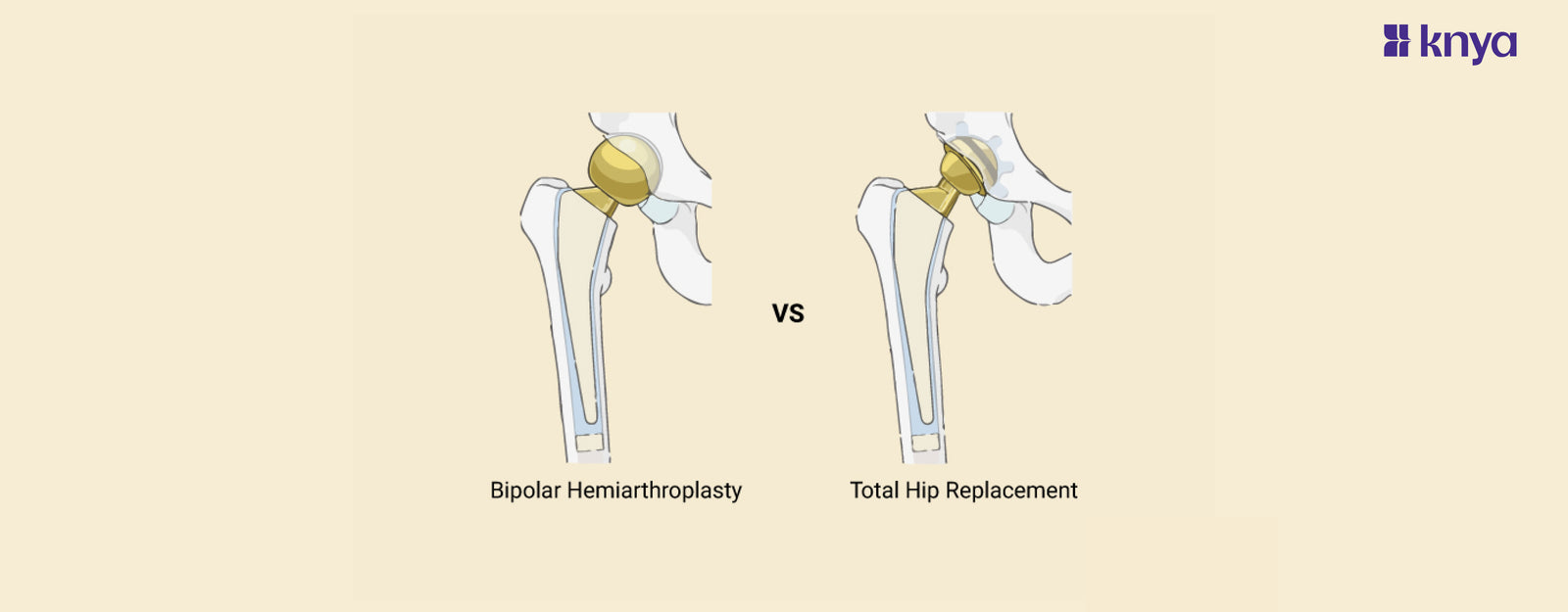
Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty Vs Total Hip Replacement: In the orthopedic interventions for hip joint disorders, both bipolar hemiarthroplasty and total hip replacement stand as effective surgical options. These procedures are designed to address specific conditions and offer distinct advantages based on the nature and extent of hip joint pathology. Let's delve into the key differentiators between bipolar hemiarthroplasty and total hip replacement, exploring their difference between to better understand when each approach becomes the preferred choice.
Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty Vs Total Hip Replacement
Here's a concise comparison between Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty and Total Hip Replacement in a table format:
|
Aspect |
Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty |
Total Hip Replacement |
|
Procedure Scope |
Addresses femoral neck fractures and avascular necrosis, preserving the native acetabulum |
Comprehensive solution for various hip conditions, involving the replacement of both femoral head and acetabulum |
|
Articulation Design |
Two-piece prosthesis with femoral head articulating within a metal shell |
Single-piece prosthetic ball-and-socket joint, mimicking natural hip mechanics |
|
Indications |
Femoral neck fractures, avascular necrosis, and conditions where preserving the native acetabulum is beneficial |
Severe hip joint diseases, degenerative conditions, and cases with compromised femoral head and acetabulum |
|
Patient Demographics |
Often preferred for elderly patients with limited mobility |
Suited for a broader demographic, irrespective of age, especially for advanced arthritis or hip joint damage |
|
Joint Stability |
Provides stability and reduces the risk of dislocation |
Offers stability but may require careful positioning to minimize the risk of dislocation |
|
Movement Mechanics |
Allows movement and rotation within the prosthetic components |
Mimics natural joint movement, providing a broader range of motion |
|
Bone Resection |
Involves minimal bone resection, preserving the patient's own acetabulum |
Requires more extensive bone resection to accommodate the complete prosthetic joint |
|
Implant Durability |
May have a shorter lifespan compared to total hip replacement |
Generally has a longer lifespan, providing durable results for a wide range of conditions |
|
Recovery Time |
Typically associated with a quicker recovery period |
Recovery may take longer due to the more extensive nature of the procedure |
|
Cost Considerations |
May be more cost-effective compared to total hip replacement |
Generally involves higher costs due to the complexity of the procedure and the materials used |
Know about Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty
Bipolar hemiarthroplasty is a surgical procedure used to address specific hip joint conditions, primarily femoral neck fractures or avascular necrosis of the femoral head. It involves the replacement of the femoral head (the ball-shaped top of the thigh bone) with a prosthetic component that has a two-piece design. In this procedure, the prosthetic femoral head is allowed to move and rotate within a metal shell, which is implanted into the patient's own acetabulum (the socket in the hip bone).
