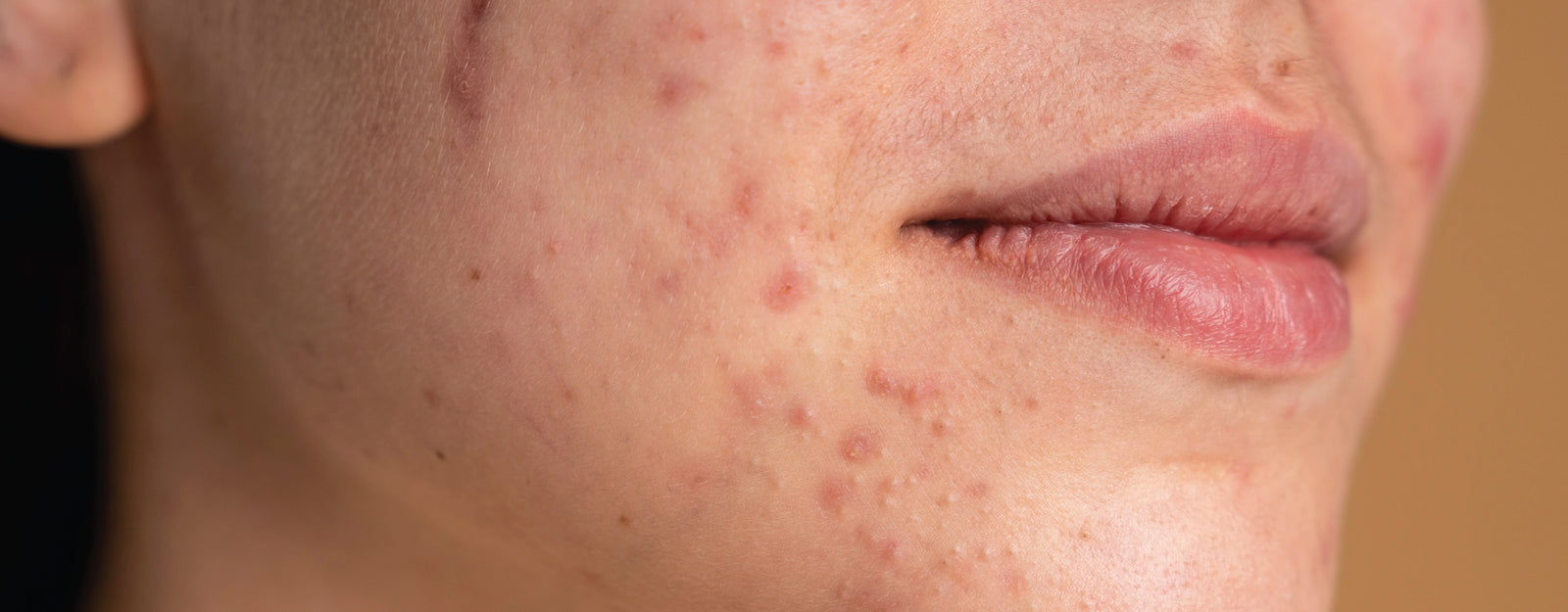
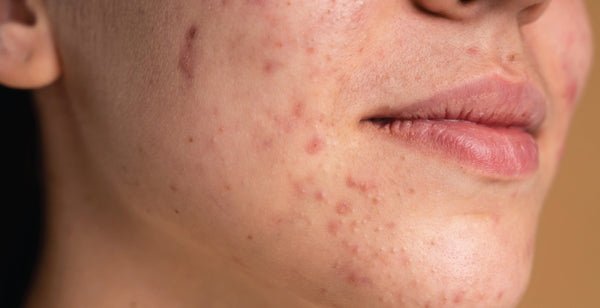
Bacterial Acne vs Fungal Acne: Bacterial Acne and Fungal Acne induce outbreaks, but the underlying reasons differ. Bacterial acne occurs when excess oil production combines with bacteria on the skin, blocking pores and producing an environment for inflammation. In contrast, fungal acne is caused by an excess of yeast, a form of fungus, on the skin. Sweating, tight clothes, and certain drugs can all contribute to this overgrowth. There are various elements to consider when distinguishing between bacterial and fungal acne. One is location. Bacterial acne is more frequent on the face, back, and chest, whereas fungal acne appears on the arms, chest, and back. Another distinction is size: Bacterial acne can create pimples and whiteheads of varied sizes, but Fungal Acne often presents with mall, flat, red bumps that are all about the same size. Additionally, Fungal Acne is often itchy, whereas Bacterial Acne usually isn't.
