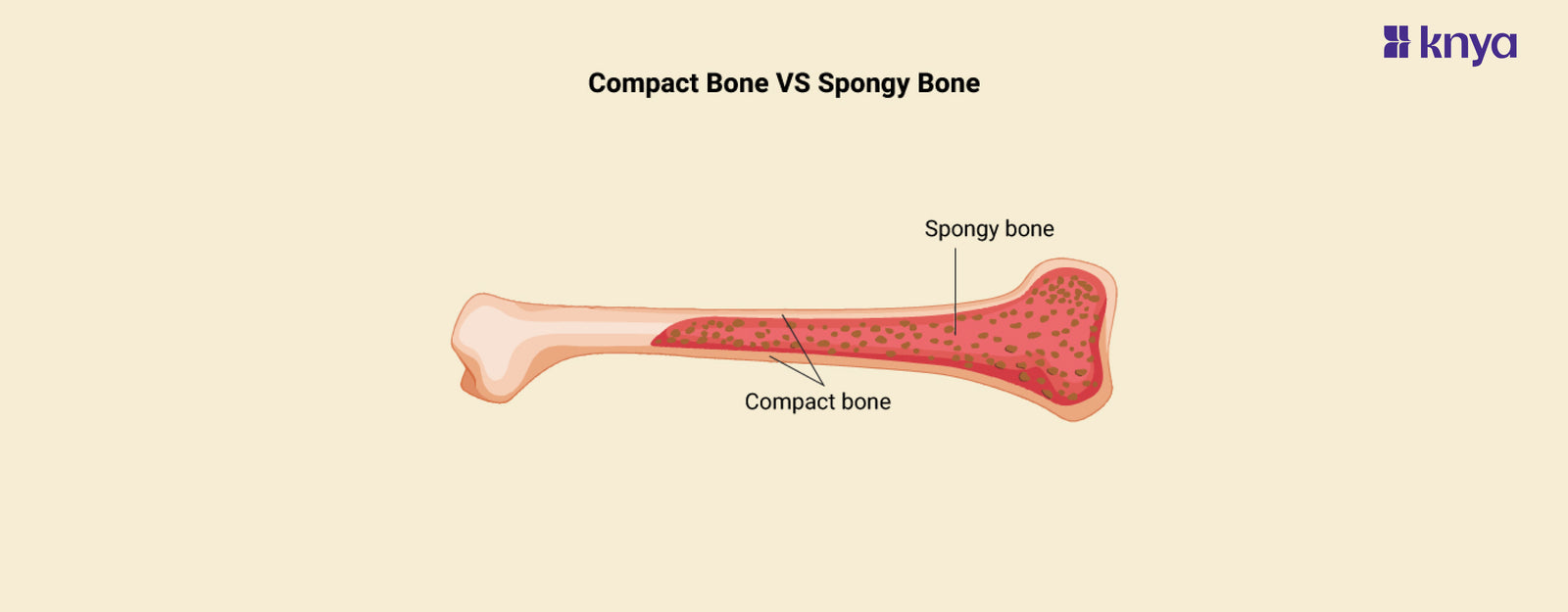
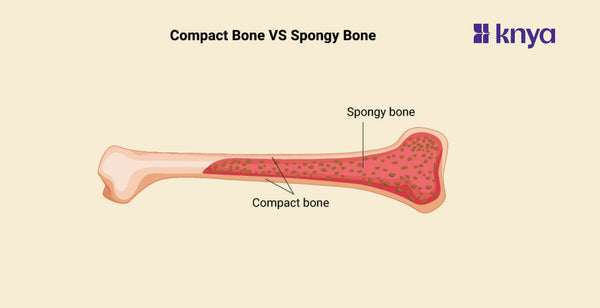
Difference Between Compact Bone and Spongy Bone: The two primary forms of bone tissue are compact and spongy bone, which differ structurally and functionally. Compact bone, also known as cortical bone, is the strong outer layer that supports and protects most bones. It is densely packed and solid, with microscopic blood vessel pathways. Spongy bone, also known as cancellous bone, is located inside the compact bone and has a lighter, honeycomb-like structure composed of thin, interconnecting plates known as trabeculae. This structure allows spongy bone to be strong while staying lightweight and allowing space for red bone marrow, which is required for blood cell synthesis. So, while compact bone prioritises strength and support, spongy bone strikes a balance between weight and support, as well as blood cell production.
