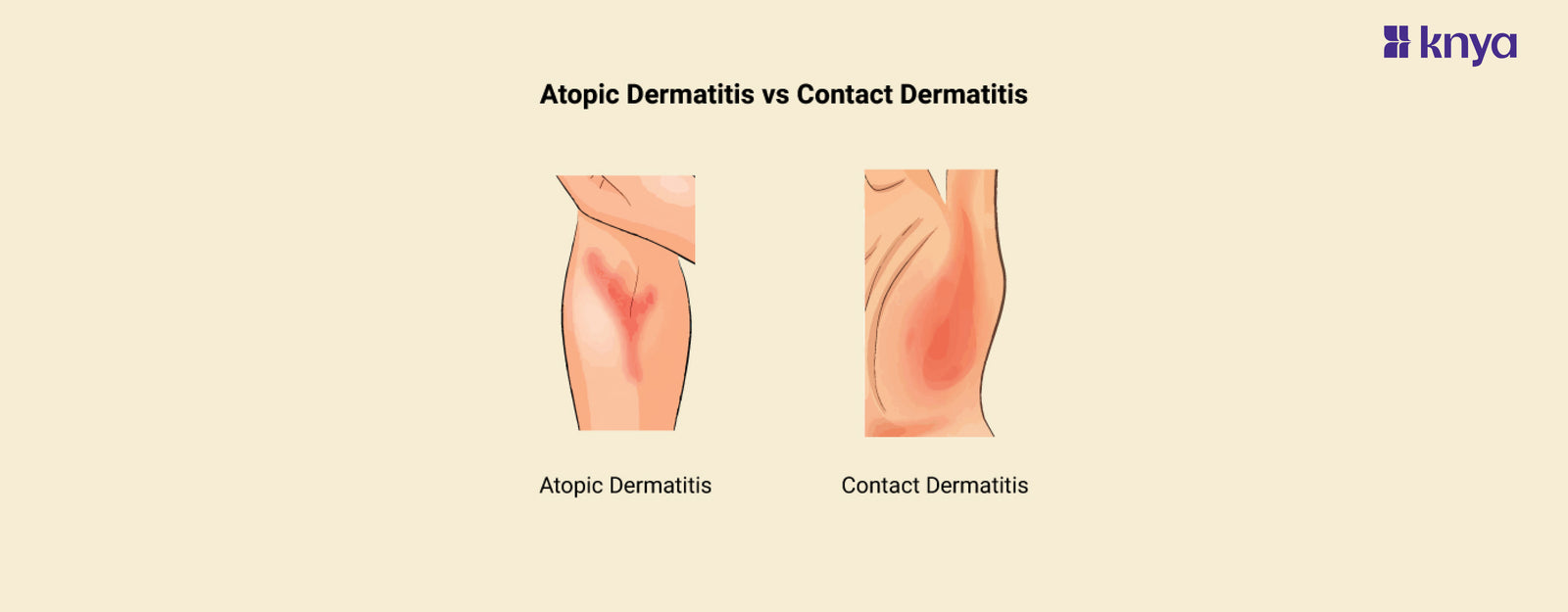
Atopic Dermatitis vs Contact Dermatitis: Eczema, which refers to itchy, inflammatory skin disorders, has two primary types: atopic dermatitis and contact dermatitis. Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as atopic eczema, is a chronic illness characterised by recurrent flare-ups of dry, itchy, and irritated skin. It is connected to genetics and frequently appears in early infancy. In contrast, Contact Dermatitis is produced by coming into direct touch with an irritant or allergen. It often flares up soon after exposure and resolves within a few weeks of removing the irritant or allergen.
