Difference between Angiogram vs Angiography vs Angioplasty: Angiogram, angiography, and angioplasty are three interventional procedures used to diagnose and treat heart conditions. While they are related and often performed together, they serve different purposes. Let's explore the differences between angiogram, angiography, and angioplasty.
Difference Between Angiogram, Angiography and Angioplasty
Here is an detailed overview on difference between Angiogram vs Angiography vs Angioplasty in table format
|
Feature |
Angiogram |
Angiography |
Angioplasty |
|
Definition |
An X-ray image of blood vessels to evaluate them |
A diagnostic procedure to visualize blood vessels |
A procedure to open blocked or narrowed arteries |
|
Purpose |
Diagnosis of blockages in blood vessels |
Visualizing and diagnosing blood vessel problems |
Treatment of narrowed or blocked blood vessels |
|
Procedure |
Involves injecting a contrast dye into blood vessels and taking X-ray images |
Uses imaging techniques like X-ray, MRI, or CT scan to visualize blood vessels |
Involves inserting a catheter with a deflated balloon into the blocked artery and inflating it to widen the artery |
|
Use |
Helps identify the location and severity of blockages |
Assists in diagnosing heart conditions and determining the need for treatment |
Restores blood flow to the heart muscle by widening the blocked arteries |
|
Risk |
Minimal |
Minimal |
Possible complications include bleeding, infection, or damage to the blood vessel |
What Is Angiogram?
An angiogram, also known as arteriography or angiography, is a medical imaging technique used to visualize the inside of blood vessels and organs of the body, with particular interest in the arteries, veins, and the heart chambers. It is a minimally invasive procedure that allows the doctor to detect any abnormalities within the blood vessels, such as narrowing, blockages, or other blood flow problems.
Key Features of Angiogram
- Diagnosis: Angiograms are primarily used to diagnose cardiovascular conditions such as coronary artery disease, atherosclerosis, aneurysms, and blood clots.
- Procedure: During the procedure, a contrast dye is injected into the bloodstream, and X-ray images are taken. The dye makes the blood vessels visible on the X-ray images.
- Purpose: It helps the doctor evaluate the blood flow within the blood vessels, identify any blockages or narrowing, and determine the need for further treatment.
What Is Angiography?
