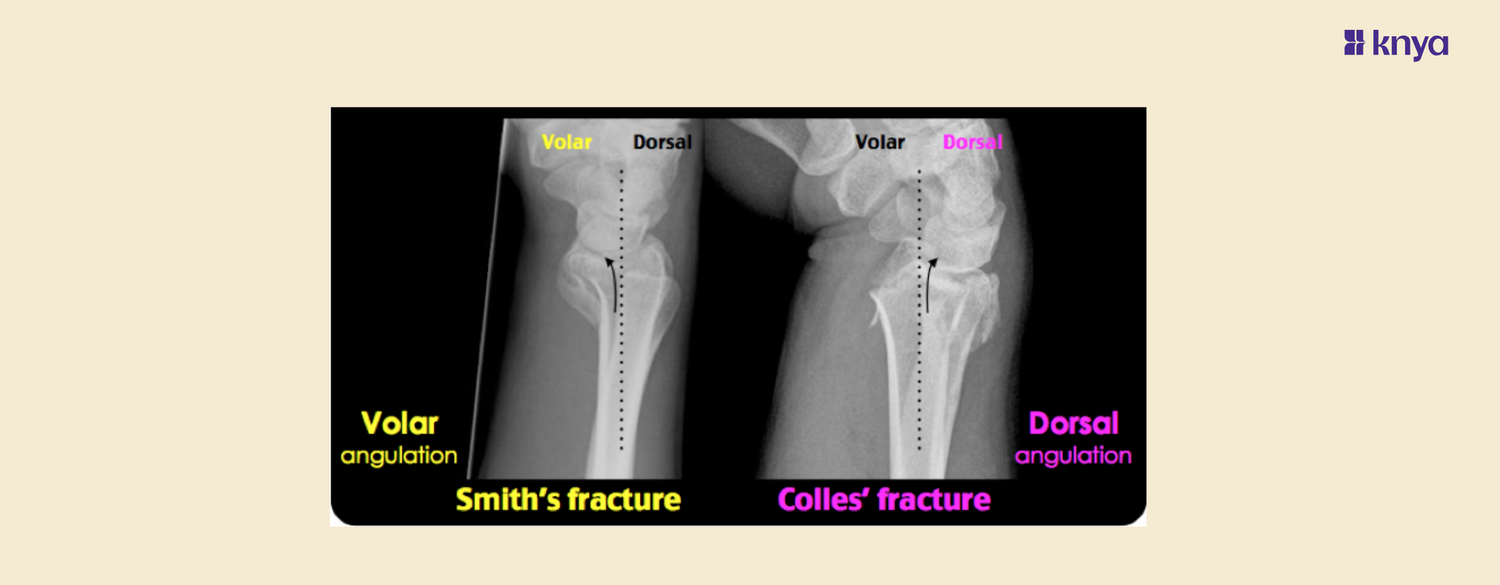
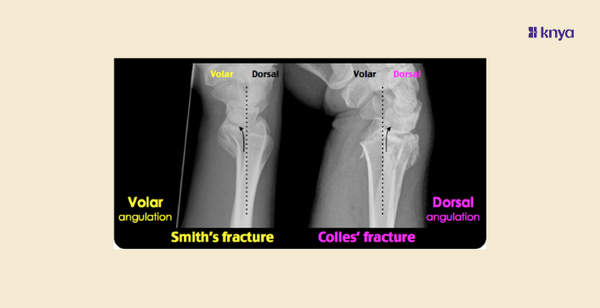
Fractures of the distal radius are common, particularly among the elderly and those who engage in high-risk activities. Two specific types of distal radius fractures that are often discussed in medical literature and practice are Colles fractures and Smith fractures. To aid in the differentiation between these two fractures, mnemonics can be a useful tool for medical students, healthcare providers.
Comparison Table
Below is the difference between Colles Fractur and Smith Fracture in a tabular format:
| Feature | Colles Fracture | Smith Fracture |
| Mechanism of Injury | Fall on an outstretched hand (FOOSH) | Fall on a flexed wrist |
| Deformity | Dinner fork or silver fork deformity | Garden spade deformity |
| Displacement | Dorsal displacement of distal fragment | Volar displacement of distal fragment |
| Common Patient Demographic | Elderly, particularly women with osteoporosis | Younger patients, often due to high-impact trauma |
| Radiographic Appearance | Dorsal angulation, radial shortening | Volar angulation, no radial shortening |
| Typical Treatment | Closed reduction and casting, sometimes surgery | Closed reduction and casting, sometimes surgery |
Browse best Scrubs Collection
What is Colles Fracture?
A Colles fracture, named after Abraham Colles who first described it in 1814, is one of the most common fractures of the distal radius. It typically occurs when a person falls onto an outstretched hand (FOOSH) with the wrist in extension. The hallmark of a Colles fracture is the dorsal displacement of the distal fracture fragment.
Mnemonic for Colles Fracture
These mnemonics help recall key points about the fractures, such as their mechanisms, clinical presentations, and radiographic appearances.
- C: Common
- O: Outstretched hand (fall on outstretched hand)
- L: Lateral view shows dorsal displacement
- L: Look for dinner fork deformity
- E: Extension injury
- S: Silver fork deformity
Symptoms of Colles Fracture
Patients with a Colles fracture usually present with:
- Pain and swelling around the wrist
- Visible deformity, often described as a "dinner fork" deformity due to the dorsal displacement
- Limited range of motion
- Bruising around the injured area
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is primarily made through physical examination and confirmed with X-rays, which reveal the characteristic dorsal displacement of the distal fragment.
Treatment
Treatment options for a Colles fracture include:
- Non-surgical: Closed reduction followed by immobilization in a cast or splint. This approach is typically used for non-displaced or minimally displaced fractures.
- Surgical: Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) with plates and screws, particularly for displaced or unstable fractures.
Prognosis
The prognosis for a Colles fracture is generally good, especially with appropriate treatment. However, complications such as stiffness, nerve injury, and post-traumatic arthritis can occur.
What is Smith Fracture?
Smith Fracture is a type of broken wrist, or fracture of the distal radius, that occurs when the wrist is bent or flexed during a fall or other trauma. This forces the wrist into flexion, causing the distal fragment to displace volarly. This is also known as a reverse Colles fracture, involving a volar displacement of the wrist and hand.
Mnemonic for Smith Fracture
- S: Smith
- M: Mechanism is fall on flexed wrist
- I: Inward (volar/palmar displacement)
- T: Transverse fracture line
- H: Handlebar injury (common in bicyclists)
Symptoms
Patients with a Smith fracture typically exhibit:
- Pain and swelling on the volar side of the wrist
- Deformity, though less pronounced than in Colles fractures, with the hand displaced palmarly
- Difficulty in wrist and finger movements
- Tenderness over the distal radius
Diagnosis
Similar to Colles fractures, diagnosis is made through physical examination and confirmed by X-rays, which show the volar displacement of the distal fragment.
Treatment
Treatment approaches for Smith fractures include:
- Non-surgical: Closed reduction and immobilization in a cast or splint, often used for non-displaced fractures.
- Surgical: ORIF with plates and screws, especially for displaced, unstable, or intra-articular fractures.
Prognosis
The prognosis for a Smith fracture is also favorable with proper treatment. However, there is a higher risk of complications such as malunion, carpal tunnel syndrome, and post-traumatic arthritis.
Shop the Best Lab Coats from Here!