Difference Between Atopic Dermatitis and Contact Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis and contact dermatitis are two common skin conditions, each with distinct characteristics and causes. Outlined below are the difference between Atopic Dermatitis and Contact Dermatitis:
|
Feature |
Atopic Dermatitis |
Contact Dermatitis |
|
Chronic Condition |
Yes |
Can be acute or chronic |
|
Genetic Predisposition |
Strong familial predisposition |
Not always genetic |
|
Age of Onset |
Typically begins in childhood |
Can occur at any age |
|
Triggers |
Allergens, environmental factors |
Direct contact with irritants or allergens |
|
Location of Rash |
Often in skin folds (e.g., elbows, knees), face |
Typically on areas in direct contact with trigger |
|
Associated Conditions |
Other atopic conditions (e.g., asthma, allergic rhinitis) |
May not be associated with other atopic conditions |
|
Immunological Mechanism |
Abnormal immune response, impaired skin barrier function |
Allergic or irritant response |
|
Resolution upon Avoidance |
Symptoms may persist despite trigger avoidance |
Symptoms usually improve upon avoiding trigger |
|
Occupational Risk |
Not directly linked to occupation |
Occupational exposure may increase risk |
|
Treatment |
Moisturizers, topical corticosteroids, immunomodulators |
Identification and avoidance of trigger, topical corticosteroids |
Order the Best Jogger Scrub from Here!
What is Atopic Dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis, often known as eczema, is an inflammatory skin disorder that you might inherit. It results in dry, itchy, and cracked skin that can flare up in response to stimuli such as dust, perspiration, or stress. These flare-ups typically occur on both sides of your body.
Browse Best Scrubs Collection
Key Features of Atopic Dermatitis:
- Atopic dermatitis is a chronic skin disorder, which means that it flares up on a regular basis throughout one's life. These flare-ups might linger for weeks or even months before they subside.
- The characteristic feature of atopic dermatitis is dry, itchy skin. This irritation can be severe and cause scratching, which can exacerbate the symptoms and create a vicious cycle.
- Atopic dermatitis frequently occurs in families, indicating a hereditary susceptibility. Individuals with a family history of allergies, asthma, or atopic dermatitis are more prone to acquire this disease.
- Atopic dermatitis affects the face, hands, inner elbows, and backs of the knees in both adults and children. In babies, it might form on the scalp and cheeks.
What is Contact Dermatitis?
Another kind of eczema is contact dermatitis, which occurs when an external irritant or allergen comes into direct contact with your skin. Irritants such as detergents or allergic responses to poison ivy can cause a rash to form just on the area of skin that was in touch with the substance.
Explore All Women's Scrub
Key Features of Contact Dermatitis
- Contact dermatitis is a skin response produced by coming into close contact with an irritating substance. This might include harsh soaps and detergents, metals such as nickel, or even some plants.
- Contact dermatitis, unlike atopic dermatitis, usually causes symptoms to appear quickly. Itching, redness, and irritation can occur within hours, if not minutes, after making contact with the trigger.
- Depending on the irritant and intensity, contact dermatitis can present in a variety of ways. It might show as red, bumpy patches, blisters, or even split, weeping skin.
- The most important component of controlling contact dermatitis is determining the trigger that produces the response. Once recognised, avoiding the chemical can help prevent future flare-ups.
Shop Best Lab Coats from Here!
Similarities Between Atopic Dermatitis and Contact Dermatitis
- Atopic dermatitis and contact dermatitis both cause skin irritation.
- Itching is a frequent symptom of both illnesses, but the degree might vary.
- Both illnesses cause red, irritated skin and may lead to a rash.
- Both disorders can be treated with topical medicines like corticosteroids and moisturisers.
- Both disorders, if not properly managed, can result in consequences such as skin infections.
- Both illnesses can have a negative influence on a person's quality of life since they cause discomfort, irritation, and cosmetic difficulties.
- Environmental variables such as allergens and irritants can cause or worsen atopic dermatitis and contact dermatitis.
Atopic dermatitis and contact dermatitis, sometimes known as eczema, produce itchy, inflammatory skin rashes. However, their beginnings are separate. Atopic dermatitis is a chronic skin illness caused by a hereditary predisposition and is frequently exacerbated by internal causes such as stress or dust mites. In contrast, contact dermatitis is caused by direct contact with irritants or allergens, resulting in a localised rash that emerges shortly after exposure. Understanding the distinction between Atopic Dermatitis and Contact Dermatitis is critical for accurate diagnosis and treatment.