Angiography is a medical imaging technique used to visualize blood vessels in various parts of the body, including the heart, brain, and other organs. It uses various imaging modalities such as X-ray, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or computed tomography (CT) scan to produce detailed images of the blood vessels.
Key Features of Angiography
- Diagnosis: Angiography is used to diagnose various heart and vascular conditions, including coronary artery disease, peripheral artery disease, and aneurysms.
- Procedure: During the procedure, a contrast dye is injected into the bloodstream, and images are captured using X-ray, MRI, or CT scan.
- Purpose: It helps the doctor visualize the blood vessels, identify any abnormalities, and determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
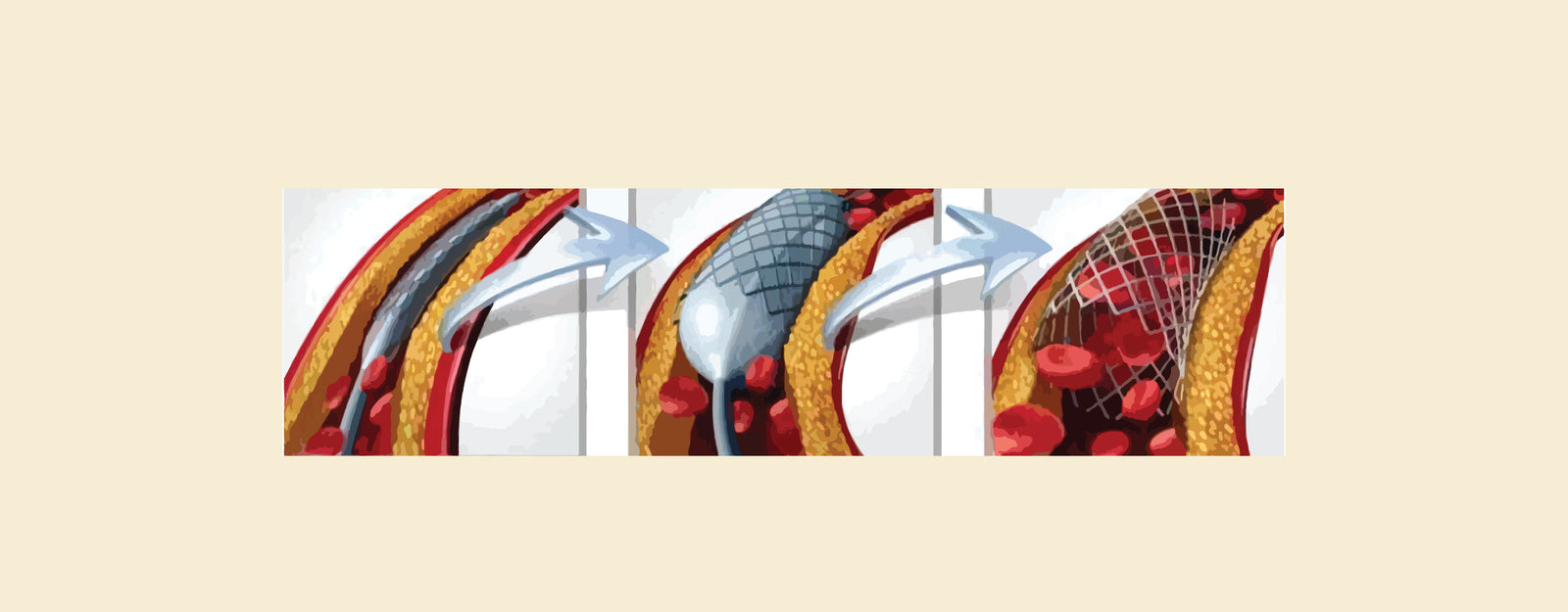
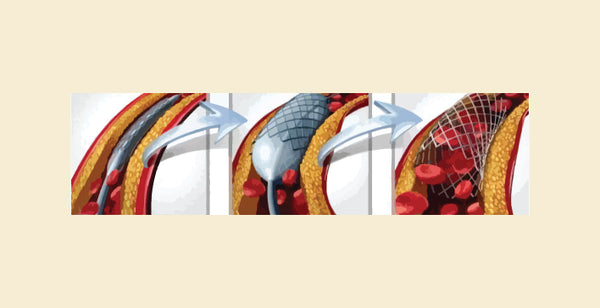
What Is Angioplasty?
Angioplasty, also known as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), is a minimally invasive procedure used to open blocked or narrowed arteries. It is often performed immediately after an angiogram or angiography to treat blockages identified during these procedures. Angioplasty is commonly used to treat coronary artery disease (CAD), peripheral artery disease (PAD), and carotid artery disease. It can help relieve symptoms such as chest pain (angina), improve blood flow to the heart, brain, or legs, and reduce the risk of heart attack or stroke.
Key Features of Angioplasty
- Treatment: Angioplasty is a treatment procedure used to restore blood flow to the heart muscle by widening blocked or narrowed arteries.
- Procedure: During the procedure, a catheter with a deflated balloon at its tip is inserted into the blocked artery. The balloon is then inflated to widen the artery and improve blood flow.
- Purpose: Angioplasty helps relieve symptoms of coronary artery disease, such as chest pain (angina), and reduce the risk of heart attack and other complications associated with narrowed arteries
Similarities Between Angiogram, Angiography and Angioplasty
- Diagnostic Tools: All three procedures are used to diagnose and treat heart and vascular conditions.
- Involves Contrast Dye: They involve the use of a contrast dye to make the blood vessels visible on imaging tests.
Minimally Invasive: They are minimally invasive procedures that are performed under local anesthesia.
| Check out More Articles | |
| Difference Between Cartilage And Bone | |
| Difference Between Endocrine And Exocrine Glands | |
| Difference Between Cell Wall And Cell Membrane | |