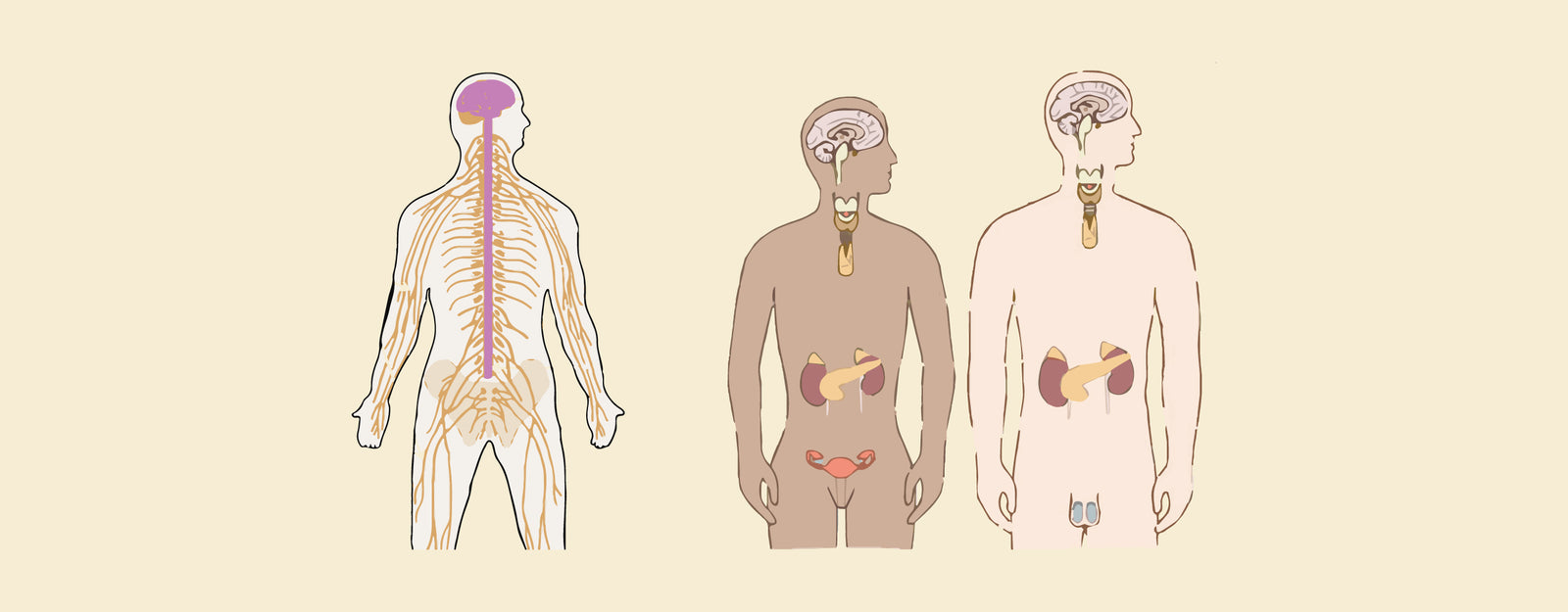
Difference Between Nervous System and Hormonal System: Our bodies have two primary communication systems: Nervous System and Hormonal System. The distinction between them is in their messengers. The nervous system relies on fast electrical impulses travelling via neurons to provide immediate reflexes, making it suitable for quick movements such as moving your hand away from a burning object. In contrast, the hormonal system uses chemical signals called hormones, which are delivered into the circulation and have slower but longer-lasting effects such as controlling development, metabolism, and mood.
Difference Between Nervous System and Hormonal System
The nervous system and the hormonal system are the human body's two principal regulatory systems, which coordinate and govern many physiological processes. Here are their definitions, followed by the difference between the two:
|
Aspect |
Nervous System |
Hormonal System (Endocrine System) |
|
Speed of transmission |
Faster |
Slower |
|
Mode of transmission |
Electrical impulses through neurons |
Chemical signals (hormones) through bloodstream |
|
Duration of effects |
Short-lived |
Long-lasting |
|
Target cells |
Specific cells or organs |
Multiple organs or systems |
|
Control over functions |
Rapid responses and voluntary actions |
Slower, long-term processes and involuntary actions |
|
Feedback mechanisms |
Primarily neural feedback mechanisms |
Often involves negative feedback loops |
|
Response to stimuli |
Rapid response to immediate changes in environment |
Slower response but more sustained |
|
Chemical nature of signals |
Electrical impulses |
Chemical substances (hormones) |
|
Transmission distance |
Short distances through neurons |
Long distances through bloodstream |
|
Adaptation to stimuli |
Quick adaptation |
Slower adaptation |
Order the Best Jogger Scrub from Here!
What is the Nervous System?
The nervous system serves as the body's electrical communicator, a fast-acting network of specialised cells known as neurons. It senses inputs (such as touch or sound) and quickly sends signals via electrical impulses and neurotransmitters. This enables for rapid reactions, such as removing your hand from the heat or synchronising muscular motions. The nervous system also has an important function in information processing, learning, and memory.
Browse Best Scrubs Collection
Key Features of Nervous System:
- The nervous system works at breakneck speed, employing electrical impulses transmitted by neurons to elicit instantaneous reactions.
- The brain and spinal cord serve as the command centre, processing data, issuing commands, and coordinating actions.
- It collects sensory input from the environment (sight, touch, taste, etc.) and regulates muscle action, allowing us to interact with our surroundings.
- Neurons link to construct complex pathways that allow communication between various regions of the body and the brain.
What is a Hormonal System?
The hormonal system is a slower-acting chemical messenger service. Glands throughout the body release chemical messengers called hormones directly into the bloodstream. These hormones travel and influence various organs and tissues, regulating functions like growth, development, metabolism, and mood. The hormonal system works on a longer-term basis, influencing processes that occur over hours, days, or even years.
Explore All Women's Scrub
Key Features of Hormonal System:
- Hormones are created by glands and circulate via the circulation to target organs, altering their functioning.
- A single hormone can have several impacts on numerous organs, affecting growth, development, metabolism, and mood.
- Hormones work over longer time periods than the neurological system, impacting processes such as growth, development, and metabolism.
- The hormonal system is a cascade of interactions in which hormones influence the synthesis and release of other hormones, resulting in a complex regulatory network.
Shop Best Lab Coats from Here!
Similarities Between Nervous System and Hormonal System
- The Nervous System and The Harmonal System, both regulate and coordinate body operations.
- They operate together to keep the body's internal environment steady, known as homeostasis.
- Both systems use feedback mechanisms to regulate their operations.
- They regulate several physiological functions, including metabolism, growth, and reproduction.
- Both systems operate together and with other bodily systems to ensure that the body functions properly.
- Both systems can respond to changing internal and external situations in order to preserve balance and health.
- Both need communication between many sections of the body to coordinate reactions to inputs.
- Both systems have a part in the body's response to stress; however, the neurological system frequently begins the initial "fight or flight" response, while the hormonal system governs the more sustained stress response.
While the nervous and hormonal systems operate together to manage the body's internal environment, they do so through different ways. The primary distinction between the nervous and hormonal systems is their communication methods. The nervous system uses neurons, which are specialised cells that transmit electrical impulses quickly. This enables precise, focused communication, such as voluntary muscle action and rapid responses to external stimuli. In contrast, the hormonal system relies on chemical messengers known as hormones. These hormones move through the circulation, affecting a broader variety of cells but with a slower and longer-lasting effect. This system regulates long-term processes such as growth, development, metabolism, and mood.