Key features and considerations of bipolar hemiarthroplasty include:
- Indications: Typically recommended for fractures of the femoral neck, especially in elderly patients, as well as for cases of avascular necrosis where preserving the patient's own acetabulum is advantageous.
- Implant Design: The prosthetic femoral head is not fixed directly to the patient's bone; instead, it articulates within a metal shell. This design allows for some degree of movement and rotation.
- Preservation of Acetabulum: Unlike total hip replacement, bipolar hemiarthroplasty preserves the patient's native acetabulum, which may be beneficial in certain clinical situations.
- Patient Demographics: Often favored for elderly patients with limited mobility, as it provides stability and reduces the risk of dislocation.
- Stability: The procedure aims to restore stability to the hip joint and alleviate pain associated with fractures or avascular necrosis.
- Bone Resection: Involves minimal bone resection compared to total hip replacement, as only the femoral head is replaced.
- Durability: The longevity of the implant may be influenced by factors such as patient age, activity level, and the specific condition being addressed.
- Recovery Time: Typically associated with a quicker recovery period compared to total hip replacement due to the less invasive nature of the procedure.
Know about Total Hip Replacement
Total Hip Replacement, also known as hip arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure designed to replace a damaged or diseased hip joint with an artificial joint, or prosthesis. This comprehensive intervention involves the removal of both the damaged femoral head (the ball-shaped top of the thigh bone) and the affected acetabulum (the socket in the hip bone). The prosthetic components, typically made of metal, plastic, or ceramic materials, are then implanted to recreate the hip joint's functionality.
Key features and considerations of total hip replacement include:
- Indications: Recommended for individuals with severe hip joint diseases, advanced osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, traumatic hip injuries, or other conditions that compromise the integrity of the hip joint.
- Implant Design: Involves a single-piece prosthetic ball-and-socket joint, aiming to closely mimic the natural mechanics of the hip joint.
- Comprehensive Joint Replacement: Addresses both the femoral head and the acetabulum, providing a complete replacement of the hip joint.
- Patient Demographics: Suited for a broad demographic, including individuals of varying ages, depending on the severity of the hip condition.
- Stability: Aims to restore stability to the hip joint, offering improved function and relief from pain associated with joint degeneration.
- Bone Resection: Requires more extensive bone resection compared to bipolar hemiarthroplasty, as both the femoral head and the acetabulum are replaced with prosthetic components.
- Durability: Total hip replacement is known for its durability, with the potential to provide long-lasting relief and improved quality of life.
- Recovery Time: Recovery may take longer compared to bipolar hemiarthroplasty due to the more extensive nature of the procedure. Physical therapy and rehabilitation are often essential components of the recovery process.
Similarity Between Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty and Total Hip Replacement
While bipolar hemiarthroplasty and total hip replacement are distinct surgical procedures, they share some similarities, particularly in the context of addressing hip joint issues. Here are commonalities between the two procedures:
- Orthopedic Interventions:
- Both bipolar hemiarthroplasty and total hip replacement are orthopedic surgical interventions aimed at restoring function and alleviating pain in the hip joint.
- Artificial Components:
- Both procedures involve the use of artificial components or prostheses to replace the damaged or diseased parts of the hip joint. These prosthetic components are typically made of materials such as metal, plastic, or ceramic.
- Treatment of Hip Pathologies:
- Both are employed to treat specific hip pathologies, including fractures, avascular necrosis, and degenerative conditions, albeit with different levels of invasiveness and goals.
- Improvement in Joint Function:
- The primary goal of both procedures is to improve joint function, restore stability, and enhance the patient's overall quality of life.
- Surgical Expertise:
- Both surgeries require the expertise of orthopedic surgeons with specialized training in joint replacement procedures.
- Postoperative Rehabilitation:
- Postoperatively, patients undergoing either procedure typically undergo physical therapy and rehabilitation to regain strength, flexibility, and functional mobility.
- Consideration of Patient Factors:
- The decision between bipolar hemiarthroplasty and total hip replacement takes into account factors such as the patient's age, overall health, lifestyle, and the specific nature and extent of the hip condition.
|
Check out More Articles |
|