's Scrub
What are UTIs?
A UTI is an infection in any part of your urinary tract, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Most UTIs involve the bladder (cystitis) and are caused by bacteria entering the urethra and multiplying. Symptoms include frequent urination, burning pain, and blood in the urine. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent complications.
Key Features of UTIs:
- Location: Can affect any part of the urinary tract, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
- Symptoms:
- Similar to cystitis, but may vary depending on the infected site.
- Kidney infections can cause fever, flank pain, nausea, and vomiting.
- Upper UTIs may not burn during urination.
- Causes: Similar to cystitis, with E. coli being the most common culprit. Other bacteria, viruses, and fungi can also cause UTIs.
- Treatment: Depends on the location and severity of the infection. Antibiotics are typically used, with longer durations for upper UTIs. In severe cases, hospitalization and intravenous antibiotics may be needed.
Similarities Between Cystitis and UTIs
- Certain populations, such as women and individuals with compromised immune systems, are at higher risk for both cystitis and UTIs.
- While cystitis itself may not lead to serious complications if promptly treated, both conditions result in complications if not properly cured or if the infection spreads to other parts of the body.
- Cystitis and UTIs, both conditions can be diagnosed through similar diagnostic methods, including urinalysis and urine culture to identify the presence of infection and the specific bacteria causing it.
- Over-the-counter medications such as pain relievers and urinary tract analgesics can provide symptomatic relief for both cystitis and UTIs.
- Cystitis and UTIs can recur in some individuals, especially if underlying risk factors are not addressed or if the initial infection is not adequately treated.
- Both conditions can significantly impact a person's quality of life due to symptoms such as discomfort, pain, and disruption of daily activities.
Cystitis and UTIs are different illnesses, despite the fact that their symptoms overlap. Cystitis is the inflammation of the bladder that can be caused by infections (bacterial UTIs) or non-infectious causes such as chemical irritants or drugs. UTIs, on the other hand, are infections of any part of the urinary system, including the kidneys, ureters, urethra, and bladder (which, when infected, produces cystitis). This important distinction emphasises that all cases of cystitis caused by infections are UTIs, but not all UTIs are cystitis. Differentiating between the two is critical for accurate diagnosis and therapy. UTIs often require antibiotics, although non-infectious cystitis may necessitate pain treatment and lifestyle changes. Seeking medical help after suffering urinary tract problems provides an accurate diagnosis and the most effective therapy.
| Check out More Articles | |
| Difference Between Tendon and Ligament | |
| Difference Between Seizure and Epilepsy | |
| Difference Between Hypothyroidism and Hyperthyroidism | |