Difference Between Compact Bone and Spongy Bone
Compact bone and spongy bone are two types of osseous tissue found in the skeletal system of vertebrates, including humans. They serve different functions within the skeletal system and have distinct structures. Listed below are the differences between compact bone and spongy bone:
|
Aspect |
Compact Bone |
Spongy Bone |
|
Structure |
Dense and solid, forming outer layer of most bones |
Porous, honeycomb-like structure with trabeculae |
|
Density |
Higher density |
Lower density |
|
Location |
Typically in shafts and outer layers of long bones |
Found at ends and within interior of bones |
|
Blood Supply |
Fewer blood vessels |
Greater network of blood vessels and marrow spaces |
|
Strength |
Provides strength and support, resistance to bending |
Provides structural support, less dense |
|
Appearance |
Smooth, marble-like appearance |
Open, lattice-like appearance |
|
Osteons |
Composed of osteons (Haversian systems) |
Lacks osteons, composed of trabeculae |
|
Red Marrow |
Limited spaces for red marrow |
More red marrow spaces |
|
Mechanical Function |
Suited for weight-bearing, mechanical stress |
Metabolically active, responsive to stress and strain |
|
Fracture Healing |
Slower healing due to denser structure |
Potentially faster healing due to vascularity and activity |
Browse Best Scrubs Collection
What is Compact Bone?
Most bones' exterior layer is thick and rigid, known as compact bone. It is composed of closely packed osteons, which are cylindrical structures with microscopic pathways for blood vessels and nerves. Compact bone strengthens and supports the skeleton, allowing it to endure weight and strain.
Key Features of Compact Bone:
- Compact bone, as its name suggests, is the dense and hard tissue that forms the outer layer of most bones. This dense structure provides strength and support to the skeleton, allowing it to withstand significant weight and stress.
- Compact bone is made up of repeating units known as osteons, or Haversian systems. These osteons are cylindrical formations with concentric lamellae, or thin layers of mineralized collagen fibres. This configuration offers outstanding strength and stiffness.
- Compact bone's blood supply is limited due to its thick nature. Blood arteries provide nutrients and oxygen to bone cells via microscopic canals known as Haversian canals within the osteons.
- Compact bone is predominantly found in the diaphysis, or shaft, of long bones such as the femur and humerus. It also creates the outer layer of flat bones such as the skull and ribs.
Explore All Women's Scrub
What is Spongy Bone?
Most bones have a lighter, inner layer called spongy bone, also known as cancellous bone. It has a honeycomb-like structure composed of thin, linked plates known as trabeculae. Spongy bone is lighter than compact bone but still robust, and it contributes to stress absorption and weight distribution. It also includes red bone marrow, which produces red blood cells.
Key Features of Spongy Bone:
- Spongy bone, also called cancellous bone, is a lightweight and porous tissue that forms the inner core of most bones. This network-like structure, resembling a sponge, is much less dense than compact bone but plays a crucial role in shock absorption and weight distribution.
- Spongy bone is composed of thin, rod-like structures known as trabeculae. These trabeculae form a network of linked compartments filled with bone marrow, which is required for blood cell formation.
- Spongy bone has a significantly greater blood supply than compact bone. The trabecular network's huge open areas allow blood vessels to flow through, supplying oxygen and nutrients to bone cells and boosting blood cell synthesis in the bone marrow.
- Spongy bone is most commonly seen at the epiphysis, or ends, of long bones such as the femur and humerus. It also makes up the inner core of short bones such as the vertebrae and carpal bones in the wrist.
Similarities Between Compact Bone and Spongy Bone
- Compact and spongy bone, Both compact and spongy bone are made up of organic components (collagen fibres, osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts) and inorganic mineral salts (mostly calcium and phosphate), which provide strength and rigidity to bones.
- Both forms of bone help regulate calcium levels in the body by storing and releasing calcium as needed for physiological activities including muscle contraction and nerve activity.
- Both forms of bone help with bone development and remodelling throughout life, with osteoblasts generating new bone tissue and osteoclasts breaking down and resorbing existing bone tissue.
- Both compact and spongy bones protect critical organs and tissues, including the brain, spinal cord, and bone marrow, from external pressures and injuries.
Although both compact and spongy bones are essential components of the skeletal system, their structure and function differ significantly. Compact bone, sometimes called cortical bone, is the solid outer layer of bones that provides strength and support. Its closely packed structure, made up of concentric rings called osteons, makes it very strong but hefty. Spongy bone, also known as cancellous bone, is found within the core of bones and has a honeycomb-like structure. This network of thin, plate-like structures known as trabeculae provides lightweight support while maximising space for red bone marrow, which produces blood cells. The contrast between thick, strong compact bone and lightweight, blood cell-producing spongy bone demonstrates the incredible diversity of our skeletal system, which allows for both support and critical blood cell synthesis.
| Check out More Articles | |
| Difference Between Cartilage and Bone | |
| Difference Between Endocrine and Exocrine Glands | |
| Difference Between Cell Wall and Cell Membrane | |