Difference Between Bacterial Acne and Fungal Acne
Bacterial Acne and Fungal Acne are two different types of skin conditions that can affect individuals, although they have some similarities, they are caused by different pathogens and have distinct characteristics. Below are the definitions followed by the differences between the two:
|
Aspect |
Bacterial Acne |
Fungal Acne |
|
Cause |
Bacteria (Propionibacterium acnes) |
Yeast-like fungi (Malassezia) |
|
Appearance |
Inflamed red pimples, pustules, cysts, nodules |
Uniform, itchy bumps or papules |
|
Location |
Face, neck, chest, back |
Chest, back, shoulders, upper arms |
|
Treatment |
Topical or oral antibiotics, retinoids, benzoyl peroxide |
Antifungal medications (topical/oral creams, shampoos) |
|
Comedones |
Presence of open and closed comedones (blackheads/whiteheads) |
Generally lacks comedones |
|
Risk Factors |
Hormonal changes, excess oil production |
Hot/humid environments, excessive sweating, immunosuppression |
|
Contagiousness |
Not contagious |
Not contagious |
|
Inflammatory Response |
Triggers inflammatory response |
May cause less inflammation |
|
Age of Onset |
Starts during adolescence, can persist into adulthood |
Can affect any age group, more common in adolescents/young adults |
|
Pore Blockage |
Blockage of hair follicles, excess sebum/dead skin cells |
Overgrowth of yeast within hair follicles |
Order the Best Jogger Scrub from Here!
What is Bacterial Acne?
Bacterial acne, the most common type, is caused by excess oil and dead skin cells clogging pores. This creates an environment for bacteria to thrive, leading to inflamed pimples, whiteheads, and blackheads.
Browse Best Scrubs Collection
Key Features of Bacterial Acne:
- Caused by the bacteria Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes), which feeds on the oil (sebum) generated by the skin glands. P. acnes causes irritation, which leads to outbreaks.
- Typically manifests as whiteheads (closed comedones), blackheads (open comedones), inflammatory papules (red lumps), and pustules.
- Frequently occurs in regions with significant oil production, such as the face, chest, back, and shoulders.
- Topical therapies with benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or antibiotics work well for this condition. Dermatologists may also recommend oral medicines for severe instances.
What is Fungal Acne?
Fungal acne, also known as Pityrosporum folliculitis, is caused by an overgrowth of yeast on the skin. This yeast feeds on oils and causes an inflammatory reaction, resulting in clusters of tiny, itchy bumps over the chest, back, and shoulders. Fungal acne, unlike bacterial acne, does not normally produce pus-filled pimples.
Explore All Women's Scrub
Key Features of Fungal Acne:
- Caused by an excess of Malassezia yeast, which is ordinarily found on healthy skin. Oily skin, excessive perspiration, and certain drugs can all contribute to this overgrowth.
- Frequently manifests as tiny, red, irritating pimples, occasionally with pustules but seldom with blackheads. It may also result in flaky spots or a harsh texture.
- Can develop on the face, chest, and upper back, similar to bacterial acne, but it also often affects the scalp and may spread to the arms.
- Antifungal drugs should be used topically or taken orally. If the scalp is impacted, treatment options may include clotrimazole, miconazole, ketoconazole, or dandruff shampoos containing these substances.
Shop Best Lab Coats from Here!
Similarities Between Bacterial Acne and Fungal Acne
- Bacterial and fungal acne can irritate the skin, causing redness and pain.
- Both illnesses may cause papules or tiny lumps on the skin.
- Both problems can be worse by poor hygiene, excessive perspiration, and certain drugs.
- Depending on the severity of the problem, both bacterial and fungal acne can be treated with topical or oral drugs.
- Proper skin care techniques, such as daily washing and avoiding pore-clogging products, can help prevent both forms of acne.
Bacterial and fungal acne, while both generating pimples, have separate causes. Bacterial acne is caused by excess oil and dead skin cells obstructing pores, providing a breeding environment for acne-causing bacteria. This usually causes varied sized whiteheads, blackheads, and pus-filled lumps on the face, chest, and back. Fungal acne, on the other hand, is caused by an excessive development of yeast on the skin. This yeast feeds on oils and thrives in warm, humid conditions. Fungal acne appears as tiny, red, itchy spots that are commonly seen on the chest, back, and upper arms, but can also show on the face. Distinguishing between Bacterial and Fungal Acne is critical for effective therapy since the two require distinct treatments.
| Check out More Articles | |
| Difference Between Cartilage And Bone | |
| Difference Between Endocrine And Exocrine Glands | |
| Difference Between Cell Wall And Cell Membrane | |