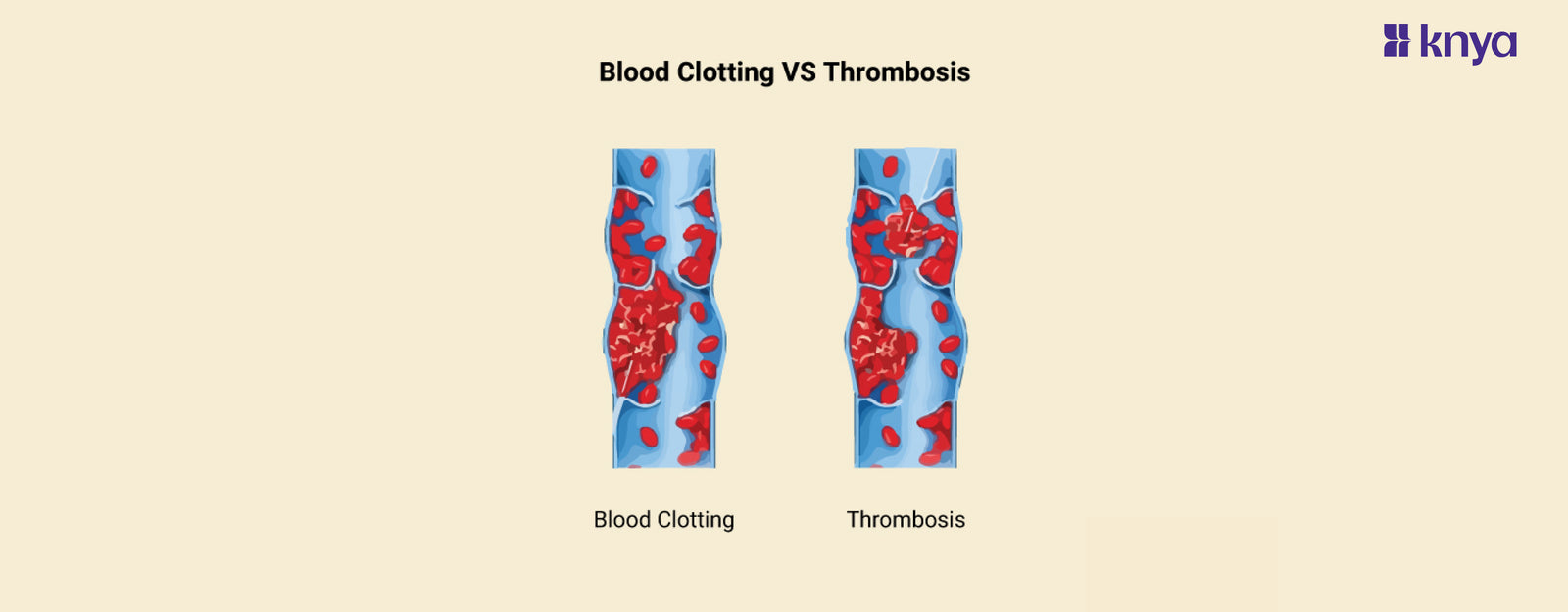
Difference Between Blood Clotting and Thrombosis: Blood clotting and thrombosis are often confused, but they have a key difference. Blood clotting is a natural process where blood thickens to seal a wound and prevent excessive bleeding. This is beneficial and essential for healing. In contrast, thrombosis occurs when a blood clot forms within a healthy blood vessel, blocking blood flow and potentially leading to serious complications. While both involve clots, Blood Clotting vs Thrombosis hinges on location and purpose, clotting occurs at injury sites, while thrombosis happens within healthy vessels and can be life-threatening.
Difference Between Blood clotting and Thrombosis
Listed below are the difference between Blood clotting and Thrombosis:
|
Aspect |
Blood Clotting |
Thrombosis |
|
Definition |
Process of forming a clot to prevent bleeding. |
Formation of a clot within a blood vessel. |
|
Function |
Stops bleeding and repairs damaged vessels. |
Can lead to blockage and tissue damage. |
|
Trigger |
Damage to blood vessels. |
Injury, inflammation, or abnormal blood flow. |
|
Process |
Enzymatic reactions leading to fibrin formation. |
Abnormal formation of a blood clot in a vessel. |
|
Purpose |
Prevents excessive bleeding. |
Obstructs blood flow, may cause complications. |
|
Control |
Tightly regulated to prevent disorders. |
Can occur due to disruptions in regulation. |
|
Occurrence |
Response to injury or trauma. |
Can occur due to various conditions or diseases. |
|
Physiological |
Necessary for wound healing. |
Often considered pathological. |
|
Regulation |
Involves clotting factors, platelets, etc. |
Influenced by genetics, lifestyle, conditions. |
|
Location |
Internally or externally, depending on injury. |
Within blood vessels, obstructing flow. |
Browse Best Scrubs Collection
What is Blood clotting?
Blood clotting is a natural process that allows your body to halt bleeding following an injury. When you cut yourself, your platelets, or microscopic cell fragments in your blood, clump together to create a plug at the wound site. This plug, known as a clot, helps close the ruptured blood artery and prevents additional blood loss.
Key Features of Blood clotting:
- This occurs when a blood clot (thrombus) develops inside a blood artery, interfering with blood flow.
- The two basic forms are venous thrombosis (veins) and arterial thrombosis (arteries).
- Can result in life-threatening diseases such as a stroke (brain), a heart attack, or a pulmonary embolism.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing risk factors, and using blood thinners as needed are all part of the prevention and treatment process.
What is Thrombosis?
Thrombosis is a condition that occurs when a blood clot forms inside one of your blood vessels. This can block blood flow to the area of the clot, which can damage tissues and organs. Thrombosis can be serious and even life-threatening, depending on the location and size of the clot.
Key Features of Thrombosis:
- Thrombosis occurs when a blood clot develops within an intact blood vessel, preventing blood flow.
- Injury, certain drugs, genetic predispositions, and medical diseases such as cancer can raise the risk of thrombosis.
- Depending on the location and size of the clot, thrombosis can result in a stroke, heart attack, pulmonary embolism (blood clot in the lung), and other serious problems.
- Thrombosis treatment options include anticoagulant pills to prevent additional clotting, thrombolytic agents to dissolve existing clots, and mechanical treatments such as stents or clot removal surgeries.
Shop Best Lab Coats from Here!
Similarities Between Blood clotting and Thrombosis
- Blood clotting and thrombosis entail the development of blood clots.
- Both procedures need the activation of platelets and clotting factors.
- Both are impacted by genetics, lifestyle, and pre-existing medical issues.
- Both mechanisms are intended to avoid excessive bleeding in reaction to injury.
- Both can cause major health problems if not appropriately managed or handled.
Blood clotting and thrombosis sound similar, but understanding their subtle differences is crucial. Blood clotting is a necessary bodily process that forms a plug to seal injured blood vessels and prevent excessive bleeding. However, thrombosis occurs when a blood clot, called a thrombus, forms abnormally within a healthy blood vessel, blocking blood flow and potentially leading to serious complications. While both involve clot formation, thrombosis is a pathological condition, whereas blood clotting is a normal physiological response. Remember, not all blood clots are thromboses, but all thromboses are harmful blood clots.
| Check out More Articles | |
| Difference Between Cartilage and Bone | |
| Difference Between Endocrine and Exocrine Glands | |
| Difference Between Cell Wall and Cell Membrane | |